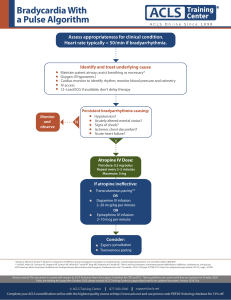
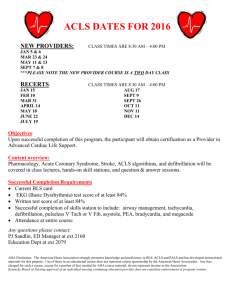
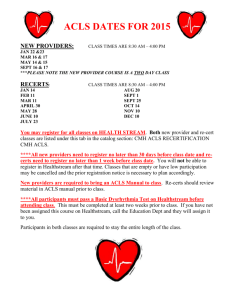
In groups of 3 people, attempt and upload ONLY a ZIP-folder of all your answer files to ACLs Folder: https://cloud.ucu.ac.ug/s/KsSFkp7jysxcwwT Deadline: 23rd March 2023, at 23:00 hours PART 1 Attempt all the questions about Access Control Lists (ACLs) in computer networking and security: 1. Discuss the role of Access Control Lists (ACLs) in computer networking and security. What are some common use cases for ACLs, and what are the benefits and limitations of using them? 2. Compare and contrast traditional ACLs and extended ACLs. What are the differences in terms of their syntax, functionality, and use cases, and how do they affect network security? 3. Explain the concept of ACL filtering and the different types of filters that can be applied using ACLs. How do ACL filters work, and what are some examples of their applications in network security? 4. Discuss the challenges of managing and maintaining ACLs in large-scale networks. What are some best practices for managing ACLs, and what tools and technologies can be used to simplify the process? 5. Analyze the impact of ACLs on network performance and scalability. What are some common performance issues that can arise when using ACLs, and how can they be mitigated? PART 2 Practical hands-on questions ACLs: 1. Set up a simple network topology with two or more hosts and routers, and implement ACLs to restrict traffic flow between specific hosts or subnets. 2. Configure a router or switch to apply an extended ACL to permit or deny specific types of traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, or protocols. 3. Configure a firewall to apply a standard or extended ACL to allow or block traffic based on specific criteria, such as IP address, port number, or application type. 4. Troubleshoot common issues that can arise when implementing ACLs, such as incorrect syntax, conflicting rules, or unintended consequences. 5. Develop a network security policy that includes guidelines for using ACLs to protect against common network threats, such as denial-of-service attacks, malware infections, or unauthorized access.