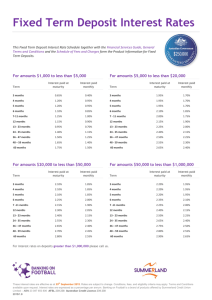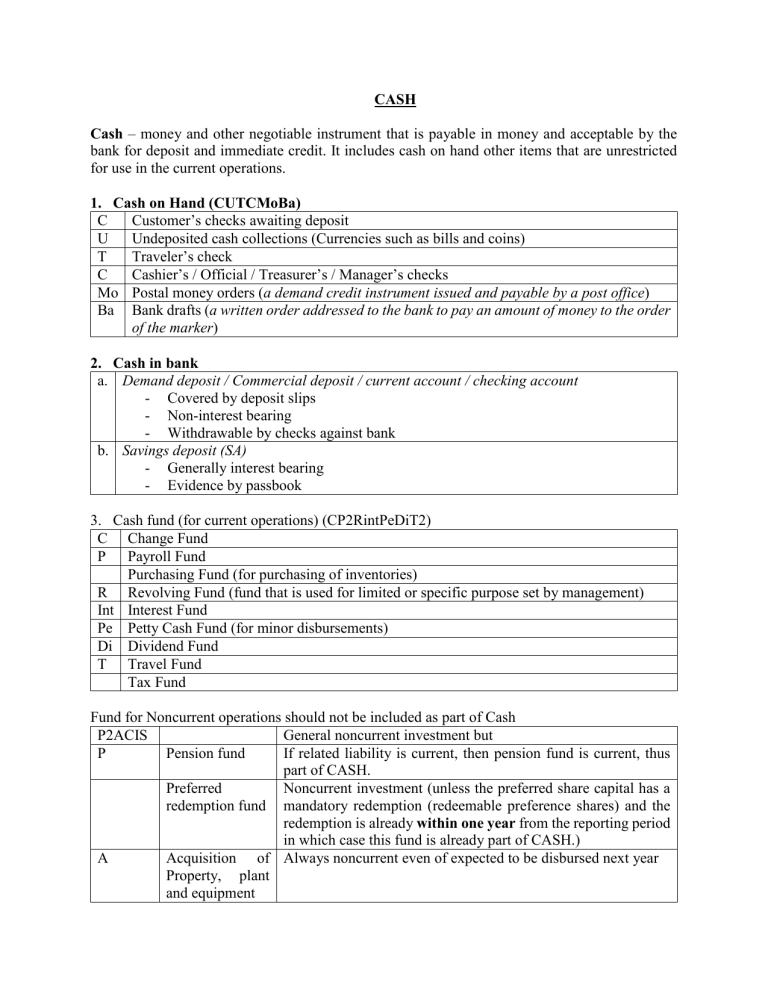
CASH Cash – money and other negotiable instrument that is payable in money and acceptable by the bank for deposit and immediate credit. It includes cash on hand other items that are unrestricted for use in the current operations. 1. Cash on Hand (CUTCMoBa) C Customer’s checks awaiting deposit U Undeposited cash collections (Currencies such as bills and coins) T Traveler’s check C Cashier’s / Official / Treasurer’s / Manager’s checks Mo Postal money orders (a demand credit instrument issued and payable by a post office) Ba Bank drafts (a written order addressed to the bank to pay an amount of money to the order of the marker) 2. Cash in bank a. Demand deposit / Commercial deposit / current account / checking account - Covered by deposit slips - Non-interest bearing - Withdrawable by checks against bank b. Savings deposit (SA) - Generally interest bearing - Evidence by passbook 3. Cash fund (for current operations) (CP2RintPeDiT2) C Change Fund P Payroll Fund Purchasing Fund (for purchasing of inventories) R Revolving Fund (fund that is used for limited or specific purpose set by management) Int Interest Fund Pe Petty Cash Fund (for minor disbursements) Di Dividend Fund T Travel Fund Tax Fund Fund for Noncurrent operations should not be included as part of Cash P2ACIS General noncurrent investment but P Pension fund If related liability is current, then pension fund is current, thus part of CASH. Preferred Noncurrent investment (unless the preferred share capital has a redemption fund mandatory redemption (redeemable preference shares) and the redemption is already within one year from the reporting period in which case this fund is already part of CASH.) A Acquisition of Always noncurrent even of expected to be disbursed next year Property, plant and equipment C I S Contingent fund Insurance fund Sinking fund Noncurrent investment Noncurrent investment If related bonds payable is current, then sinking fund is current, thus part of CASH. Note: Classification of cash fund as current or noncurrent should parallel the classification applied to the related liability. Thus, an entity should reclassify such noncurrent asset if the related liability becomes current. CASH EQUIVALENTS Cash equivalents are short-term and highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into cash and so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of change in value because of changes in the interest rates. Only highly liquid investments that are acquired three months before maturity can qualify as cash equivalents. 1. Time Deposit 2. Money Market Instrument of Commercial Paper 3. Treasury Bills 4. Redeemable preference shares with mandatory redemption acquired three months before maturity. TIME DEPOSIT, MONEY MARKET INTS., T-BILL 1. Originally invested/acquired for more than three months before maturity date a) Remaining term is three months -short-term investments or less from the BS date. b) Remaining term is more than three -short-term investments months but within one year c) Remaining term is more than one year -short-term investments 2. Originally invested/acquired for three months or less before maturity date -cash and cash equivalents Comparison among T-Bills, T-notes and T-bonds Differences in Maturity date Similarities Treasury Bills 90-days – less than 1 year All are issued government Treasury Notes 1 year – less than 10 years Treasury Bonds 10 years or more by the Note: If an item cannot be included as cash equivalent because it did not qualify the cut-off time period (ie. three months), it will always be classified as investments (short-term or long-term) depending on the period up to maturity. Note: If the problem is silent with regard to: 1. Treasury Note-assumed investment 2. Cash in Money market account-cash and cash equivalent 3. Time Deposit-cash and cash