Computer 8: Using & Maintaining Hand Tools - Self-Learning Kit
advertisement

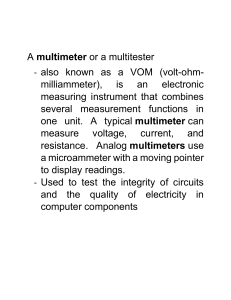
COLEGIO DE LA PURISIMA CONCEPCION The School of the Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas City Self- Learning Kit in Computer 8 USING AND MAINTAINING HAND TOOLS (1ST Quarter – Week 1-3) Prepared by: CYNTHIA V. MERISCO, LPT What Is This SLK About? To complete hardware repairs, it is important to have a toolkit that should contain all of the necessary tools. As you gain experience, you will learn which tools to have available for different types of jobs. Using and maintaining hand tools will help you to become a reliable computer technician. One of the key issues associated with hand tool safety is choosing and using the right tool. Unfortunately, many people use tools improperly at home, where they improvise with what they have on hand. Also, many people view hand tools as simple to use, so there is little concern for safety. In reality, a person using hand tools, no matter what they are, should always follow safety precautions and the manufacturer’s instructions. Injuries range from simple cuts, contusions, and abrasions to amputations, fractures, and punctures. What Will You Learn from This SLK? At the end of this module, you are expected to: 1. Identify tasks to be undertaken properly; 2. Identify and select appropriate hand tools according to the task requirements; 3. Check appropriate hand tools for proper operation and safety; 4. Identify and mark unsafe or faulty tools for repair according to standard company procedure; 4. Use tools according to tasks undertaken; 5. Always observe all safety procedures in using tools and use appropriate PPE; and 6. Report malfunctions, unplanned or unusual events to the supervisor; and 7. Do not drop tools to avoid damage; carry out routine maintenance of tools according to standard operational procedures, principles, and techniques. Let’s See What You Already Know Before you begin with the module proper. Take this test to find out how much you already know about our topic. ACTIVITY 1 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Choose the correct words from the box below. Write your answers on the blank provided. 1. The purpose of an antistatic wrist strap is to ________ the electrical charge between you and the equipment. 2. Turn the screwdriver _________ to tighten the screw 3. Turn the screwdriver ________________ to loosen the screw. 4. Use a ________ head screwdriver with crosshead screws. 5. On electrical components, an excessive build-up of dust will act like a _________ and trap the heat. 6. When compressed air is used to clean inside the computer, the air should be blown around the components with a minimum distance of ______ inches from the nozzle. 7. Pencils should not be used inside the computer to change the setting of switches or to pry off jumpers because the tip contains _____ which can act as a conductor and may damage the computer components. 8. To clean the screens of CRT monitors, dampen a soft, clean, lint-free cloth with _______ water and wipe the screen from top to bottom. 9. Clean the contacts on components with _________ alcohol. 10. Use a __________ to loosen and tighten bolts that have a hexagonal (six-sided) head. LIST OF WORDS equalize philips insulator isopropyl counterclockwise distilled hex driver clockwise four lead ACTIVITY 2 Direction: Conduct a maintenance activity on the given hand tools. Write the following maintenance activity you will be going to perform on the following tools, you can write more than one maintenance activity. 1. Clean 2. Magnetize 3. Lubricate 4. Calibrate 5. Change batteries if drained 6. Sharpen TOOLS 1. Flat Head Screwdriver 2. Philips Head Screwdriver 3. Torx Screwdriver 4. Hex Driver 5. Needle-Nose Plier 6. Wire Cutter Turn to next page to begin the lesson. MAINTENANCE ACTIVITY Clean and magnetize Let’s Read Definition of Terms Computer Chassis the enclosure or box that contains most of the components of a computer. Equipment physical components that constitute a computer system, including monitors, keyboards, printers, modems, scanners, pointing devices, and other computer peripheral equipment, cables, servers, and routers. "Computer equipment" also includes digital cameras and computer software. Tool a handheld device that aids in accomplishing a task. