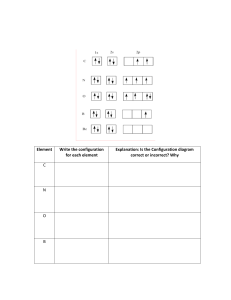
1. Which of the following notations shows the electron configuration of a neutral atom in an excited state? Name the element, and explain how you know it is excited: (a) 1s2 2s22p1 (b) 1s2 2s22p3 3s1 (c) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p1 2. Isoelectronic species have the same electron configurations. Which of these are isoelectronic? (a) Li+, H-, He (b) Ca2+, Ne, S23. For the following elements list the electron configuration. a. oxygen b. cesium c. krypton e. scandium f. nitrogen g. chlorine i. arsenic j. francium k. selenide m. potassium n. antimony(II) o. thorium d. titanium h. fluoride l. copper(I) p. lead (II) 4. For the following elements list the shorthand electron configuration a. boron b. cadmium c. phosphorus d. neon e. radon f. iodine g. strontium ion h. chromium(III) j. nickel k. iron l. astanine m. molybedenum(III) n. rubidium o. bromide p. xenon q. potassium ion 5. For the following electron configurations choose 3 possible elements (or ions) they may represent a. 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 b. [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p6 c. 1s2 d. [Ne] 6. Draw the orbital diagram for the following: a. F b. N c. Cld. 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p5 e. [Ne] 3s2 3p2 f. [He] 2s2 2p3 7) Increasing Radius Li, C, F Li, Na, K Ge, P, O Mg, Si, S Mg, Mg+, Ne F-, Ne, Na+ Increasing Ionization NRG Increasing Electronegativity 8) What is the difference between electron affinity and ionization energy? 9) Why does fluorine have a higher ionization energy than iodine? 10) Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties? 11) State the four quantum numbers and the possible values they may have. 12) Give the n and l values for the following orbitals a. 1s b. 3s c. 2p d. 4d e. 5f 13) Which sets of quantum numbers are unacceptable? a. n=3, l= -2, ml= 0, ms= +½ b. n=2, l= 2, ml= -1, ms= -½ c. n=6, l= 2, ml= -2, ms= +½ 14) Write the values for the quantum numbers for the circled electron in the following diagrams: a. 3p orbitals ` c. 4d orbitals 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹 🡹 🡹 b. 5s orbital d. 3d orbitals 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹🡻 🡹