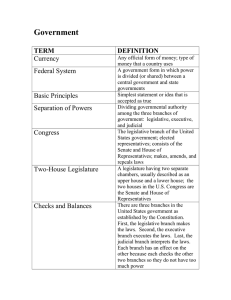
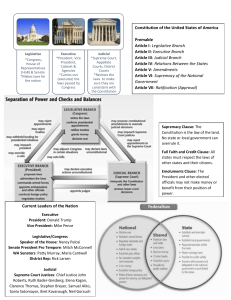
Law 4: The Legal Environment of Business Week 1 https://bit.ly/3RoUKUV Lecture Overview Syllabus Course Assignments/Polices Who is my professor? Sources of Law Come to Office Hours! Office: MBA 351 Tuesday: 7:25-7:55am; 10:05-11:25am Wednesday: 3:55-6:25pm Tuesday: 7:25-7:55am nmcgrue@elcamino.edu Textbook The Legal Environment of Business, 8th ed. by Beatty & Samuelson Online Access NOT required Textbook Buy as a group Rent Subscription Library Reserves Assignments 5 Due at BEGINNING of class on due date NO LATE WORK ACCEPTED Submitted through Canvas Lowest Assignment Dropped Tests, Quizzes & Exams 2 Midterm Tests (Non Cumulative) 1 Final Exam– Covers EVERYTHING Multiple Choice; T-F; Short answer Midterms and finals on Canvas NO MAKE UP EXAMS Class Participation Attendance Discussion Extra Credit Course Policies No Plagiarism Check emails and Canvas regularly Phones Laptops/Tablets Respect How to do well Buy/Rent/Have Access to the Book! Do the reading BEFORE CLASS Take notes Come to Class Take notes on powerpoint slides Ask Questions How to do well continued Review Reading notes Class notes Come to office hours Complete Assignments—Important! Participate in class discussion This Class is Complex The law is complex and new Take the easy wins Don’t fall behind Come to office hours Life Happens Communicate with me Sooner the better Who is this Guy? Let’s Acquainted Questions? Introduction Who has ever been part of a law suit? Who has ever been party to a contract? History of Law English Common Law Except for Louisiana? 2 Types of Law Criminal Law Civil Law Federalism Dual System of Government Unified National Government Localized State Governments Each has limited powers Why do we have federalism? Why do we have Federalism? Founders came from a Monarchy One ruler for all The Monarchy ruled in absolute power Founders didn’t want the government to have so much power Created Checks and Balances 3 Branches of Government Legislative Executive Judicial 3 Main Sources of Law Statutes Administrative Law Common Law Who gets the front seat? How do these all work together? Cases Many are old The book only has excerpts Take notes on parts you don’t understand and ASK me Closing Get your textbooks Add Codes Come visit me! Next Class: Chapters 1 & 4 Recap 3 Branches Legislative Executive Judicial 3 Sources of Law Statutes Administrative 3 Branches of Govt-Legislative Legislative Branch Creates laws, tax and spend, interstate commerce, declares war Legislative Branch CREATES Laws 3 Branches of Govt-Executive Executive Branch Appoints judges & heads of admin agencies Commander in chief of the military and negotiates treaties Executive Branch ENFORCES Laws 3 Branches of Government Contd. Judicial Branch Adjudication Judicial Review Judicial Branch INTERPRETS the law Branches of Government Recap Congress CREATES Laws Executive Branch ENFORCES Laws Judicial Branch INTERPRETS Laws Checks and Balances-President Rock, Paper Scissors President appoints cabinet members and Supreme Court Justices President can take certain executive actions? Checks and Balances- Congress Congress passes laws Congress approves President’s nominations Congress can change law if they don’t like the Supreme Court’s interpretation Checks and Balances- Sup. Court Supreme Court reviews everything Supreme Court is mainly reactionary instead of affirmative Sources of Law Statutes Administrative rule making Common Law Statutes Known as Black Letter Law Passed by Legislature Why do we pass new laws? New Issues Unpopular ruling from court Social Changes Admin Law Agency power from Congress Legislative Interpretive Same strength as Congress statutes Common Law Court decisions Lower courts must follow precedent Sources of Law Recap Statutes and Administrative Rule making Laws affirmatively created by congress or the agency Common Law/Case Law Laws created through the courts by interpreting black letter law and applying it to specific situations Statutory Interpretation What does this statute mean? 3 principles Plain Meaning Rule Legislative History & Intent Public Policy Example Statute: It is illegal to cross the street in a crosswalk that doesn’t have a stop light at dusk. Plain Meaning Rule Use the ordinary words and their everyday significance Legislative History & Intent Look deeper in to the statute If not clear, look at subcommittee minutes and notes. Public Policy What were we trying to achieve? What was the public goal here? Interpretation Recap Plain Meaning Legislative History Public Policy Administrative Law Agencies all around us Admin Law History Railroads everywhere Passed interstate commerce Act. Created first Agency Hired staff. Developed experts. Regulate, investigate, and punish Enabling Legislation Establishes the agency and gives them power Why is this required? Agency Function Legislative Interpretive Legislative Admin Rulemaking Requiring companies or citizens to do something Changes or adds law Examples Pillows and FTC Food and FDA Similar to congress Interpretive Rulemaking Interprets their current rules Example- FDA Label Sizes Similar to judiciary Rulemaking Process Informal Notice and Comment Agency then makes decision and publishes rule Formal Publish Rule Public Hearing Like a trial Agency makes the final determination and must respond to everything that was brought up. Rulemaking Checks and Balances Congress gave the enabling statutes Judicial review—all rules are subject to judicial review Admin Rulemaking recap Legislative New rules Interpretive Interprets old rules Similar to case law Sources of Law Recap Statutes Administrative Common Law Closing Get your textbooks Add Codes Come visit me!