Periodic Table Groups, Periods, Metals, Non-Metals, Metalloids
advertisement

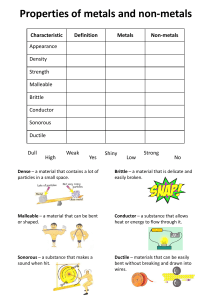
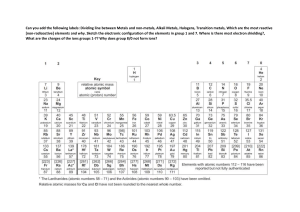
Groups Periods and groups are used to organize the iconic periodic table into columns and rows. Groups, also called families, are the vertical columns. There are 18 groups The elements arranged into groups are based on certain characteristics such as chemical or physical properties. As you go down a column the atomic radius increase Reactivity of elements increases down the group as down the group number of shells increases and thus nuclear pull on the outermost electrons decreases. Periods Each horizontal row of an element is called a period There are 7 periods Each period denotes a new energy shell. From hydrogen down to francium the elements increase in atomic orbitals. The first element in a period is always a solid and the last element is always a gas Periods are arranged according to their electronic configuration As you go across a period (Left to Right), then the atomic radius decreases Reactivity decreases as you go from left to right across a period Properties of Metals Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Metals are shiny They are ductile and malleable They are solid at room temperature except mercury (Hg) They have high densities, and melting and boiling points They have low ionization energy and low electronegativity They form metallic bonds Properties of Non-Metals Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity except graphite Non-metals are not ductile or malleable Solid non-metals are very weak and brittle which means that they can break easily They are dull and do not have lustre like metals Most of the non-metals are gases at room temperature Non-metals are neither tough nor strong Non-metals have high ionization energy and high electronegativity They form covalent bonds Properties of Metalloids Metalloids (metal-like) have properties of both metals and non-metals Physically they are shiny and brittle solids They are semi-conductors of heat and electricity They usually look like metals but behave largely like non-metals Metalloids are known to form amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides They can generally form alloys with metals They form covalent bonds but sometimes they also form ionic bonds