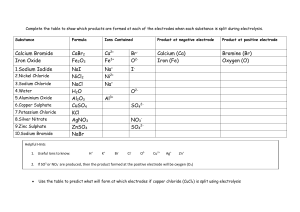
Topic 9 – Electrolytic cells www.msjchem.com Electrolytic cells 1. 2. (i) Draw a diagram of apparatus that could be used to electrolyse molten sodium chloride (NaCl). (ii) Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity but molten sodium chloride does. Explain this difference, and outline what happens in an electrolytic cell during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using carbon electrodes. (iii) State the products formed and give equations showing the reactions at each electrode. (iv) State what practical use is made of this process. (i) Draw a diagram of apparatus that could be used to electrolyse molten potassium bromide. Label the diagram to show the polarity of each electrode and the product formed. (ii) Describe the two different ways in which electricity is conducted in the apparatus. (iii) Write an equation to show the formation of the product at each electrode. Determine the mole ratio in which the substances are formed. MSJChem – tutorials for IB chemistry www.msjchem.com Topic 9 – Electrolytic cells www.msjchem.com Answers: 1. (i) (ii) Sodium chloride crystals consist of ions in a rigid lattice that cannot move about - when melted the ions are free to move. The positive sodium ions are attracted to the negative electrode (cathode) and the negative chloride ions are attracted to the positive electrode (anode) (iii) At the anode: chlorine gas is formed 2Cl-(l) Cl2(g) + 2eAt the cathode: sodium metal is formed Na+(l) + e- Na(l) (iv) manufacture of sodium and chlorine (not mentioned in the video but worth knowing). MSJChem – tutorials for IB chemistry www.msjchem.com Topic 9 – Electrolytic cells 2. www.msjchem.com (i) (ii) Electrons flow through connecting wires Ions move through the electrolyte to the electrodes and are oxidized or reduced. (iii) Anode: 2Br-(l) Br2(l) + 2eCathode: K+(l) + e- K(l) mol ratio K : Br2 2:1 MSJChem – tutorials for IB chemistry www.msjchem.com