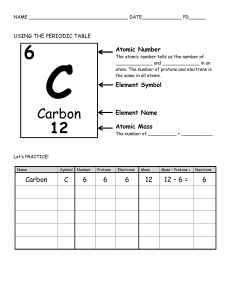
Worksheet Unit 3 – Subatomic Particles, Atomic and Mass Number Name: _______________________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: ______ Subatomic particles, Atomic Number & Mass Number Relationships Learning Goals/Objective: • • • I can discuss atoms in terms of their number of electrons, neutrons, and protons and define the terms of atomic number and mass number. I can use mass number and atomic number to describe various isotopes. I can calculate the average atomic mass of an element. Electrons = -1 charge Protons = + 1 Charge Neutrons = 0 Charge In a neutral atom, the # of electrons = the # of protons. Atomic Number (AN) a) Every atom has protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with electrons orbiting the nucleus. b) All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. c) The Atomic number (Z) is the number of protons Mass Number (MN) a) Mass number is the total number of particles in the nucleus. This is a whole number and may be different than the Atomic Mass seen on the periodic table. b) Mass Number (MN) # of protons + # of neutrons OR # of neutrons = MN - # of protons c) Generally, the mass number for each element is the element’s atomic mass rounded to the nearest whole number. This will be different when we are looking at isotopes. Element Naming/Notation: 1) Name Element – Mass Number 2) Symbol MN AN Symbol 3) Example: Name: Sulfur – 32 BRYAN WALTERS Symbol: 32 16𝑆 1 Worksheet Unit 3 – Subatomic Particles, Atomic and Mass Number The Element Table – for this exercise, consider the atoms to be neutral. You will need a periodic table. Name Symbol Atomic Number (AN) Name - MN 𝑀𝑁 𝐴𝑁𝑆𝑦𝑚𝑏𝑜𝑙 AN = # of P # of Protons (P) # of Neutrons (N) Mass Number (MN) # of Electrons (E) #P = AN or MN - #N #N = MN - #P MN = #P + # N E = #P in neutral atoms Hydrogen -1 4 2He 3 4 4 9 6 11 12 7 6 7 Oxygen -16 19 9F 10 10 44 BRYAN WALTERS 101 2 Worksheet Unit 3 – Subatomic Particles, Atomic and Mass Number Name Symbol Atomic Number (AN) # of Protons (P) # of Neutrons (N) Mass Number (MN) # of Electrons (E) Name - MN 𝑀𝑁 𝐴𝑁𝑆𝑦𝑚𝑏𝑜𝑙 AN = # of P #P = AN or MN - #N #N = MN - #P MN = #P + # N E = #P in neutral atoms Tin – 119 64 29Cu 26 30 31 70 54 96 133 55 Radon – 222 190 76Os 77 92 54 238 125 207 91 BRYAN WALTERS 40 3 Worksheet Unit 3 – Subatomic Particles, Atomic and Mass Number Name Symbol Atomic Number (AN) # of Protons (P) # of Neutrons (N) Mass Number (MN) # of Electrons (E) Name - MN 𝑀𝑁 𝐴𝑁𝑆𝑦𝑚𝑏𝑜𝑙 AN = # of P #P = AN or MN - #N #N = MN - #P MN = #P + # N E = #P in neutral atoms Cobalt - 60 47 108 40 19K 65 31 23 30 28 51 27 13Al 45 80 Iron - 56 16 16 Sodium - 23 35 17Cl BRYAN WALTERS 4