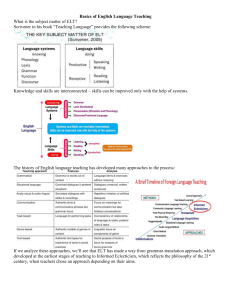
LEARNERCENTERED TEACHING • deepen your understanding on how to become proficient in implementing a learner-centered teaching approach. Checklist on LearnerCentered Pedagogy • Were you allowed by your teachers to set specific learning goals for your self? • Have you experienced being given the freedom to choose a topic for a course requirement? • Have you experienced being asked by your teacher for your input or opinion in deciding what topics to learn in a course? • Have you experienced being given a chance to choose a type of assessment task you can do to effectively demonstrate what you already know? • Do your teachers frequently check first what you already know about a certain lesson? • Has collaboration among students emphasized more than competition in your learning experience through the years? • Have you experienced being given the opportunity to develop your self- and peer-assessment skills? • Have you experienced being given a flexible date for submitting your project? LEARNER-CENTERED TEACHING • has become a popular phrase among educators nowadays. • t has been named in several ways such as student-centred approach or learner-centered pedagogy in many textbooks and journal articles. • a book published in 2002 by Maryllen Weimer stands as one of the earlier attempts to comprehensively discuss and define what is LCT about. ‘Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice’ Balance of Power • learners are frequently consulted and given immediate and ongoing feedback by the teacher. • the teacher empowers students by giving them the opportunity to choose and make decisions like selecting among lesson topics, choose learning activities, determine pace of learning, and select an assessment task to demonstrate one’s mastery of targeted learning competencies. Function of Content • teachers need to allow learners to raise their own questions, generate their own answers or solutions. • "Students must construct their own meanings” (Stage, Muller, Kinzie, and Simmons, 1998, p. 35). In other words, learners are capable of constructing and reconstructing their knowledge through active personal effort. • teachers must begin by finding out students’ prior knowledge or conceptions and then design Role of Teacher • Constructivism theory brings the role of the teacher as that of a facilitator of learning, not as the fountain of learning. • greater involvement with students by the teacher is central to student motivation. • Teachers must become comfortable with changing their leadership style from directive to consultative-- from "Do as I say" to "Based on your needs, let's codevelop and implement a plan of action. Responsibility for Learning • the goal of 21st century education ought to be the creation of independent, autonomous learners who assume responsibility for their own learning. • Learning skills of autonomous self-regulating learners can be learned and must be taught even at an early age. This is even more important when entering higher education. • Learning is cooperative, collaborative, and community-oriented. • Students are encouraged to direct their own learning and to work with other students on research projects and assignments that are both culturally and socially relevant to them. Evaluation Purpose and Process • The literature on self-directed learning also underscores the importance of assessment, only in this case it is the ability of students to self-assess accurately. Sophisticated learners know when they do or do not understand something. • They can review a performance and identify what needs improvement. • They have mechanisms for its collections and methods for evaluating it and acting on it. Four Principles of Student-centered Approach Top 20 Principles for Teaching and Learning LESSON 2 Lesson Structure Learner-centered pedagogical approach talking to each other in small and large groups making public their personal knowledge and beliefs constructing and testing their knowledge with peers and teachers. ACCORDING TO THIS IMAGE OF TEACHING AND LEARNING, THE IDEAL CLASSROOM FOR THE 21ST CENTURY LEARNERS WILL NO LONGER BE ONE IN WHICH 30-50 STUDENTS ARE ALWAYS LISTENING TO THE TEACHER OR SILENTLY WORKING ON THEIR OWN. ALTHOUGH CONTEMPORARY TEACHING PRACTICES STILL INVOLVE LECTURE, DRILL, AND PRACTICE, STUDENTS NEED TO BE TRAINED TO WORK IN ALTERNATIVE ARRANGEMENTS SUCH AS: FIVE FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF COOPERATION Personalized Learning Approach (PLA) • In personalized Learning systems, instead of counting the number of hours students are in their seats, students move through coursework and graduate based on their ability to show they have mastered the material • Personalized learning refers to instruction in which the pace of learning and the instructional approach are optimized for the needs of each learner (United States National Education Technology Plan 2017). Learning objectives, instructional approaches, and instructional content (and its sequencing) may all vary based on learner needs. • Personalized learning is a progressively student–driven model where students deeply engage in meaningful, authentic, and rigorous challenges to demonstrate desired outcomes (Zmuda, Curtis & Ullman, 2015). • Four design elements have been associated to the personalization movement (Olofson et. al, 2018). Differentiated Instructional Approach (DIA) • was first popularized by Carol Ann Tomlinson with her book How to Differentiate Instruction in Mixed-Ability Classrooms, published in 1995. • she described teachers in differentiated classes as using time flexibly, applying a range of instructional strategies, and becoming partners with their students so that both what is learned and the learning environment are shaped to authentically support the learning process of the student. • teachers usually differentiate their teaching by modifying three aspects in his/her classroom practice. Each aspect of practice is presented below with examples on how each is applied in actual teaching practice. Differentiating 3 Aspects of Pedagogy Design Elements of Personalized Learning Approach Teaching Strategies According to Approach A comparison of teaching approaches Thank You Application • You may conduct a one-on-one interview with a new and seasoned teacher in your school, or among your relatives and friends, or those within your neighborhood. List down his or her practices in terms of applying the learnercentered teaching approach. • After conducting the interview, what was the most interesting response you received from your interviewees? Why do you say so?