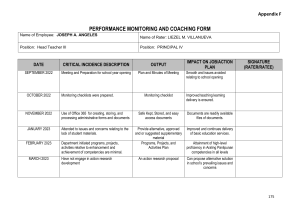
‘Mechanical dynamics’ Part 1: Introduction / Statics FH-Kärnten - Villach / Oct/Nov 2022 Dipl.-Ing. Georg Schmeja References • • • • Hibbeler, Statics and Mechanics of Materials (SI-Edition) / Pearson Education Horst Herr, Technische Mechanik (Alfred Böge, Technische Mechanik) (ÖH-TU-Graz, Prüfungsbeispielsammlung Statik) All pages marked with "© Pearson Education" contain copies out of: "Hibbeler: Statics and Mechanics of Materials (SI-Edition)" Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 2 Technical Mechanics • Technical Mechanics – – – – – – Statics Kinematic (geometric relations of motion) = Dynamics Kinetics (motion by forces) Dynamics (acceleration and forces) Material-/Structural Strength (stresses, deflection and stability) Hydromechanics (Hydrostatics / Hydrodynamics) • Knowledge about statics has to be considered as a precondition to understand dynamics. • This dynamic-course will also teach some basics of statics to safeguard the principle knowledge of mechanics among all students. Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 3 Statics means ... • ΣF = 0 • ΣM = 0 = Equilibrium • F = m*a • M = F*x • 3 degrees of freedom in 2 dimensional systems • 6 degrees of freedom in 3 dimensional systems • Moment [DE/EN) = torque, bending-moment, torsional moment • Momentum [EN] = Impuls [DE] Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 4 Some essential (basic) units • • • • • • • • • Mass m in [kg] Time t in [s] Length/Distance s in [m] Force F in [N] before in [kp] Torque (moment) M in [Nm] Velocity v in [m/s] Acceleration a in [m/s²] Work / Energy W or E in [J] = [Ws] Power P in [W] • • • • F = m*a M = F*r W = F*s P = W/t Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 5 Symbols Symbol Reaction-Forces Degrees of Freedom supported hinged clamped Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 6 Basic Triangular Formulas • General C γ b – Sine law: a / sin = b / sin = c / sin γ – Cosine law: A c² = (a² +b² - 2ab cos γ) a c B • Right angle triangle γ = 90° – c = Hypotenuse – a, b = Cathetus sin = oposit leg / hypotenuse = a / c cos = adjacent leg / hypotenuse = b / c tan = oposit leg / adjacent leg Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 7 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 8 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 9 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 10 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 11 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 12 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 13 Graphic Solution Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 14 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 15 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 16 Vector Addition and Forces © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 17 Moment © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 18 Moment © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 19 Moment d) explain and indicate the distribution of shear-force and momentum The sketch shows a beam with 1500 mm length. A mass of m=25 kg is fixed to the free end a) Calculate the weight in N b) Calculate the max. moment c) How could the moment be called d) explain and indicate the distribution of shear-force and moment Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 20 Moment © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 21 Moment © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 22 Moment and Force © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 23 Moment and Force © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 24 Graphic indications • http://www.statik-lernen.de/grundl_zustandslinien_2.html Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 25 Free body diagram © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 26 Free Body Diagrams © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 27 Free Body Diagrams © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 28 Free Body Diagrams © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 29 Replacing supports by forces and moments © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 30 Free body diagram for hinges, clamps, bearings ... © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 31 Principles free body NOT possible © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 32 Draft the free body diagram Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 33 Draft the free body diagram Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 34 Draft the free body diagram Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 35 Draft the free body diagram Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 36 Draft the free body diagram Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 37 Draft the free body diagram of the piston Schmeja / 2022/2023 Draft the free body diagram of the crane Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 38 Free body diagram © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 39 Free body diagram © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 40 Free body diagram Solution to 5-32 © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 41 © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 42 FA Determine the size and direction of the reaction force in A ΣFx = 0 = F2*cos45 – F3*cos60 +F5*cos60 +FA = 0 Fx = - 294,9 N Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 43 Determine the forces in beams 1,2,3,4 by drafting. F = 40 kN Tip: Start with F1 and F2; then determine F3 and F4 from F2 Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 44 Graphic Solutions Graph of geometry Graphical solution with multiple forces not in one point: Create the graph of forces and the resultant Graph of forces Choose a pole 0 and draft the polelines, starting with No. 0 Shift the pole-lines into the graph of geometry Shift the resultant to the intersection of first and last pole-line Graph of geometry Schmeja / 2022/2023 © Pearson Education Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 45 Determin the size of F_res using the “Seileckverfahren” Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 46 The trick of the “final line”: Start with pole-line 0/1 (a) in one of the supports. Draw a line between this point and intersection of 5 and the actionline of F_By (b). Connect a and b (final line”s”). Shift s back into the plan of geometry and measure the distribution between F_Ay and F_By Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 47 Determin: F_Ax; F_Ay; F_By Determine F_A and F_B analytically. FAy = F1+F2y+F3y+F4+F5y-FAy FAy = 11,8 kN FAres = wurzel(FAx² + FAy²) Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 48 If the lines of action are known, the resultant of four forces can be determined by the “Cullmann-Line”. Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 49 Cullmann Solution Determin the forces in A and B: • Draft the geometry graph and the force graph • Indicate the resultant force in the geometry graph and find the intersection with the line of action of one support • Draw the Cullmann-Line to the 2nd support • Shift the Cullmann-Line into the plan of support-forces, thus defining the support reactions Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 50 a) Determine F3 with alpha = 32° b) Determine the reaction forces in D Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 51 Homework A pantograph is designed out of a bent lever. Determin Fz to gain equilibrium. Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 52 Center of Gravity © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 53 Center of Gravity © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 54 Center of Gravity Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 55 Truss evaluation • Staticly defined if s=2*k–3 s = number of beams k = number nodes no bending of beams no stiffness of joints Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 56 Method of joints © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 57 Zero-force members © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 58 Method of joints © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 59 Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 60 Method of joints Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 61 Resolve by using the cullmann principle Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 62 Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 63 Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 64 Friction (static/dynamic) • FR_0 = µ0 * FN • FR = µ * FN Static friction Dynamic friction • Fricion is independent from the size of the contact area Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 65 Friction • M56 © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 66 Friction © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 67 Loco towing force • What is the maximum theoretic force a locomotive with 4 axles and an axle-load of 20 t can develop? • Estimation µ = 0,12 – 0,35. • What is the relevance of the given range for µ ? • 80t * 9,81 * 0,12 = 94 kN for operation • 80t * 9,81 * 0,35 = 274 kN for design (gearbox, axle, ..) Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 68 Friction © Pearson Education Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 69 Seilreibung (Belt friction) F1 = F2 * e µ in rad A rope is slung around a wheel n=2,25 times. µ = 0,35 • Which force is transmitted into A when the cylinder is turning and F_G = 2kN • What is the braking torque if d=500 mm Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 70 References • • • • Hibbeler, Statics and Mechanics of Materials (SI-Edition) / Pearson Education Horst Herr, Technische Mechanik (Alfred Böge, Technische Mechanik) (ÖH-TU-Graz, Prüfungsbeispielsammlung Statik) All pages marked with "© Pearson Education" contain copies out of: "Hibbeler: Statics and Mechanics of Materials (SI-Edition)" Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 71 Helpful links • • • • • • • • http://www.bau.hs-wismar.de/boddenberg/tm1/ http://www.statik-hilfen.de/Mechanik/Mechanik_01.html http://www.tm-aktuell.de/TM1/ http://www.tm-aktuell.de/TM2/ http://www.tm-aktuell.de/TM3/ http://www.tm-aktuell.de/TM5/Animationen/animationen.html http://www.statik-lernen.de/grundl_kraefte_1.html http://www.engr.uky.edu/statics/Content/ContentHome.html • http://www.strandbeest.com Schmeja / 2022/2023 Mechanical Dynamics - Statics 72