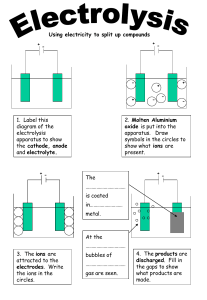
ELECTROLYTIC CELLS Activity 1 Watch the video What is electrolysis? Video Electrolysis is the process by which electric current is passed through a substance to effect a chemical change. The chemical change is one in which the substance loses or gains an electron (oxidation or reduction). The reaction takes place in an electrolytic cell. Electrolytic cells In electrolysis, electric force is applied from the external circuit using a battery or power source and this forces the species in the electrolyte to break up. In electrolytic cells, electrolytes are broken down using electric current. In the electrolytic cells electricity is used to break electrolytes into its components. Arrows indicate the motion of ions, which are released into the electrolyte by oxidation reactions at the anode and then deposited on the cathode in reduction reactions. Figure 1: Electrolytic cell (source) 1 For example, the electrolysis of molten lead (II) bromide results in the breaking up the compound into its constituent elements. The ionic substance is broken to produce the original ions, which loss or gain electrons at the electrodes to form pure elements. Hence electrolysis of molten lead II bromide will give lead and bromine. PbBr2 consists of Pb2+ ions and Br- ions in an ionic compound. When melted (molten) these ions are free to move. At the cathode The Pb2+ ions go to the cathode where they pick up electrons and become Lead atoms Pb2+ + 2e Pb At the anode The Br- ions go to the anode where they lose electrons and become Bromine molecules. 2Br- Br2 Answer the following questions. a) Define electrolysis and an electrolyte. b) Describe the electrolysis of one of the following molten or liquid electrolytes using carbon electrodes. (i) NaCl (ii) CuCl2 (iii) ZnO c ) Draw a labelled diagram of the electrolytic cell in (b) above (d) write the half equations on each electrode. 2 Application of electrolysis Extraction of aluminium video 3