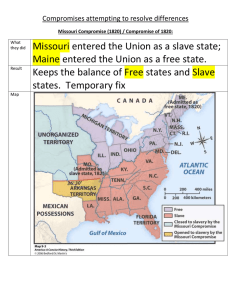
Road To The Civil War Compromise Assessment Dylan Samuel 1. ● What issue was at hand? 2. ● What did the actual compromise state? 3. ● How did it affect the balance of power in Congress? 4. ● Why was it successful/unsuccessful? The ⅗ Compromise (1788) ● ● ● ● The three-fifths compromise issue was an agreement reached at the United States Constitutional Convention between delegates from the Northern and Southern states that three-fifths of the slave population would be counted for direct taxation and representation in the House of Representatives. “Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other Persons.” By including three-fifths of slaves in the legislative apportionment, the Three-fifths Compromise provided additional representation in the House of Representatives of slave states compared to the free states. It was successful because it made slavery in the northern states not as bad. It was unsuccessful because slavery was still a thing which was a casue of the civil war. The Commerce Compromises (1788) ● ● ● ● The Issue of the compromise was that the Northern and Southern states of the United States of America reached an agreement on commerce and slave trade. For at least twenty years, it prohibited Congress from interfering with slave trades or taxing state exports. The Compromise, on the other hand, allowed it to impose taxes on every imported slave that was brought into the country, as well as taxes on imported goods. “to regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with Indian Tribes.” The Commerce Clause changed the balance in power by, having been frequently invoked by Congress to justify imposing legislative power over the activities of states and their residents, resulting in major and ongoing debate about the congressional state power balance. This causes, the Commerce Clause to have been seen as a power in congress that has control over states. It was successful because there was tax on slaves that were imported in the country. It was unsuccessful because the congress had control over the imported taxes. It was also unsuccessful because even though slavery was better in the north it was get worse every year in the south. The Fugitive Slave Act (1793) ● ● ● ● The issue was even if slaves were in a free state, the act required that they be returned to their owners. The act also made the federal government responsible for tracking down, returning, and prosecuting slaves who had escaped. It also made anti-slavery in the north a big thing. “No person held to service or labour in one state, under the laws thereof, escaping into another, shall, in consequence of any law or regulation therein, be discharged from such service or labor, but shall be delivered up on claim of the party to whom such service or labour may be due.” California settlers had a proposal to be admitted to the Union as a free state as they applied for annexation, which would tip the Senate's power balance. Southern politicians who didn't want to lose control of the federal government, argued that the federal government had no right to interfere with slave owners' rights, and threatened secession if Congress admitted California as a free state. This prompted a slew of measures aimed at appeasing both Northern and Southern congressmen, as well as restoring a more equitable power balance between slave and free states. Due to widespread opposition, the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 was successful in that manner. There were only about 330 enslaved people were successfully returned to their Southern masters by 1860. It was unsuccessful because people were required to assist in the capture of fugitive slaves. A fugitive's right to a jury trial was denied. The Missouri Compromise (1820) ● ● ● ● The issue was that Missouri was admitted to the Union as a slave state, whereas Maine was admitted as a free state, and slavery was outlawed on the remaining Louisiana Purchase territory north of the 36o 30' parallel. With the purchase of the Louisiana Territory and the application of Missouri for statehood, the long-standing balance between the number of slave states and the number of free states would be changed. Controversy arose within Congress over the issue of slavery. The Kansas-Nebraska Act abolished the Missouri Compromise. The Supreme Court deemed the Missouri Compromise illegal three years later in the Dred Scott decision, ruling that Congress lacked the jurisdiction to ban slavery in the territories. This only happened because they couldn't control the slave state anymore. What made it successful is this compromise was reached by 1820, when two bills were passed. Maine became the 23rd state as a result of the first. As the country expanded, the second added Missouri as a slave state and established the parallel 36°30' as the dividing line between enslaved and free states.It was unsuccessful because it promoted sectionalism between Northern and Southern states, the Missouri Compromise was ineffective in dealing with the