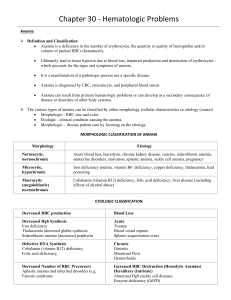
LAB VALUES: - RBC: 4-6 Million - WBC: 5-10,000 - PLT: 150-400,000 - Hgb: 12-18 - HCT: 37-52% - PT: 11-12.5 seconds - aPTT: 30-40 seconds - INR: 0.8-1.1 Hemolytic anemia: - S/S: jaundice Anemia: - More common in older people - ANEMIA IS NOT NORMAL!!! - Deficiency in the number of erythrocytes (RBC) - Problems with the quantity/quality of Hgb - Issues with volume of the packed RBCs Causes of Anemia: - Deficiency in nutrients o Iron o Vitamin B12 o Folic acid - Decreased EPO (erythropoietin) which means decrease in RBC - Decreased in iron availability - Blood loss o Chronic (ex: ulcers, liver disease) o Acute (ex: trauma, bleeding, aneurysm) - Increase in RBC destruction o Sickle cell anemia!!! o Medications o Incompatible blood o Trauma Assessment: what will the person look like? - Skin: pale, cold skin - Cardiac: increased HR, angina, HF, murmurs - Pulmonary: increased RR, dyspnea at rest!! - Neuro: vertigo, irritability, depression, impaired thought process - GI: anorexia, difficulty swallowing Diagnostics: - CBC o Hgb o HTC o Total RBC o RBC morphology - ESR - PT, INR, PTT - CT - MRI - Folic acid, vitamin B12, iron IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA: - MOST COMMON NUTRITIONAL DISORDER!! - People most susceptible: o Women in reproductive years (esp. when on periods) o Very young o Poor diet - Causes: o by low iron levels o poor intake o pregnancy o loss of iron (from periods, GI bleed, ulcers, hemorrhoids) o malabsorption - Malabsorption (iron absorption occurs in duodenum) so surgeries or diseases that alter, or remove the absorption area can cause anemia - Signs & Symptoms: o MAY BE VAGUE IN THE BEGINNING!! o Lethargic o SOB o PICA (random ass cravings for weird shit loll) o Cheilitis (INFLAMMATION OF LIPS) o Glossitis (INFLAMMATION OF TONGUE) o Change in RBC o Nails change o Neuro changes (confused and moody, so me all the time lol) - Diagnostics: o CBC o Iron levels o Blood smear o Stool o Endoscopy - Interventions: o MONITOR FOR BLEEDING!! o Iron supplements Take on empty stomach to INCREASE absorption Take with orange juice to INCREASE absorption DO NOT take with antacid/milk/Ca+, OR wait at least 2 hours in between Black tarry stools may occur, this is NORMAL Constipation may occur so make sure you stay hydrated and increase fiber o Medications o Good iron diet!! Egg yolks Apricots Tofu Legume, leafy greens Oysters, tuna, sardines (ew lol) Potatoes Red meat Raisins, nuts Iron fortified cereal PERNICIOUS ANEMIA: - Form of a vitamin B12 deficiency - Affects nervous system, heart, and GI - Vegans are at risk bc of their diet - Caused by absence of intrinsic factor o Intrinsic factor is a protein secreted by parietal cells of gastric mucosa o It is REQUIRED for cobalamin absorption o If intrinsic factor is NOT secreted, cobalamin will NOT be absorbed - Insidious onset (comes on slowly, may not have obvious symptoms at first) - Begins in middle age or older - Predominant in Scandinavians and African American’s - Signs & Symptoms: o Pale o Fatigue o SOB o Red, smooth, BEEFY tongue o Numbness/tingling in hands and feet o Intestinal issues Diarrhea Constipation Bloating Indigestion o Confusion, depression o Loss of appetite, weight loss!! - Interventions: - Replace vitamin B12 o Cobalamin o Weekly IM injections which move to MONTHLY - Educate patients on safety due to paresthesia - Increase iron intake, vitamin C, and folic acid - Educate on oral hygiene!! Sickle Cell Anemia: - INCURABLE!!! - Genetic blood disorder (recessive gene) o PARENTS MUST BE CARRIERS OF SICKLE CELL TRAIT!! - More common in African American’s, Asian’s, middle eastern, and Eastern Mediterranean’s - ABNORMAL Hgb in RBC - Triggered by low oxygen in the blood - INFECTION most COMMON precipitating factor - RBC’s change shape and become: o Stiff o Weak Diagnostics: - Newborn testing Signs & Symptoms: - Dactylitis in INFANTS (swelling of fingers or toes, looks sausage-shaped lol) - Pain in the joints, back, and spleen - Tired - Increased HR - SOB - Pale, fatigue - Gallstones - STROKE - Eye problems - Leg ulcers in OLDER CHILDREN - VERY PAINFUL!!! Complications: - INFECTION (major cause of morbidity and mortality) - Can lead to shutdown of RBC production - Autosplenectomy is a result of scarring o Severe infections can cause aplastic crisis o Pneumococcal pneumonia is MOST common Sickle Cell Anemia CRISIS: - VERY PAINFUL - Severe capillary hypoxia which can lead to tissue necrosis - Life threatening shock could occur due to severe O2 depletion - Vaso-occlusive o RBCs are sticking to vessels - Hyper-hemolytic o Increase death of RBCs - Aplastic o No production of RBCs - Splenic o Spleen sequestration o Swelling/infection Interventions: - Provide HYDRATION - Oxygen - PAIN CONTROL!! (Opioids around the clock) - Bed rest - Monitor RR - Assess for pneumonia - WATCH FOR IRON TOXICITY!!! - Give antibiotics if they have an infection Prevention: - Avoid high altitudes - Avoid stress!! - No smoking - Do NOT overdue exercise - Stay HYDRATED!! - Vaccines Medications: - Hydroxyurea o Creates fetal Hgb o Helps with the sickling of cells o Side effects: decreased WBC - Stem cell transplant Things to AVOID: - S: significant blood loss - I: illness, infections - C: climbing/flying to high altitudes - K: keeping continuous stress (mental or physical) - L: low fluid intake (dehydration) - E: extreme temperatures (hot, cold, exercise) Thrombocytopenia: - Low platelets (< 150,000) - Increased risk for bleeding due to low platelets, prolonged bleeding from trauma or random without an injury - NO PLATLETS= NO CLOTTING FACTOR!!! - Risk Factors: o Heparin induced o DIC o ITP o Drugs (chemo, aspirin) o Cancer, infections - Usually, an acquired disorder - Heparin can induce thrombocytopenia - Patient will have petechiae (round spots that appear on the skin that happen because of bleeding, think of your grandparents: they probably have little round red blood spots on their arms/hands/legs lol) - Patients will also have ecchymosis (bruising) Teaching: o Be aware of bleeding gums o Use an electric razor o Soft toothbrush o Watch for nose bleeds (don’t blow nose too hard) Neutropenia: - Neutrophils < 1000 - Normal range is 2200-7700 - So, they are VERY LOW!! - LOW WBC - Patient is at an increased risk for infection!! - STRICT PRECAUTIONS - Risk factors: o Chemo o Immunosuppressant therapy - Neutropenic fever: o Little ability to have an immune response o Quickly progresses to sepsis and death!! o Low grade fever (> 100.4) o Monitor and report ASAP!! o Blood cultures and antibiotics within 1 hour of fever starting o Neutropenic precautions Strict hygiene Single room, not sharing with someone else in hospital Avoid contact with crowds Daily skin and oral hygiene are essential Wear a mask No flowers NO FRESH FRUIT ALLOWED!!! All foods MUST BE COOKED!!! NOTHING UNCOOKED!!! Leukemia: - A group of cancers affecting the blood and blood-forming tissues of: o Bone marrow o Lymph system o Spleen - No single cause - Can be from environmental factors or genetics BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS: - 2 nurses MUST sign for the transfusion!! - 18-20 gauge IV is used - DO NOT INFUSE WITH ANYTHING ELSE!! Just the BLOOD - Bag of 0.9% NS to prime and flush IV tubing - Check orders for type and cross match - - - - - ID Patient, draw blood for T+C in red topped tube, place blood band and label Check consent Pick up blood from blood bank o MUST be administered within 30 minutes of receiving blood!! o This is to avoid infection Take vital signs Blood warmer IF large amounts Explain the process + what to report Rate of infusion o Start slow o 2 ml/min for first 15 minutes, then start increasing slowly o Infuse for no more than 4 hours Remain with the patient for 15 minutes after the infusion o Monitor for adverse reactions o Monitor vital signs q 15 mins, then q 30 mins, then q 1 hour after the transfusion is complete If the patient is having a reaction to the transfusion: o STOP TRANSFUSION!! Call MD o Elevate HOB (head of bed) o Give oxygen and comfort measures o Change IV tubing and continue with NS (normal saline) o Give fluids, epinephrine o Re-check crossmatch record o Monitor fluids and electrolytes o STAY WITH PATIENT!! Types of reactions to transfusions: o Febrile non-hemolytic reaction Most common reaction Reaction to DONOR’s WBC, plasma, proteins, or contamination (bacteria) Give acetaminophen before the transfusions s/s: 1 degree rise in temperature, chills, malaise no need to stop the infusion unless hemolytic reaction develops o Sepsis o Hemolytic reaction (WORST ONE!!) Pain at site of reaction LOWER BACK PAIN!!! Fever, chills, nausea/vomiting, tachycardia, LOW blood pressure, dark urine, septic shock STOP THE TRANSFUSION ASAP!! o TACO Transfusion associated circulatory overload Most common in elderly and chronic anemia patients s/s: dyspnea, edema give blood SLOWLY over 3-4 hours diuretics before or between units of blood o TRALI Transfusion related acute lung injury Most common cause of death associated with transfusions Fluid in alveoli= RESPIRATORY DISTRESS!! Better prognosis than ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome) s/s: dyspnea, hypoxemia, bilateral chest infiltrates stop the infusion, airway control, supportive care o Allergic reactions Antibodies in the patients’ blood Give them Benadryl before if they know they are prone to allergic reactions for transfusions or during the infusion