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is an equipment worn to minimize exposure to hazards that cause serious workplace injuries, illnesses and accident. Nozzle a projecting part with an opening, as at the end of a hose, for regulating and directing a flow of fluid. Toolkit a set of tools designed to be used together or for a particular purpose. Insulation a material that reduces or prevents the transmission of heat or sound or electricity. PROPER TOOL SELECTION A tool is a handheld device that aids in accomplishing a task. Tools range from a traditional metal cutting part of a machine to an element of a computer program that activates and controls a particular function. Preparing for the task to be undertaken includes proper tool selection. Select the best tool by knowing and understanding in details the scope of work to be accomplished, and by planning for the scope taking into account the sequence of tasks. Selecting the best tool for each task requires training in the proper use of the tools, field experience in their safe use, and following the manufacturer’s guidance and instructions for that specific tool. When obtaining the tool all the associated tooling and consumable parts, as recommended by the manufacturer, must be included. In addition, related consumable parts must also be selected and used according to their manufacturer’s instructions. Safe Use of tools Once selected, use the tool for the purpose for which it was designed. Not all tools come with detailed instructions, but there are those that do spell out the safety ―Do’s and Don’ts‖ for your safety. If there are set-up/use options, operator judgment must always be based on what is the safest way to use the tool. Remember that Safety is the first Priority. Environmental Safety and Health Program requires the following: All tools be kept in good condition with regular maintenance The right tool be used for the job Each tool be examined before use; damaged or defective tools NOT to be used Tools be operated according to manufacturer’s instructions The right protective equipment for the tool and activity be used COMPUTER HARDWARE TOOLS Hardware tools are grouped into these four categories: ● ● ● ● Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) tools Hand tools Cleaning tools Diagnostic tools Hand Tools and its uses Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) Tools Static electricity is easily generated by friction on carpets, tile flooring, clothing, hair, fabric, and etc. The friction of moving air alone will charge suspended particles and cause the build-up of static electrical charges on people and objects in the environment. Grounded antistatic work mats used with antistatic wrist straps provide the most basic means for the controlled discharge of electrostatic electricity. Tool Description Anti-static wrist strap – a piece of safety gear use to prevent build-up of static electricity to sensitive electronic part that may cause damage or safety issue to computer equipment. Anti-static mat – safeguards an individual or piece of equipment like a Personal Computer from an electrostatic discharge (ESD). This is useful when working on computer components. Just place the Anti-static mat under the equipment. Hand Tools A hand tool is a device for performing work on a material or a physical system using only hands rather than a motor. Tool Description Flat head screwdriver – used to loosen or tighten negative slotted screws. Philips head screwdriver – used to drive or fasten positive slotted screws Torx screwdriver - used to loosen or tighten screws that have a star-like depression on the top, a feature that is mainly found on laptop. Hex driver – sometimes called a nut driver, is used to tighten nuts in the same way that a screwdriver tightens screws. Photo from web Needle-nose plier – used for holding, bending and stretching the lead of electronics component or connecting wire. Wire cutter – used to strip and cut copper, brass, iron, aluminium, and steel wire Tweezers – used to manipulate small parts. Part retriever – used to retrieve parts from location that are too small for your hand to fit. Flashlight – used to light up areas that you cannot see well. Photo from web Soldering iron - used to join two or more metal conductors with the support of soldering lead melted around it. Photo from web Soldering Stand – made out of metal and comes with a cleaning sponge to clean the soldering irons tip. Photo from web Desoldering Tool – is used to unsolder unwanted parts or component in the circuit with the support of soldering pencil. Photo from web Soldering Lead – is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal work pieces? Solder is melted in order to adhere to and connect the pieces after cooling. Photo from web Crimping tool – is a device used to conjoin two pieces of metal by deforming one or both of them to hold each other. The result of the tool's work is called a crimp. network cables and phone cables are created using a crimping tool Photo from web Cleaning Tools Having the appropriate cleaning tools is essential when maintaining or repairing computers. Using these tools ensures that computer components are not damaged during cleaning. Tool Description Lint-free cloth – used to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris. Brush – used to remove accumulated dust on computer peripherals and