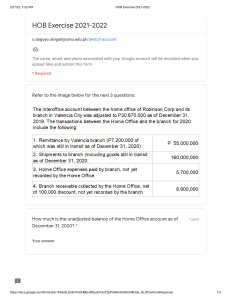
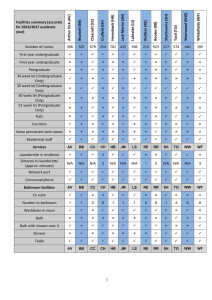
lOMoARcPSD|21977766 Bed Positionsfornursing PDF HESI Saunders (Glendale Career College ) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Josephus Estadilla (josephusestadillarmrn@yahoo.com) lOMoARcPSD|21977766 @ShopWithKey on Etsy Position Arm elevated on pillow Turn only to unaffected side and back Why? Promotes lymphatic fluid drainage from accumulating (decreases lymph edema). Semi-Fowler’s (HOB usually about 30-45 degrees); Head midline, no head flexion Do not position client on side where there is a removed bone flap Side-lying Reduces ICP by allowing venous drainage from head. Head flexion will increase ICP. Lying on side where there is a bone flap will increase ICP. Allows secretions to drain from mouth and prevents aspiration. COPD/Respiratory Distress High Fowler’s Elevate HOB 90 degrees Tripod or orthopneic position Increases maximum lung expansion, allowing for more ventilation and oxygenation. Enema administration Left-lateral or Sim’s position Allows solutions to flow by gravity into the natural direction of the colon. Leg amputation Elevate affected limb on pillow x 24 hours only Reduces edema post-op, however, after 24 Prone as tolerated, 20-30 mins at a time, at hours, DO NOT elevate stump because it can least twice daily lead to contractures. Prone position will stretch out hip and leg muscles to prevent hip flexion contraction. Head midline Reduces swelling and edema in the neck area. Semi-Fowler’s to Fowler’s (30 to 45 degrees) Support neck while turning/moving Mastectomy Patient Type Head injury/surgery Immediate post-op/post procedure (in clients who aren’t yet alert) Thyroidectomy Shock Modified Trendelenburg This will aid in perfusion of upper body and head without causing pulmonary edema. 1 Downloaded by Josephus Estadilla (josephusestadillarmrn@yahoo.com) lOMoARcPSD|21977766 @ShopWithKey on Etsy Thoracentesis Seated upright at side of bed, with an overbed table in front of client. This will exposure required area for procedure. Liver biopsy During After During: On the client’s left side to exposure liver area (which is on the right). After: On the client’s right side. Left side during the procedure will expose the area for biopsy site. Right side after procedure will use gravity to help stop bleeding. Paracentesis Seated upright in chair or semi-Fowler’s in bed. To exposure area for puncture site, as this will assist in insertion of needle. Nasogastric or gastrostomy tubes Nasogastric insertion NG/GT feeding, irrigation High Fowler’s for NG insertion. HOB at least 30 degrees (semi-Fowler’s) for NG/GT feeding, irrigation. Laminectomy Keep client straight Logroll the client For insertion: It will aid in insertion by closing off the trachea and opening the esophagus. For NG/GT feed and irrigation: To prevent aspiration of gastric contents. To avoid twisting of the spine, as this may cause complications. CVA Ischemic – Usually flat Hemorrhagic – HOB 30 degrees Ischemia – Head flat to perfuse blood to head. Hemorrhagic – HOB 30 degrees to avoid ICP. S/P Cardiac catherization Bedrest x 6 hours Affected extremity straight HOB no more than 30 degrees This position avoids pressure on the puncture site. Client can turn from side to side, but must avoid pressure on insertion site. Maternal patient with dizziness Left lateral As the uterus enlarges, pressure on the inferior vena cava increases. This pressure compromises venous return and causes blood pressure to drop, which may lead to syncope and accompanying symptoms when the client is supine. Turning the client on her left side relieves pressure on the vena cava, restoring normal venous return and blood pressure. Ischemic Hemorrhagic 2 Downloaded by Josephus Estadilla (josephusestadillarmrn@yahoo.com)