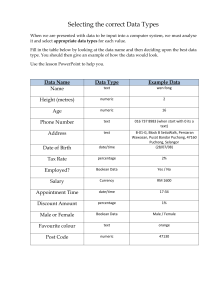
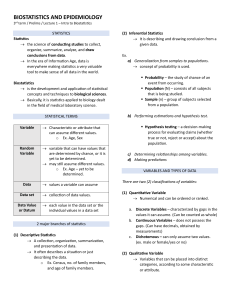
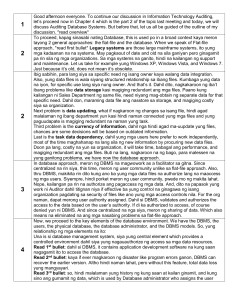
Biostatistics: Descriptive & Inferential Statistics, Research
advertisement

Biostatistics A statistical processes and methods applied to the collection, organization, analysis and interpretation. Biological data and especially data relating to human Descriptive stats - Summarized data Easier to analyze, interpret and understand Tabulation, graphical presentation, computation of averages Inferential statistics - Generalization or conclusions Estimation of parameters Hypothesis testing What is research? A problem solving activity using the scientific method of inquiry aimed at the discovery and interpretation of new knowledge Research process Problem identification Formulating objectives Review of related literature Methodology Data collection Data processing analysis Writhing the report Dissemination of findings Utilization of results Variables Qualitative Health status Place of residence Section Quantitative variables Discrete Continuous Number of recoveries Number of family members Levels of measurement Nominal – labels such as sections, the color of eyes, health status Ordinal – ordered or rank. Yung variable ng health status but ranked like under weight, normal, over Interval – scale of measurement. Numeric like BMI, height, weight Ratio – numeric din o arbitratry RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VARIABLES Independent variable Dependent variables Confounding variable DEFINING THE VARIABLES Conceptual – HOW YOU DEFINE THAT VARIABLE BY ITS COMMON DIFINITON or general definition based on dictionaries Operational – how you define a variable based on yourself or your study 1. Using the variables listed below, create your own operational definition. a. Sex - sex is the distinction between male, female, and others who do not have biological characteristics b. Education c. Smoker d. Nutritional status e. Blood pressure IMPORTING OF DATA Open – data – choose your folder – documents – section and name