Chemical Reactions: Combustion, Oxidation, and Metal Reactions
advertisement

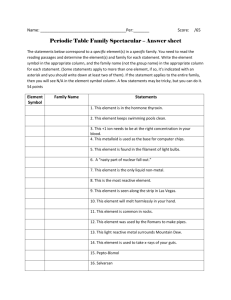
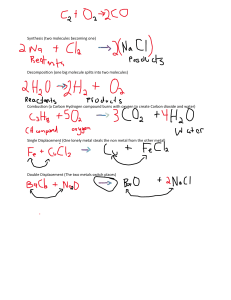
CHEMICAL REACTIONS UNIT - 8 2 Combustion reactions A combustion reaction is a chemical reaction which a fuel undergoes oxidation by reacting with an oxidizing agent, resulting in the release of energy (usually in the form of heat). 3 4 5 6 7 8 EXOTHERMIC REACTION 9 10 oxidation reaction Oxidation is a process in which a substance either adds oxygen or removes hydrogen 11 WITH WATER WITH ACID 12 ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS 13 14 Citric acid + sodium hydrogen carbonate sodium citrate + water + carbon dioxide 15 Ammonium nitrate with water When ammonium nitrate is dissolved in a beaker containing water, the beaker becomes cold because it is an endothermic reaction that is it absorbs energy from the surroundings in the form of heat. 16 17 89,5 18 Reaction of metals with O2 metal + oxygen → metal oxide. All metals react with oxygen except silver (Ag(s)), platinum (Pt(s)) and gold (Au(s)). In general, metals react with oxygen to form metal oxides. 20 Rusting of iron Rusting is an oxidation reaction. The iron reacts with water and oxygen to form hydrated iron oxide, which we see as rust. Iron and steel rust when they come into contact with water and oxygen – both are needed for rusting to occur. 21 How to prevent rusting of iron ? Use an Alloy: The use of alloys, like stainless steel. Apply Oil: A coating of oil will help to prevent rust or slow it down, since it inhibits moisture from reaching the iron in the metal. Apply a Dry Coating: Special rust preventative products dry with no residue and form a protective barrier over metal parts and equipment. Store Properly: Store metal parts or products in a low-moisture area, or inside a temperature and humidity-controlled environment to significantly slow down rust. Powder Coating: A layer of acrylic, vinyl, epoxy or other substances will prevent moisture from reaching the metal, thereby preventing rust. Paint the Metal: A good quality paint will slow down rusting by preventing moisture from reaching the metal. 22 Galvanization It is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to iron or steel, to prevent rusting. The most common method is hot dip galvanizing, in which steel sections are submerged in a bath of molten zinc. 23 Reaction of metals with water Metal + Water ⇨ Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen Most of the metals do not react with water. However, alkali metals react vigorously with water. Na + H2O ⇨ NaOH + H2 K + H2O ⇨ KOH + H2 Ca + 2H2O ⇨ Ca(OH)2 + H2 Mg + H2O ⇨ MgO + H2 25 2Al + 3H2O ⇨ Al2O3 + 2H2 Zn + H2O ⇨ ZnO + H2 3Fe + 4H2O ⇨ Fe3O4 + 4H2 26 27 Reaction of metals with dilute acid Metal + dil. acid ⇨ Metal salt + Hydrogen When a metal reacts with dilute acid, salts are formed. During this reaction hydrogen gas is evolved. Some metals reacts vigorously with dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid for example, potassium, sodium, lithium and calcium. 29 Link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=53T5WZHQ_Ck 30 Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2 31 Reactivity series of metals 32