components contact. Photo from web Compressed air – used to blow away dust and debris from different computer parts without touching the components. Cable ties – used to bundle cables neatly inside and outside of a computer. Parts organizer – used to hold screw, jumpers, fasteners and other small parts and prevents them from getting mixed together. Erase – used to eliminate foreign debris that stick from component contact, like Random Access Memory (RAM) and HDD connector. Photo from web Diagnostic Tools Computers are easier to use and more dependable with each new generation of hardware and operating system update, but that doesn't mean they're problem-free. Here's the most popular tools for diagnosing your computer problems: Tool Description Multi-tester– used to test the integrity of circuits and the quality of electricity in computer components. LAN Tester – for RJ11, 12, 45 & BNC w/ Remote Unit This ergonomic tester is designed to test most network cable wiring. You can either conduct an auto or manual test. Photo from web Loopback Adapter – used to test the functionality of computer ports. PROPER USE OF TOOLS As a computer Technician, proper use of hand tools within the toolkit should be observed when repairing or building a computer. 1. Anti-Static Wrist trap a. Connect the cable to the metal chassis of the computer. b. Wrap the strap around your wrist. c. The connection will keep your body at the same voltage (potential) as the computer. d. Attach the wire on the same side of the equipment as the arm wearing the antistatic wrist strap to keep the wire out of the way while you are working. 2. Anti-Static Mat a. Lay the computer on the mat. b. Connect the computer to the mat with the cable. c. Connect the mat to a reliable electrical ground with its cable. d. Now, you and the computer are at ground potential. 3. Flat Head screwdriver- Use a flat head screwdriver when you are working with a slotted screw. Do not use a flat head screwdriver to remove a Phillips head screw. Never use a screwdriver as a pry bar. If you cannot remove a component, check to see if there is a clip or latch that is securing the component in place. 4. Phillips head screwdriver- Use a Phillips head screwdriver with crosshead screws. Do not use this type of screwdriver to puncture anything. This will damage the head of the screwdriver. 5. Screw- Match each screw with the proper screwdriver. Place the tip of the screwdriver on the head of the screw. Turn the screwdriver clockwise to tighten the screw and counter clockwise to loosen the screw. 6. Hex driver- Use a hex driver to loosen and tighten bolts that have a hexagonal (six-sided) head. Hex bolts should not be over-tightened because the threads of the bolts can be stripped. Do not use a hex driver that is too large for the bolt that you are using. 7. Part retriever, Needle-nose pliers, or tweezers- The part retriever, needlenose pliers, and tweezers can be used to place and retrieve parts that may be hard to reach with your fingers. Do not scratch or hit any components when using these tools. Make sure to apply lubricants after using them to avoid becoming rusty and dull. 8. Soldering Iron and Stand- Soldering iron heats very quick, avoid touching the metal parts. After using the Soldering Iron, place it on the stand to avoid burning and damage things. 9. Crimping Tool- Inspect the tool before its use to make sure to foreign substance sticking to it. Check the spring resistance by squeezing and releasing the tool handle. Be careful with the blade, it is very sharp. 10. LAN Tester and Multi-Tester- To maintain its accuracy of measurement, regularly check its reading and functionality if something is not accurate, check its battery and LED lights. Proper Use of Cleaning Materials Keeping computers clean inside and out is a vital part of a maintenance program. Dirt can cause problems with the physical operation of fans, buttons, and other mechanical components. On electrical components, an excessive build-up of dust will act like an insulator and trap the heat. This insulation will impair the ability of heat sinks and cooling fans to keep components cool, causing chips and circuits to overheat and fail. 1. Computer Cases and Monitors - Clean computer cases and the outside of monitors with a mild cleaning solution on a damp, lint-free cloth. Mix one drop of dishwashing liquid with four ounces of water to create the cleaning solution. If any water drips inside the case, allow enough time for the liquid to dry before powering on the computer. 2. LCD & LED Screens- The LED and LCD screen is not intended to get wet. Do not use ammoniated glass cleaners or any other solution on an LCD screen, unless the cleaner is specifically designed for the purpose. Harsh chemicals will damage the coating on the screen. There is no glass protecting these screens, so be gentle when cleaning them and do not press firmly on the screen. 