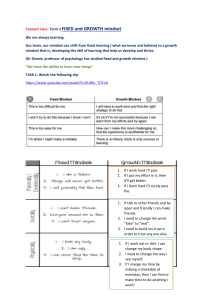
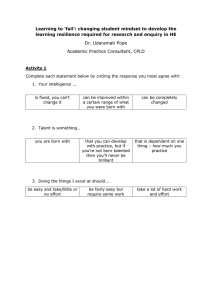
Creative Problem Solving Different Problem Solving Process ANALYTICAL CREATIVE 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the problem? 2. Plan the solution. 3. Look for ways of getting there. 4. Carry out the plan. 5. Check the results. What is the real problem? Brainstorm many ideas. Make the ideas better; pick the best solution. Implement the best solution. How does the solution work? What have you learned? What else can you do? Herrmann Whole Brain Thinking Model Cerebral A Authoritarian Materialistic Academic Realistic What? ANALYZER Logical thinking Analysis of facts Critical evaluation Processing numbers VISUALIZER Right Brain Detailed organization Reliable Operational planning Traditional Manuals, schedules Task-Driven Preventive action B © 2004 Herrmann International Experimental Futuristic Inventive Flexible Conceptualizing Strategic thinking Imaginative design Big-picture viewpoint Left Brain Bureaucratic D What if? ORGANIZER How? Social, interpersonal Care giving, sensing Spiritual, intuitive Expressing ideas PERSONALIZER Why? Limbic ValueOriented Humanistic Cooperative C Modern Chinese Characters for Crisis wei ji CRISIS = 危 机 DANGER + OPPORTUNITY The EXPLORER looks for context, trends, opportunities Problem Finding EXPLORATION How to Practice the Explorer’s Mindset Be adventuresome. Take one afternoon a month off to look around in other areas. Read outside your own field. Look for trends, context, “the big picture” and opportunities. Explorer Tools Studying Trends Networking Web Surfing Preliminary Patent Search Creative Idea File Modeling a Problem Mindmapping Morphological Creativity and Synectics (advanced tools requiring special training) “Don’t Sell Me” Game The DETECTIVE searches for clues and root causes Problem Definition INVESTIGATION Tasks to Do in the Detective’s Mindset Find the REAL problem. Ask questions. Collect information; analyze data; identify the root causes of problems. Write a problem briefing and positive problem definition statement. Detective Tools Asking questions (Kepner-Tregoe approach) Customer surveys SPC (including Pareto diagram) FMEA, FTA Experiments and statistical analysis Assets and liability analysis Sequence-attribute/modifications matrix QFD House of Quality 8-D and other in-house methods Introspection: What do you already know? Checklist for Problem Definition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Use a whole-brain problem solving team. Choose or look at the assigned problem topic or area. Focus the topic: diverge to context or converge to smaller parts. Collect data: customer surveys, web and other searches. Record all information in a notebook, design journal, or inventor’s log. Analyze the data; rank root causes of the problem; visualize in the form of a Pareto diagram. Briefing document: summarize the REAL problem. Develop a positive problem definition statement. Idea Generation A D B C The Artist changes information into ideas Idea Generation IMAGINATION Tasks to Do in the Artist’s Mindset Brainstorm with a team or alone. Keep a positive, playful attitude. Expect to come up with all kinds of ideas: wild and crazy, mundane, novel, exciting, weird, odd, plain … that’s fine! Rules for Brainstorming 1 Generate as many solutions as possible; quantity counts. 2 “Wild” idea are encouraged. 3 No judgment or criticism at this time. 4 Idea pinching is allowed. Rules for Brainstorming Review the problem’s background; post the problem definition statement. State the four brainstorming rules. Explain the procedure that will be used. Conduct a create thinking warm-up exercise. Start the idea generation process; record all ideas. Conclude the session after 30-45 minutes. Collect all ideas; thank and dismiss the group. SCAMPER Example: Nuts & Bolts Manufacturing Substitute: High-speed steel? Carbon fiber? Plastics? Glass? Nonreactive material? Combine: Integrate nut & bolt? Bold & washer? Bolt & spanner? Adapt: Allen key or star head on bolt? Countersink head? Modify: Pre-painted green bolts? Screw-in plugs? Bolts for bridge? Mini bolts for watches? New Uses: Bolts as hinge pins? As axles? Eliminate: Nuts, washers, heads, threads, etc.? Reverse: Bolts that cut threads? Idea Evaluation A D B C Creative Concept Evaluation “ENGINEERING” IDEAS Tasks to Do in the Engineer’s Mindset Sort, group, combine, supplement and develop ideas. Build on ideas. Synthesize ideas. Put ideas to practical use. Create better solutions. Work in teams or alone. Integrate left-brain and right-brain thinking. Keep a positive attitude. Idea Evaluation 1 Look for quality, not quantity. Make ideas better. 