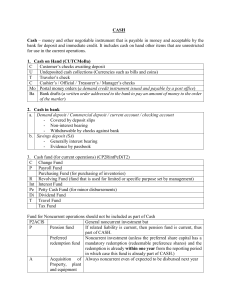
CHAPTER 1: Cash and Cash Equivalent Cash According to layman, cash means money. According to accounting, cash includes money and any other negotiable instrument that is payable in money and acceptable by the bank for deposit and immediate credit. Noncurrent: pension fund, except related liability is current acquisition of PPE contingent fund insurance fund sinking fund, except related liability is current Cash equivalents It is a short – term and highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of changes in interest rate. (PAS 7, paragraph 6) acquired three months before maturity can quality as cash equivalents Money standard medium of exchange in business transactions refers to the currency and coins which are in circulation and legal tender Examples of cash equivalent Unrestricted cash An entity shall classify an asset as current when the asset is cash or cash equivalent unless it is restricted to settle a liability for more than twelve months after the end of the reporting period. (PAS 1, paragraph 66) to be recorded as cash, if the item is unrestricted in use cash must be readily available in the payment of current obligations and not be subject to any restrictions three – month treasury bill three – month treasury bill purchased three months before maturity date three – month time deposit three – month money market instrument or commercial paper Date of purchase Cash items included in cash a. customer’s check cashier’s or manager’s check traveler’s check bank drafts money order Cash in bank – unrestricted as to withdrawal c. important in cash equivalent Cash on hand – undeposited cash collections and other cash items awaiting deposit b. demand deposit checking account saving deposit Investment of excess cash Cash equivalents – three months or less Current assets – more than three months but within one year Noncurrent assets – more than one year If the problem is silent Noncurrent assets – treasury notes and bonds Cash fund – set aside for current purposes Cash and cash equivalents – cash in money market account Current: Cash and cash equivalents – time deposit petty cash fund payroll fund dividend fund tax fund change fund purchasing fund revolving fund travel fund interest fund Cash measurement Cash measured at face value (original cost stated). In bankruptcy or financial difficulty, cash measured at estimated realizable value. Cash in foreign currency must translated using current exchange rate. Example: dollar to peso Note: If foreign bank is subject to restriction it is classified as noncurrent asset. Bank overdraft credit balance in the cash in bank account results from the issuance of checks in excess of the deposits classified as current liability and should not be offset against other bank accounts with debit balances generally not permitted Exception to the rule on overdraft • entity maintain two or more accounts in one bank, overdraft can be offset against other bank account • overdraft can be offset against other bank account if the amount is not material • overdraft can be offset against other bank account when payable on demand and often fluctuates from positive to negative as an integral part of cash management Compensating balance • form of minimum checking or demand deposit account balance that must be maintained in connection with a borrowing arrangement with a bank Classification of compensating balance • Not legally restricted or informal – cash • Legally restricted or formal – current or noncurrent asset • If silent – cash Undelivered or unreleased cash • merely drawn and recorded but not given to the payee before the end of reporting period