equivalent Some measurement issues on cash Items Remarks Cash Measured at face value Cash in foreign currency Should be translated to Phil. peso using the current exchange rate (spot rate) at B/S date Deposit in foreign bank a. Unrestricted – included as cash b. Restricted – if material, classified separately among non-current assets as receivables Cash in closed bank/ Banks in Measured at estimated realizable value and be included Bankruptcy among noncurrent assets if the amount recoverable is lower than face value. Bank overdraft The company is maintaining two accounts in a. Different banks – current liabilities or may be netted against other bank if immaterial. b. Same bank – maybe netted against the account with positive amount but you cannot offset against restricted account. Note: An overdraft may also be netted against other account if it is part of cash management. Compensating balance Compensating balance are minimum checking or demand deposit account balance that must be maintained in connection with a borrowing agreement with a bank a. Not legally restricted – part of cash b. Legally restricted – if the account is legally restricted as to withdrawal, check the related loan: 1) Short-term – presented as “cash held as compensating balance” (current receivable) 2) Long-term – presented as “cash held as compensating balance” (noncurrent receivable) Note: If the problem is silent with regard to compensating balance, it is assumed not legally restricted. Effect of compensating balance on: a. Yield rate (lender) – increase b. Effective rate (borrower) – increase yield rate (Effective rate) = Net interest income (expense) Net Proceeds Undelivered/unreleased check Reverted back to cash by a Cash XXX Accounts Payable XXX Stales checks/checks long -checks not encashed by the payee with a relatively long outstanding period of time (identification if a check is stale should be based in the company’s policy regarding encashment of check) -reverted to cash by a Cash XXX Accounts Payable XXX (if material) Miscellaneous income XXX(if not material) Postdated checks a. Company’s own – reverted to cash Cash XXX Accounts Payable XXX b. Customer’s check – not yet cash ( Accounts Receivable) IOUs Included as part of receivable, not cash and cash equivalents Equity securities Cannot be classified as cash equivalents because shares do not have a maturity date (with the exception of redeemable preference shares) Redeemable Preference shares Preference shares with specified redemption date and acquired three months before redemption date is classified as cash equivalents Callable preference shares Not classified as cash equivalents NSF/DAUD/DAIF Included as part of receivables NSF – no sufficient fund DAUD – drawn against unclear deposits DAIF - drawn against insufficient funds Expense Advances (ex. travel Receivables or prepaid expense advances, postage stamps) Temporary Investments in Shares Either trading securities or AFS but never to be included as of stocks part of cash Unused Credit Line Disclosed in the notes (Difference between the amount of line of credit applied for and approved by a bank and the amount actually borrowed) Treasury Warrants A warrant for the payment of money into or from public treasury. Classified as cash Escrow Deposit Part if other current/noncurrent asset and reported as liability (Restricted amount held in trust for another party, e.g., a deposit required by a court of law for a pending case) Postage stamps on hand Should be reported as office supplies or as a prepaid expenses Unrecorded cash disbursements -record the disbursements by debit to Account payable or other appropriate account and credit to cash. Unrecorded cash -record collection by debit to Cash and Credit to Accounts collections/receipts receivable or other appropriate account. Certificate of Deposit Investment not unless invested within three months before maturity.