3. CRT Screens- To clean the screens of CRT monitors, dampen a soft, clean, lint-free cloth with distilled water and wipe the screen from top to bottom. Then use a soft, dry cloth to wipe the screen and remove any streaking after you have cleaned the monitor. Clean dusty components with a can of compressed air. Compressed air does not cause electrostatic build up on components. Make sure that you are in a well-ventilated area before blowing the dust out of the computer. A best practice is to wear a dust mask to make sure that you do not breathe in the dust particles 1. Component Contacts- Clean the contacts on components with isopropyl alcohol. Do not use rubbing alcohol. Rubbing alcohol contains impurities that can damage contacts. Make sure that the contacts do not collect any lint from the cloth or cotton swab. Blow any lint off the contacts with compressed air before reinstallation. 2. Keyboard- Clean a desktop keyboard with compressed air or a small, hand-held vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment. 3. Mouse- Use glass cleaner and a soft cloth to clean the outside of the mouse. Do not spray glass cleaner directly on the mouse. If cleaning a ball mouse, you can remove the ball and clean it with glass cleaner and a soft cloth. Wipe the rollers clean inside the mouse with the same cloth. Do not spray any liquids inside the mouse. IMPORTANT REMINDERS IN THE PROPER USE OF TOOLS 1. If excessive force is needed to remove or add a component, something is probably wrong. Take a second look to make sure that you have not missed a screw or a locking clip that is holding the component in place. Refer to the device manual or diagram for additional information. 2. Some tools are magnetized. When working around electronic devices, be sure that the tools you are using have not been magnetized. Magnetic fields can be harmful to data stored on magnetic media. Test your tool by touching the tool with a screw. If the screw is attracted to the tool, do not use the tool. 3. Pencils should not be used inside the computer to change the setting of switches or to pry off jumpers. The pencil lead can act as a conductor and may damage the computer components. 4. When compressed air is used to clean inside the computer, the air should be blown around the components with a minimum distance of four inches from the nozzle. The power supply and the fan should be cleaned from the back of the case. 5. Before cleaning any device, turn it off and unplug the device from the power source. 6. Never use a standard vacuum cleaner inside a computer case. The plastic parts of the vacuum cleaner can build up static electricity and discharge to the components. Use only a vacuum approved for electronic components. TOOL AND EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE All tools and equipment must be properly maintained so that workers are not endangered. Preventive maintenance is the systematic care and protection of tools, equipment and machines in order to keep them in a safe, usable condition, limit downtime and extend productivity. We must always be aware that maintenance tasks themselves are potentially hazardous and can result in injury. 1. Obtaining a copy of the maintenance schedule recommended by the manufacturer. 2. Ensuring that maintenance is performed as required. 3. Ensuring that the person(s) performing the maintenance are competent or license professional. 4. Retaining records of maintenance/service conducted. 5. Specifying who is responsible for overseeing equipment maintenance and where the records are kept. 6. Putting in a system for removal and tagging of damaged or defective tools and equipment. PROPER STORAGE OF TOOLS, PARTS, AND EQUIPMENT To ensure that tools and equipment remain in good condition and last for a long time, store them properly. Properly stored tools and equipment will be easy to find when needed and are less likely to be lost. Good practices include: ● parts should be properly stored and labelled (Figure 1); ● tools should be properly placed on the board, and labelled (Figure 2). Consider drawing the shapes of the tools on the board so that they always get put back in the same position; ● use bins for storing small parts (Figure 3); and ● consider making an individual (or individuals) responsible for the good maintenance of tools and parts. Figure 1. Figure 2. Figure 3. Benefits ● Tools and parts are kept in good condition and are easy to find ● Costs are reduced. ● Productivity is increased because time is not wasted looking for tools, parts and equipment. ● Workshop staff develop a sense of responsibility and pride in their work. