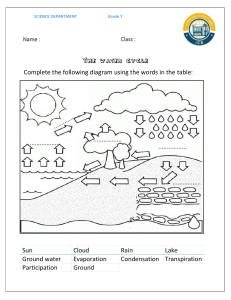
Plot 48 Muwaire Rd (behind IHK Hospital) P.O.BOX 5337, KAMPALA - UGANDA Tel: 256783111908 Email: info@stagnes.co.ug Website: www.stagnes.co.ug P.4 SCIENCE LESSON NOTES WEATHER CHANGES - Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given place at a particular time. - It is also the condition of the atmosphere at a given time. 2. Elements/ factors of weather Sunshine Temperature Cloud cover Rainfall Wind movements Humidity 3. Types of weather Cloudy weather Rainy weather Sunny weather Windy weather 4. Weather instruments These are instruments used to measure different elements of weather. WEATHER INSTRUMENT USE Rain gauge Measures the amount of rainfall received in a given place. Measures the speed of wind. Anemometer Shows the direction of wind. Wind vane Six’s thermometer Measures the maximum and minimum temperatures of the day. Shows the direction of wind. Wind sock Barometer Measures atmospheric air pressure. Hygrometer Measures the humidity in the atmosphere Sources of water a. Natural sources of water Rivers Swamps Lakes Rainfall b. Artificial sources of water Bore holes Wells Valley dams Ponds 2. Properties of water It has no colour It has no taste It has no smell It takes the shape of the container uses of water to people and other animals. - Used for cooking - For drinking - For washing cloths - For watering crops - Water is a habitat for water animals. Uses of water to plants. - It is used for germination - For photosynthesis - For transpiration - It dissolves mineral salts. 3. Water in air This is called water vapour Formation of water vapour i. Through evaporation from water bodies ii. Through transpiration Importance of water vapour i. It changes into clouds on condensation which results in rain 4. Rain The drops that fall down from the clouds in the sky. Rainfall The water collected on the ground from the rain drops The water cycle This is the process by which rain is formed. It involves i. Evaporation ii. Transpiration iii. Condensation Evaporation is the change of water from liquid to gas. Transpiration is the loss of water from a plant to the atmosphere through leaves as vapour. Condensation is the change of state from gas to liquid. During the water cycle; i. The sun heats the water bodies and vegetation ii. Evaporation takes place from the water bodies and transpiration takes place in plants iii. The water vapour rises up into the sky and condenses to form clouds iv. The clouds become heavy and fall down as rain. A—Heat from the sun B—Evaporation from water bodies C—Transpiration from vegetation D—Condensation forming clouds E—Rain Clouds Clouds are formed when water vapour in the sky condenses. Types of clouds i. Cirrus—highest and lightest clouds ii. Stratus iii. Cumulus iv. Nimbus—heaviest clouds Effects of clouds on the environment Clouds block direct sunlight This reduces the brightness in our environment. Clouds lower the temperature in our environment by reducing heat from sun. Clouds bring rain. Effects of rain on the environment i. Rain reduces temperature in the environment ii. Rain reduces dust iii. Rainfall softens soil. Wind. Wind is moving air. Effects of wind in the environment: - Strong wind is an agent of soil erosion. - Strong wind breaks down crops and trees. - Strong wind blows off roofs of houses. - Wind is an agent of pollination. - wind is an agent of seed dispersal. Uses of wind to people and plants: - used for sailing engineless boats. - For generating electricity. - For flying kites’ - For winnowing. - Plants use wind for pollination. - For seed dispersal. Uses of sunshine in the environment. - For drying harvests. - For warmth’ - For solar electricity. the Effects of sunshine in the environment: - Strong sunshine dries up water bodies. - Strong sunshine dries up plants in the garden. - Strong sunshine dries and hardens the soil. Temperature: - Temperature is the hotness or coldness of an object or place. - The instruments used for measuring temperature are: . six thermometer for measuring the highest and the lowest temperature of the day. . clinical thermometer for measuring human body temperature. - Temperature is measured in degrees. The weather chart 1. It is a chart that shows the daily weather changes in our environment. 2. A weather chart is produced through observation and recording. The elements of weather in a weather chart include; 1. How much rainfalls 2. How much cloud is in the sky 3. How strong the wind is 4. How hot is the sunshine 5. How warm or cool is the air in our surroundings. Examples of a weather chart Element Temperature Cloud of weather MON TUE WED THUR FRI TOPICAL QUESTIONS cover Rainfall Cloud Wind cover movement Sunshine 1. Briefly explain the term weather. 2. Mention four elements of weather. 3. Identify four types of weather. 4. Match the items in A with those in B. A B Thermometer Day’s highest and lowest temperature Barometer Rainfall Six’s thermometer Temperature Rain gauge Air pressure Anemometer Speed of wind 5. How do people manage the following changes in their environment? a) Strong wind b) High temperatures c) Very low temperatures d) Flooding 6. Name two examples of each water source below; a) Natural sources of water b) Artificial sources of water 7. Mention two properties of water 8. Describe, in four sentences, how rain is formed. 9. How do the following affect temperature in the environment? a) clouds b) Rain PERSONAL HYGIENE 1. Personal hygiene is the way we keep our bodies clean. It is the general cleanliness of the body. 2. Importance of personal hygiene. It controls the spread of germs. It prevents bad body smell. It prevents skin diseases It prevents teeth diseases It prevents lice, mites and ticks. 3. Ways of keeping good personal hygiene. Bathing every day Cutting finger and toe nails short Brushing teeth every day Washing hands after visiting the toilet or latrines. Washing hands after a physical task like digging, picking rubbish, etc. Washing hands before eating food. Washing clothes regularly Washing beddings regularly Combing hair daily. Ironing clothes and beddings. 4. Items used to keep the body clean Soap Clean water Sponge Tooth brush Comb Towel Razor blade Basin Sandals Tooth paste 5. Dangers of poor personal hygiene. The body smells bad. Jiggers, mites, ticks and lice can breed and affect the body. The teeth may develop tooth decay. Diarrhea diseases can spread easily. Accidental injuries from long finger nails to self or others. 6. Diseases brought by poor personal hygiene. DISEASES CAUSE Tooth decay Bacterial Scabies Itch mite Dysentery Bacteria Amoeba Diarrhoea Virus Bacteria Ring worm Fungus Trachoma Chlamydia TOPICAL QUESTIONS 1. Briefly explain personal hygiene. 2. Name four items used in keeping good personal hygiene. 3. Why is it important to keep good personal hygiene? 4. State four ways of keeping personal hygiene. 5. Name the diseases that affect the following parts of the body. a) eyes b) skin c) teeth 6. Suggest four ways of keeping good personal hygiene. 7. Why are the following habits important to the individual. a) Cutting finger nails b) Combing hair c) Washing hands before eating d) Washing hands after using a toilet or latrine