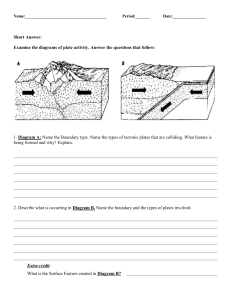
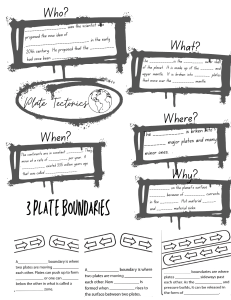
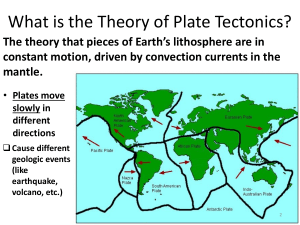
STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION OF OCEAN BASINS AND FORMATION OF FOLDS, FAULTS, TRENCHES, VOLCANOES, RIFT VALLEYS, AND MOUNTAIN RANGES THROUGH PLATE MOVEMENT CHANGE is truly inevitable Earth is a planet defined by change, going throughout periods of intense heat and freezing, which have led to the formation oceans and continents that are reshaped by the actions of plate tectonics. It looked very different from 250 million years ago, from a single continent called Pangaea and one ocean called Panthalassa. Two types of lithosphere 1. Oceanic lithosphere is associated with oceanic crust, and is slightly denser than continental lithosphere. Two types of lithosphere Oceanic lithosphere is typically about 50-100 km thick (but beneath the mid-ocean ridges is no thicker than the crust). The oceanic lithosphere consists mainly of mafic crust and ultramafic mantle and is denser than the continental lithosphere, for which the mantle is associated with a crust made of felsic rocks. Tectonic Plates are broken pieces; they are like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle found in the Earth’s Lithosphere. Tectonic Plate activity plays a vital role in the GEOLOGIC changes in the EARTH that occurs in the LITHOSPHERE. How? How Plates Move? - When mantle convection drives plate tectonics. The hot material rises over midocean ridges and sinks into deep trenches, which keeps the plates moving along the Earth's surface. Plate Boundary/Margin is the edge where two plates meet. Most geological activity, including volcanoes, earthquakes and mountain construction, take place at plate boundaries. How can two plates move relative to each other? Convection currents drive the movement of Earth's rigid tectonic plates in the planet's fluid molten mantle. In places where convection currents rise up towards the crust's surface, tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading Divergent plate boundaries: -the two plates move away from each other. Convergent plate boundaries: - the two plates move towards each other. Transform plate boundaries: - the two plates slip past each other. What is the RESULT of tectonic plate activity when it occurs within the different boundaries of the plate in the CONTINENTAL LITHOSPHERE? 1. Divergent Plate Boundary also known as Constructive Plate Boundary - Plates move apart from one another. The magma from the mantle rises up to make (or construct) new crust. - EARTHQUAKES occurs when plates move over the mantle - Landforms at a divergent plate boundary include a) Mid-Ocean Ridges; (b) Rift Valleys; and (c)Shield Volcanoes. - As plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges where new seafloor forms. Between the two plates is a rift valley. Figure 6 (a) Iceland is the one location where the ridge is located on land: the Mid-Atlantic Ridge separates the North American and Eurasian plates; (b) The rift valley in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on Iceland. Figure 7 The Arabian, Indian, and African plates are rifting apart, forming the Great Rift Valley in Africa. The Dead Sea fills the rift with seawater What is a Mid- Oceanic Ridge? An underwater mountain range, formed by plate tectonics What is a Rift Valley? o A lowland region that forms where Earth's tectonic plates move apart What is a shield volcano? A broad domed volcano with gently sloping sides, characteristic of the eruption of fluid, basaltic lava. o e.g. Mauna Loa volcano on Hawaii 2. Convergent plate boundary also known as a Destructive Plate Boundary, - usually involves an oceanic plate and a continental plate. The plates move towards one another and this movement can cause EARTHQUAKES and VOLCANOES. (Figure 8) SUBDUCTION occurs when the plates collide; the oceanic plate is forced beneath the continental plate which formed an OCEAN TRENCH - - This happens because the oceanic plate is denser (heavier) than the continental plate. - When the plate sinks into the mantle it melts to form magma. The pressure of the magma builds up beneath the Earth's surface. The magma escapes through weaknesses in the rock and rises up through a composite volcano, also known as a STRATOVOLCANO. The volcanic eruptions are often violent, with lots of steam, gas and ash. - FOLD MOUNTAINS is formed when two continental plates collide, neither can sink and so the land buckles upwards. - This is called a collision boundary. Earthquakes can occur at collision boundaries What is an Ocean Trench? o A long, narrow depression on the seafloor. o e.g. Philippine Trench, Tonga Trench, the South Sandwich Trench, the Eurasian Basin and Malloy Deep, the Diamantina Trench, the Puerto Rican Trench, and the Marianas. • What is a Stratovolcano? o A tall, conical volcano composed of one layer of hardened lava, tephra, and volcanic ash o e.g, Krakatoa in Indonesia, Mt. Pinatubo • What is a Fold Mountains? o A wave-like geologic structure that forms when rocks deform o e.g. Himalayas, The Andes and the Alps 3. Transform Boundary or Conservative plate boundaries - Plates slide past each other in opposite directions, or in the same direction but at different speeds. (Figure 9) - A smaller number of transform faults cut continental lithosphere. - The most famous example of this is the San Andreas Fault Zone of western North America. - The San Andreas connects a divergent boundary in the Gulf of California with the Cascadia subduction zone. (Figure 10) - Another example of a transform boundary on land is the Alpine Fault of New Zealand. What o is a FAULT? A fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. 1. OFSDL -a wave-like geologic structure that forms when rocks deform 2. UTFLSA -fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. 3. MDAIENCO ERISDG -an underwater mountain range, formed by plate tectonics 4. TRIF VELAYLS -lowland region that forms where Earth's tectonic plates move apart 5. ALVOCESNO -an opening in Earth's crust that allows molten rock from beneath the crust to reach the surface 6. RNECSTHE - are long, narrow depressions on the seafloor. 7. ANS DENRAS TLFAU - the sliding boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. 8. KEHTUEARQA -shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. 9. TLAPE OBNUDRYA -the location where two plates meet 10. AGAMM -molten rock