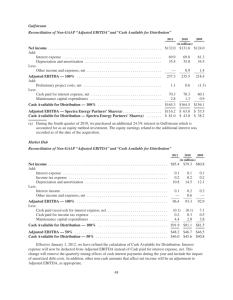
Is there one approach to calculate operating profit / EBITDA? There are different types of earnings or profit: gross profit, operating profit, net profit before tax, net profit after tax etc. Financial statements under local GAAPs or IFRS normally do not include EBITDA. Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortisation (EBITDA) are widely used in corporate finance: business valuation, project finance and many other purposes. They include Operating profit which is ~ to Earnings before interest and profit taxes. So you may add back DA and get EBITDA. It is assumed to be close to operating cash flows, with some adjustments to be made. However, there is no one for all approach to calculate EBITDA in theory / practice of CF. IMPORTANT: Calculation may differ depending on the purpose. − For business valuation purposes – we usually use normalized EBITDA excluding some extraordinary items of income / expense − For bank finance and covenants − For management decisions and other. You need to be careful with items of income and expense as there is a room for manipulation to demonstrate better or worse case for some particular reason. However, in order to properly calculate EBITDA you may need several notes and breakdowns of different types of historical or projected income and expense. Description RUBmln. 100 (40) 60 (10) (10) 5 (15) Renenue COS* Gross margin S&D expenses* G&A expenses* Other income Other expense* Operating profit ~ EBIT 30 … * Including depreciation expense for the period in total => EBITDA ~ (15) 45 Income and expense items to be included in the calculation of EBITDA: Not included Profit / loss from revaluation of assets and liabilities and other assets / liabilities Profit / loss from sale of FA / IFA Income and expense on exchange rate differences Income from interest subsidies Loss / profit received in the previous periods May be included Income from subsidies related to the operating activities of the company Subject to agreement due to specifics of the project / business Income / expenses for accrual / release of reserves One-time and non-operating income / expenses Income / companies expenses with Study QUESTIONS: − Consider example. Assume Other expenses include RUB 12 mln for death of cattle. How we treat them in EBITDA for (i) business valuation, (ii) financial covenants? − Consider Loan agreement in project finance. Do we need to prescribe all components of EBITDA calculation? Why / why not? − What are the major EBITDA ratios / multiples in corporate finance? affiliated Fines, penalties, forfeits, etc. Profit / loss from the sale of goods and other assets Expenses for social. needs and other nonproduction. costs − What is EBITDAR? / EBITDARM / OIBDA? − Normal EV/EBITDA multiple is from 4 to 10. In some cases it could be 10-15. Name 2-3 reasons for that. Source: KPMG illustrative FS 2018 Source: PWC illustrative FS 2018 Examples