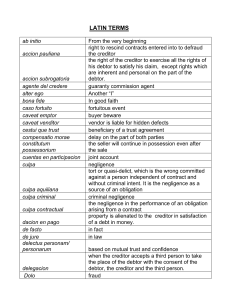
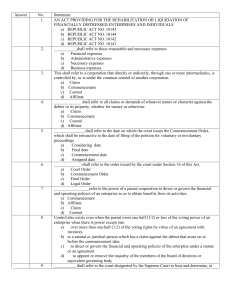
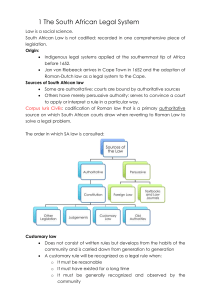
Assignment – is a contract by which one person (creditor/assignor) transfers to another his rights and actions against a third person (debtor) in consideration of a price certain in money or its equivalent. Credit – this refers to those Assets, which anything that has material value or usefulness from a person or a judicial entity. Incorporeal – this refers to those property or assets which does not have any material/physical form. Examples: rights and patent. Rights – in technical term, rights refer to a just, title or legal claims. *first slide Subrogation – this is when a person, which in this case, the creditor (assignor) transfers all the rights and credits to another person called as the assignee and the assignee would then be legally capable to enforce performance or satisfaction of the credit from the third person or the creditor. Article 1627 – which after the perfection of the contract the article 1627 states that the assignment of credit includes all the accessory, such as guaranty, mortgage, pledge and preference. This follows the rules that the accessory follows the principal. Article 1626 – which provides that a notice to the debtor is a must because the effect of payment would differ if such notice has not been acquired by the debtor. But, the art. 1626 also provides that a consent from the debtor for the assignment of credit is not required for such assignment to produce legal effects. Rules on donation or as a sale or purchase *Second slide Article 1475, and 1458, which the assignment of credits and other incorporeal rights having those three essential requisites (COC) and as being consensual, of course, there is must be meeting mind makes it the assignment perfected. Article 1625 – an assignment of credit, right, or action shall produce no effect as against third persons, unless it appears in a public instrument, or the instrument is recorded in the Registry of Property in case the assignment involves real property. Binding effects: o 1) between the parties, assignment is valid although such assignment appears only in a private document as long as the law does not require any form for its validity. (Art. 1356) o 2) but to affect third person, it must appear in a public instrument which is to be attested or certified by a public officer such as notary public and in case it involves real property, it is indispensable that it be recorded in the Registry of Property. *third slide Only the number 3: the assignee has already become the creditor and has already acquired all the rights, so the all defenses put up by the debtor to the original creditor (such as fraud, prescription) is also subrogated to the assignee.