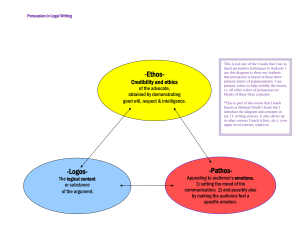
Second Quarter: Lesson 1 The Neoclassical Period Joseph Addison (1672-1719) - was a man of cheerful and amiable disposition - was a master of the art of living with his fellowmen - set himself to strip off the mask of vice, to show ugliness with all its deformity, and to reveal the truth with all its loveliness - wrote “The Visions of Mirzah”, an essay rich in symbolism and human values Thomas Gray (1716-1771) - was a minor figure in English literature - wrote one of the best loved elegies in the English language; “Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard” William Blake (1754-1827) - was the son of a London tradesman - was labelled as a strange and imaginative child - claimed to see visions of God and angels - claimed to receive visits from Homer, Dante, and Virgil - highly developed imagination made him see nature as a vast spiritual symbol - wrote exquisite lyrics that mean more than what lies on the surface, like: “The Lamb” “The Tiger” Authors: John Milton (1608-1674) - was like a counterpart of Shakespeare; they are the two figures who stand most prominently in English literature. - works focused on or are concerned with the soul. - was a poet of steadfast will and purpose. - believed that the things of the world are trivial and momentary. - represents the religious consciousness of the Puritans of England. - was already a scholar in spirit at the age of 12; the joy that his studies gave him made him restless - became blind because of his restlessness - dictated his verse to someone who writes them down for him - Some of his literary pieces: Lost Paradise – inspired by the story of “Adam & Eve” On His Blindness – according to his personal experience On His Having Arrived at the Age of Twenty-Three Alexander Pope (1688-1744) - was the top literary figure of his time and for more than half a century dominated the literary world in England - was a versatile writer - wrote various kinds of verses on a variety of subjects - was one of the most prominent English poets in the early 18th century - wrote satirical works - wrote “The Universal Prayer” which shows that in the heart of all humans is a deep longing for God Parts of a Word 1. Prefix – part of the word that goes before the main part of the word 2. Root Word – main part of the word; simplest form of word; where several words, or “variants” grew out from 3. Suffix – added to the end of the word; element of the word added after the root UNFAITHFUL ENTRUSTED IMMORALLY Communicative Styles a. Intimate – used between people who know each other well; sometimes, speaker only uses a few words to be able to convey their message to the listener; also uses facial expressions and gestures (Ex: Telling loved ones that you love them, sharing fear or problems) b. Casual – an informal kind of communicative style that is often used with friends or family members; slang words and colloquialisms may be used; grammar is simplified [Ex: Wassup? (What’s up), Nope. (No.), Watcha gonna do? (What are you going to do?)] PROPORTION OF CONVICTION AND PERSUASION o o o Forms of Argumentation c. Consultative - uses polite words; uses the standard rules of grammar; often characterized by the speaker giving background information about the topic (Ex: Reciting in class, talking to your teachers or school administrators) d. Frozen – prepared beforehand; often, there is almost no interaction; if there is interaction, it is formulaic and symbolic (Ex: Mass, wedding ceremony) For a highly educated and intelligent audience, use conviction. For a hostile or indifferent audience, use persuasion. To produce an action, use persuasion. Propaganda - common form of argumentation - presents only one side of a proposition - Ex: Business establishments (Advertisement) Brainwashing - type of argument that uses coercion - uses rigidly controlled persuasion and propaganda in a mixture of sound and spurious arguments Types of Reasoning Inductive - using specific observations to form a general conclusion Deductive - using a general premise to form a specific conclusion Argumentation - a form of discourse by means of which we try to persuade others truth or falsity of a disputed manner reasoning systematically seeks to persuade others that certain ideas are true or false Persuasion and Conviction I. - Persuasion appeals to the emotion seeks to produce an action - Conviction logical reason seeks to move the mind II. Recognizing and Identifying Faulty Reasoning 1. Lack of understanding of terms. All terms used in an argument must be clearly defined. 2. Hasty generalization. Enough cases should support the conclusion arrived at. 3. Opinion substituted for a fact. Opinions are just that – opinions – and they should not be taken as facts. 4. Misuse of facts. Be sure facts, not just halftruths, are given. 5. Lack of reliable authority. Authorities must be reputable, recognized as authorities, and up-todate. 6. Name-calling. This fault in reasoning seriously weakens an argument and should be avoided. CONDITIONAL IF CLAUSES A. ZERO Conditional – describing situations that are ALWAYS TRUE or FACTUAL B. FIRST Conditional – speculating situations that are POSSIBLE to happen in the future C. SECOND Conditional – speculating situations that are LESS LIKELY to happen D. THIRD Conditional – speculating situations that are IMPOSSIBLE to happen Lesson 2 The Romantic Period Authors: 1. Robert Burns (1759- 1796) the songwriter of Scotland (many of his poems have been set to music) musicality is his leading quality son of a farmer; lived his sad, toilsome life Poems: addressed himself to the common people simple human emotions wrote “A Red, Red Rose” 2. Sir Walter Scott (1771-1823) born in Edinburgh, Scotland spent boyhood filling his mind with Scottish songs, ballads, and legends contribution to English lit. was many-sided poetic narratives based on Scottish legends, life, and manners wrote “Lochinvar” 3. William Wordsworth (1770-1850) England’s greatest poet of nature 3 things about his poems: 1. loved to be alone 2. felt the presence of a living spirit in nature 3. impressions are similar to our own Philosophies of his life: 1. sensitive childhood 2. pleasures of childhood are the true standards of happiness 3. truth is found in the common people of the country 4. in every object is a reflection of the living God “I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud” & “She was a Phantom of Delight” 4. Percy Bysshe Shelley (1792-1822) was a great nature lover dwelt on nature’s beauty drowned at the age of 30 A wanderer following a vague vision, forever sad, and forever disappointed. “The Indian Serenade” “To a Skylark”: a great favourite; popular for the thoughts and feelings the bird and its song inspires in the poet, one of the shorter masterpieces of English literature 5. George Gordon, Lord Byron (1788-1824) Two sides to the poetry; cynical and pessimistic – the thoughts of a bitterly disillusioned man, honest in his unhappy outlook – the other with a poetic feeling about nature expressed in stirring rhythmic lines widely misunderstood by his contemporaries died young in self-imposed exile from England, like Shelley “She Walks in Beauty” “The Destruction of Sennacherib” 6. Jean Keats (1795-1821) born of poor parents set dreaming by his reading of poetry, and he decided a poetic career helped by Shelley and Leigh Hunt who both gave him encouragement and hospitality first poem was attacked by literary reviewers brief literary career; important poems written in the span of four years died of tuberculosis at 25 last sonnet when he was dying: “When I have Fears that I May Cease to Be” “Ode on a Grecian Urn” INFOGRAPHICS - information + graphics uses visuals and text to highlight key information and ideas graphical representation of concepts, or of patterns in data or info. medium that uses visual cues to communicate information Uses of Infographics 1. Simplify communication and clarify messages infographics can help simplify and demystify complex idea World Health Organization COVID19 Outbreak 2. Get complex information across in the classroom promotes critical thinking in students encourages them to take on multiple perspectives improve students’ informationgathering chops and sharpen research skills improves memory retention 3. Spread awareness about an issue a relevant infographic can have a wider reach 4. Explain procedures visuals, images, and icons to make learning more memorable and fun for your audience 5. Compare your ideas or products illustrate similarities and differences of two opposing concept by Ruan Careese Artus Ferolino