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) - it refers to protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other gear designed to protect the wearer's body or clothing from injury by electrical hazards, heat, chemicals, and infection, for job-related occupational safety and health purposes. It is important that students and teachers during their laboratory period should be required to use personal protective equipment. Some of these are: Goggles - a large spectacles, with shields around the rims, for protecting the eyes from dust, excessive light, wind, etc. Rubber sole - a special type of shoes used to prevent electrical shock and for waterproofing and insulating purposes. Apron - a garment worn over the front of the body as a protection for one’s cloth. Face mask - a covering for the face to prevent the inhaling or absorbing dust and other chemicals Gloves - the covering material with a separate sheath for each finger used for hand protection. Time to check your understanding. Ready? Kindly turn to next page. Review of Lesson!!! ACTIVITY 3 Direction: Name the tools on the boxes and identify its category (ESD tool, Hand tool, Cleaning Tool, Diagnostic Tool). Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper. Picture 1. 2. 3. 4. Name of the Tool Category 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Assessment Instruction: Select the letter only of the correct answer and write it on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Which tool is used for hardware to stand on to prevent static electricity from building up? A. anti-static mat C. Philips head screwdriver B. hex driver D. wire cutter 2. Which tool is used to loosen or tighten cross-head screws? A. anti-static mat C. Philips head screwdriver B. hex driver D. wire cutter 3. Which tool is sometimes called a nut driver, which is used to tighten nuts in the same way that a screwdriver tightens screws? A. anti-static mat C. Philips head screwdriver B. hex driver D. wire cutter 4. Which tool is used to strip and cut wires? A. anti-static mat C. Philips head screwdriver B. hex driver D. wire cutter 5. Which tool is used to retrieve parts from location that are too small for your hand to fit? A. part retriever C. cable ties B. lint-free cloth D. flat head screwdriver 6. Which tool is used to clean different computer components without scratching or leaving debris? A. part retriever C. cable ties B. lint-free cloth D. flat head screwdriver 7. Which tool is used to bundle cables neatly inside and outside of a computer? A. part retriever C. cable ties B. lint-free cloth D. flat head screwdriver 8. Which tool is used to loosen or tighten slotted screws? A. part retriever C. cable ties B. lint-free cloth D. flat head screwdriver 9. Which tool is used to loosen or tighten screws that have a star-like depression on the top, a feature that is mainly found on laptop? A. anti-static mat C. Philips head screwdriver B. Torx screwdriver D. wire cutter 10. Which tool is used to blow away dust and debris from different computer parts without touching the components? A. anti-static mat C. compressed air B. hex driver D. wire cutter 11. What tool is used to test integrity of circuit the quality of electricity in computer components? A. multi-meter C. loopback adapter B. LAN tester D. brush 12. What tool is used to join two or more metal conductors with the support of soldering lead melted around it? A. soldering stand C. soldering lead B. soldering iron D. soldering pump 13. Which is not a proper use of tool? A. Use the proper type and size of screwdriver by matching it to the screw B. Do not over tighten screws because the threads may become stripped. C. Use compressed air to clean heat sinks. D. Use Rubbing alcohol and lint-free swabs to clean RAM 14. Which in the subsequent isn’t a good practice in storing tools, parts and equipment? A. Use bins for storing small parts B. Tools should be properly placed on the board, and labelled C. You can leave the tools at the workplace so that it can be easy to find D. Consider making an individual (or individuals) responsible for the good Maintenance of tools and parts. 15. Which in the subsequent is not a general requirements for tools and equipment maintenance? A. Ensuring that the person(s) performing the maintenance is your relative B. Retaining records of maintenance/service conducted C. Set up a system for removal and tagging of damaged or defective tools and equipment D. Ensuring that maintenance is performed as required E-CONNECT: https://www.academia.edu/29846618/LM_Cookery_Grade_10 - retrieved September 6, 2020 https://www.google.com/search?q=PICTURE+OF+NUTRITIVE+VALUE+OF+EGG+WIT H+LABEL&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwjpqanZ2dbrAhXMx4sBHeTrC7YQ2cCegQIABAA&oq=PICTURE+OF+NUTRITIVE+VALUE+OF+EGG+WITH+LABEL&gs_l cp=CgNpbWcQA1C9zQVY6O0FYJXzBWgAcAB4AIABjAKIAfgLkgEGMC4xMC4xmAEA oAEBqgELZ3dzLXdpei1pbWfAAQE&sclient=img&ei=S_lVX6nYBsyPr7wP5NevsAs&bih =722&biw=1536#imgrc=3ODE5REhUYJZpM – retrieved September 7, 2020 https://www.bwc.ohio.gov/downloads/blankpdf/safetytalk-handtools.pdf