issue of slavery. The Second Missouri Compromise (1821) ● ● ● ● The issue was that Missouri could not join the Union until Congress agreed that the exclusionary clause would never be applied in a way that would abridge the privileges and immunities of American citizens. Slavery would be banned in all of the former Louisiana Purchase lands north of an imaginary line drawn at 36º 30' latitude, which ran along Missouri's southern border. The Kansas-Nebraska Act abolished the Missouri Compromise. The Supreme Court deemed the Missouri Compromise illegal three years later in the Dred Scott decision, ruling that Congress lacked the jurisdiction to ban slavery in the territories. This only happened because they couldn't control the slave state anymore. What made it successful is this compromise was reached by 1820, when two bills were passed. Maine became the 23rd state as a result of the first. As the country expanded, the second added Missouri as a slave state and established the parallel 36°30' as the dividing line between enslaved and free states.It was unsuccessful because it promoted sectionalism between Northern and Southern states, the Missouri Compromise was ineffective in dealing with the issue of slavery. The “Gag Rule” in Congress (1831-1844) ● ● ● ● The House of Representatives enacted a resolution that automatically "tabled," or postponed action on any slavery-related petitions without a hearing. In subsequent Congresses, stricter versions of the gag rule were passed. “The relation which now exists between the two races,” he said, “has existed for two centuries. It has grown with our growth and strengthened with our strength. It has entered into and modified all our institutions, civil and political. We will not, cannot permit it to be destroyed.” The balance in power didn’t really change in congress. The southern states didn’t want the rule so they ignored the petitions. John Quincy Adams later then Rescind the rule. It was successful in the manner of getting there point across. The American Anti-Slavery Society started a petition effort against slavery in 1834. The number of petitions sent to Congress climbed dramatically during the next few years. It was unsuccessful because On a proposal by John Quincy Adams, the House repealed the gag rule in 1844. The Compromise of 1850 ● ● ● ● The 1850 Compromise is a set of five laws in to address the issues of slavery and territory expansion. California applied to join the Union as a free state in 1849, potentially upsetting the balance of power in the US Senate between free and slave states. The bills provided for slavery to be decided by popular sovereignty in the admission of new states, prohibited the slave trade in the District of Columbia, settled a Texas boundary dispute, and established a stricter fugitive slave act. The balance had shifted to sixteen free and fifteen slave states, while runaway slaves in the north face harsher penalties. This was seen as a good compromise by the Southern states. The 1850 Compromise revoke the Missouri Compromise, leaving the subject of slavery unresolved. It was unsuccessful because the Fugitive Slave Act. Citizens were required to aid in the capture of fugitive slaves. A fugitive's right to a jury trial was denied. The new law was a tragedy for slaves hoping to start new lives in the North. The Kansas Nebraska Act (1854) ● ● ● ● The Kansas Nebraska Act issue gave each territory the power to decide on slavery through popular sovereignty. Slavery in Kansas would be a violation of the Missouri Compromise, this compromise had kept the Union together for the previous thirty-four years. This act repealed the Missouri Compromise. “with or without slavery, as their constitutions may prescribe.” Known as “popular sovereignty,” This affected the balance of congress with the bleeding Kansas. Proslavery and antislavery advocates flocked into the territories to affect the vote, resulting in a violent revolt known as Bleeding Kansas. This act allowed slave owners to have power in the west. This act was not successful. It brought nothing but chaos because the pro and anti slavery went and fought and slave owners were able to get there runaway slaves back. The Crittenden Compromise (1860) ● ● ● ● The issue in the Crittenden Compromise was they proposed that slavery should be enshrine. There were also 6 amendments that gave the south concerns. They didn’t want the abolishing of slavery fro federal land in slave states. “Crittenden Compromise was a constitutional amendment to revive the Missouri Compromise line by extending the southern boundary of Missouri (36 degrees, 30 minutes) west to the Pacific Ocean.” This was a not successful. It was unsuccessful because it was too direct and unreasonable. It was mainly unsuccessful because the amendments stated that they will never be changed again. The balance of power for congress was firm. Even though they proposed all the amendments for the compromise were rejected they tried to make it so the balance of power couldn't have an effect on the amendments.