2 Make “wild” ideas more practical. 3 Continue to defer negative judgment. 4 Synthesize and optimize ideas! Procedure for Creative Idea Evaluation Task 1 Sort ideas into at most 7 categories. Task 2 Do a creative thinking warm-up. Work within each category; synthesize, develop and improve ideas. Use wild ideas as stepping stones to more practical ideas. Procedure for Creative Idea Evaluation Task 3 Force-fit ideas between categories. Continue synthesis to obtain high-quality ideas. Often, the best ideas are generated during this phase. This is the process underlying the Pugh method which is a creative concept evaluation technique using a matrix format. Idea Synthesis New Ideas 1 2 Synthesis Force-Fitting 3 4 Idea Judgement A D B C Idea Judgment CRITICAL EXAMINATION Tasks to Do in the Judge’s Mindset Establish criteria. Sift and rank ideas. Examine shortcomings and identify flaws, then look for ways to overcome the negatives. Asses timing, risks and bias. Then make the decision. What Are Your Assumptions? Cleopatra and Anthony are found dead on the floor in the middle of a pool of water and broken glass. What happened? 1. Brainstorm and jot down some ideas. 2. Now think about your underlying assumptions. 3. Change your assumptions. Does this lead to an entirely new direction in your “story”? Idea Judgement • • • • • • • • Consensus Vote Single Criterion Advocacy method Reverse brainstorming Experimentation Trial and Error Designed Experiment Pugh Method • No failures; degrees of success • Examine biases, assumptions • No judgement • No perfect solution Example of an Advantage/Disadvantage Matrix Evaluating Job Options LIST OF CRITERIA 1 JOB OPTION 2 3 4 5 Pay + 0 0 0 + Other benefits + 0 0 0 + Personal growth + + + 0 0 Good for family + + 0 + 0 Independence 0 + + + 0 Status 0 + 0 0 + Excitement and challenge 0 + + 0 0 Co-workers + + 0 + 0 Boss + + 0 + + Fit with life goals + + 0 0 + 7 8 3 4 5 3 2 7 6 5 TOTAL SCORE + 0 Implementation A D B C Solution Implementation GOING INTO ACTION Tasks to Do in the Producer’s Mindset Make an action plan. Have good communications. Implementation is hard work and takes time. But here is the payoff! Implementation is a new problem requiring creative problem solving. Pay attention to monitoring and follow-up. What have you learned? Two Phases of Implementation SELLING YOUR IDEA Analyze the problem – plan your strategy. List the benefits. Make a presentation for selling the idea. Work for acceptance. PUTTING THE IDEA TO WORK Develop a work plan. Do the implementation. Monitor the results. Evaluate the problem solving process. The Selling Approach Pick the right audience/target Don’t oversell Don’t give up too soon Watch your timing Be brief and to the point (30-sec message) Plan your presentation carefully; use visual aids Make your ideas easy to accept Avoid confrontation Reasons for Opposition Lack of understanding Not following “the rules” Prejudice Other loyalties No direct benefits Idea seen as criticism Fear of change Habit (mental block) The only person who likes change is a wet baby Working for Acceptance Agree with the opposition Listen carefully for better ideas Don’t feel hurt; don’t attack Stay casual; get others involved—have a champion Work for continuous improvement Show benefits to the other party Have change as a reversible process Or plan needed change in incremental steps To get acceptance, would you be willing for someone else to get the credit? Implementation Planning Tools Copycat For similar conditions, copy a previously successful procedure. 5-W Method Answer who, what, where, when, why for each implementation task. Let people decide the “how” Flow Chart Visually represent all activities that must be performed in sequence. This shows prerequisites. PERT This complicated program evaluation and review technique is for large, complex projects. Gantt Chart This simple work plan visually presents the time required for each task. Cost Budget Used with information from Gantt chart. Risk AnalysisUsed for very important projects where major implementation obstacles are anticipated.