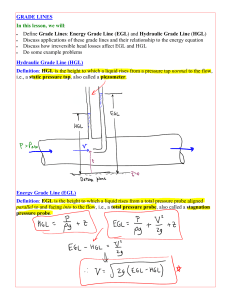
Open-Channel Flow • any flow that occupies a defined channel and has a free surface (free surface flow) • the free surface is subject to atmospheric pressure (if pipe flow, pipe is not flowing full) - not completely enclosed by solid boundaries • the flow is caused by gravity component along the slope of the channel (gravity flow) • the pressure distribution within the fluid is hydrostatic CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS 1 Classification of flow • Open-channel flow – There is a free surface open to the atmosphere. – Driven by gravity. – Examples: • Streams, rivers CIVL3011: Hydraulics • Pressurized pipe flow: – There is not a free surface. – Mainly driven by pressure. 2 Basic Terminologies Hydraulic Grade Line (HGL) line drawn through the tops of piezometer columns Energy Grade Line (EGL) line indicating total head Kinetic Energy velocity Head vertical distance between HGL & EGL CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS 3 Definitions 1 1 2 1 ℎ𝑙 : headloss between 𝑣12 2𝑔 section 1 and section 2 ℎ𝑙 𝑆𝑓 y1 𝑆𝑓 : 𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 𝑠𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 𝑆𝑤 : 𝑊𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑠𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 𝑆𝑜 : 𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑙 𝑠𝑙𝑜𝑝𝑒 𝑣1 𝑆𝑤 𝑣22 2𝑔 z1 L 𝑆0 𝑣2 Dx Datum y2 z2 Figure: Definition Sketch y Dx L = = = CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS flow depth (measured vertically) Horizontal distance between sections Length between sections (along the channel) 4 Channel Properties/Definitions • flow depth - vertical distance from the lowest point in a channel to the water surface • flow stage - elevation of water surface relative to a datum • top width - with of the channel section at the water surface • flow area - cross-sectional area of flow normal to the direction of flow • wetted perimeter - length of the line which is the interface between the fluid & the channel boundary • hydraulic radius - ratio of flow area to wetted perimeter • hydraulic mean depth - ratio of flow area to top width CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS 5 Geometric Functions Source: Mays (2011) CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS 6 Channel Properties Source: Chanson (2002) CIVL3011: HYDRAULICS 7