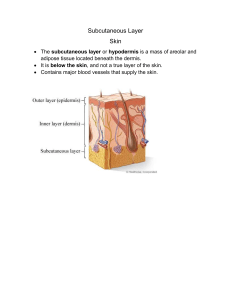
What is an organ? What is the largest organ in the body? A. Liver B. C. D. E. Skin Brain Stomach Large intestine An organ is made up of at least 2 main tissues types (Chapter 4) that work together for a common function? Describe how the skin is an organ after you study it. Integumentary system: The skin and its derivatives such as hair and nails. • Protection: Covers all of the body. There is a layer of fat below the skin that acts as a cushion. The skin protects us from dehydration as well. • Regulation of body temp: Skin does this through sweating and hairs on the skin (when hair stands on end it helps warm the body = goose bumps). Fat also acts as an insulator just below the skin. • Defense: Covers the body to act as a first line of defense to keep things out. There are also white blood cells in the skin to act as defenders. • Helps synthesize “vitamin D”: Precursor to vitamin D is made in the skin when exposed to sunlight. • Sensory reception: Many sensory receptors in the skin that gives us information about the world around us. How many skin cells do you think you can shed per second? A. B. C. D. 4,000 15,000 25,000 40,000 Much of the dust found in your house is made up of dead skin cells. There are also dust mites feeding on these skin cells, even in your bed. Sleep well and don’t let the bed mites bite (they don’t bite you). They actually help clean up your mess. Epidermis: Remember this is a thin layer (only mm thick). This picture shows a blown-up image of the epidermis to show detail. • • • • Made of epithelial tissue Replaced often Waterproof (keratin in cells) Made up mostly of keratinocytes • Contains melanocytes (produce melanin that gives color to the skin and some protection from the sun). • No blood vessels (thin enough layer that things can diffuse in and out from the blood vessels in the dermis). Skin color originates in the epidermis People all have about the same number of melanocytes. How active they are and thus how much melanin they produce results in the different skin colors we see. That is it! Skin color tends to be darker towards the equator while it tends to be lighter towards the poles. There is a hypothesis that suggest skin color is the result of balancing certain nutrients made and destroyed by the sun to help with fetal development. Dermis • Mainly dense fibrous connective tissue • Lends strength & flexibility to the skin • Contains many structures such as glands, muscle, blood vessels, nerves etc… Hypodermis • Layer just below the skin and mostly made of adipose tissue • Anchors skin • Acts as a cushion and insulator ASK YOUSELF THESE QUESTIONS: Where is nervous tissue found in the skin? Where is muscle tissue found in the skin? Where is epithelial tissue found in the skin? Where is connective tissue found in the skin? See if you can answer these questions before looking at the next slide. The answers are provided here. ASK YOUSELF THESE QUESTIONS: Where is nervous tissue found in the skin? Mostly in the dermis (I left some information out that you don’t Need to know) Where is muscle tissue found in the skin? Dermis Where is epithelial tissue found in the skin? Epidermis is made of epithelial tissue and the glands in the dermis Where is connective tissue found in the skin? Dense fibrous tissue and blood vessels in dermis, also adipose below in the hypodermis 30% 65% 5% These are a result of ridges at the top of the dermis. They are unique in all humans, even among twins. What gives fingerprints their patterns? Dermal ridges at the top of the dermis /hypodermis Miocrobiota (microbiome) – microbes that live on and in you Made up of bacteria, mites and fungi Microbiota Bacteria and yeast that are normally found in and on our body such as on the skin in moist areas such as the groin, feet, folds and armpits as well in the digestive system. They are beneficial to us. Skin Microbiota: they get on and in everywhere. A new perspective on your skin! Microbiota varies between regions: Oily, moist and dry areas with host different microbes. I thought this was fun to look at! Microbiota varies between people as well. We are different in so many ways! Sharing microbiota • http://www.scientificamerican.com/video/wh y-we-live-in-a-cloud-of-microbes/ - Required: listen to this short 2-minute audio clip! Who lives in your home? A study was done looking at dust on the tops of doors in 1100 homes and this is what they found (Dec 2015): • Dogs appear to alter indoor bacteria more extensively than humans or cats. • Men shed more bacteria into their surroundings than women do and thus have a bigger impact on the variety of bacteria inside a home, too. The variation comes down to skin biology and maybe body size and hygiene practices. • The bacterial signatures of each of these living beings are unique enough that by simply testing dust in a home, investigators can accurately predict if more women or men live there and if dogs or cats do as well. https://www.theguardian.com/science/2015/aug/26/house-dust-can-revealwho-you-live-with-and-what-your-pet-is-study-shows - optional, article is summarized on this slide Writing Response 1 Assignment: Be sure to read the microbiota essay at the link under assignments (link is below as well) and then type a 2 paragraph (a good 8-10 sentence minimum) response which should be at least 1 page in length, double-spaced, 12-point font and 1” margins. The first paragraph should be what you learned whether it be one thing that most interested you or many and the second paragraph should be what it made you think about and/or your opinion. Write everything in your own words. Do not copy anything from the essay even if you put quotations around it. Save your response as a word DOCX or PDF, click on the title of the assignment on Blackboard and attach it using the browse my computer button. Click submit. Effort counts!!!!!! http://michaelpollan.com/articles-archive/some-of-my-bestfriends-are-germs/ Due by Wednesday, February 24th, by 11:59pm. Remember it must be in PDF or DOCX format!!!! The skin, sunlight and cancer Damages of sunlight on the skin • Cells in the epidermis can be damaged • Fibers in dermis are damaged (think wrinkles) • Small blood vessels • DNA (think cancer) A sunburn is essentially a first degree burn. The red color is from the dilated blood vessels. What effect does sun (UV light) have on the skin? • Ages skin – Wrinkles – Age spots – Leather-like skin • Cancer Age spots to the left. Result of sun exposure. Above you see the loss of elasticity of the dermis and results in wrinkles. Where does skin cancers occur…all skin cancers originate in the epidermis. The 3 arrows show the origin of the 3 skin cancers: 1. Basal cell carcinoma 2. Squamous cell carcinoma 3. Melanoma Skin Cancers: Melanoma is the least common but most dangerous. It is the most likely to metastasize. The important thing is for early detection of skin cancer! Basal cell Squamous cell Melanoma Signs of skin cancer: Things to look for! A B C D ABCDE’s of Skin Cancer Evolution (not shown in the picture). There is a change in the size, shape, symptoms (such as itching or tenderness), surface (especially bleeding) or color of a mole or patch of skin. Check your skin regularly for changes!