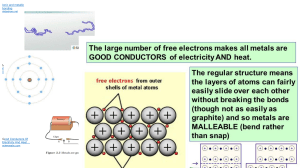
LESSON PLAN Teacher: Howard Zulu Mr. Date:……………Class. 10 Time: ………………………….. Duration: 80 MINUTES Subject: CHEMISTRY Topic: CHEMICAL BONDING Sub-Topic: Chemical bonding-Metallic bonding Rationale: This is the 3rd lesson in the series of 6 lesson to cover this topic. The learner will learn about metallic bonding and properties of metallic .This will grow their appreciation and awareness for metals and their properties as well as their use in every day lives. The method used are demonstration, discussion, video demonstration, answer and question. Lesson outcomes: Describe metallic bonding. Describe the electrical conductivity and ductility of metals. References: IGCSE chemistry, Longman chemistry, Progress in science, Teaching Resources/Aids: Periodic table, Chart, white board marker TIME LESSON CONTENT LESON DEVELOPMENT METALLIC BONDING Metallic bonding is the attraction between the positively charged metal ions and the free electrons in a metallic lattice.\ In metals, the atoms are packed tightly together in a regular lattice. The tight packing allows outer electrons to separate from their atoms. The result is a lattice of ions in a ‘sea’ of electrons that are free to move The electrons are free to move anywhere in the metallic lattice. The electrons are said to be delocalized. Copper atoms, for example, lose two single electron from the outer most shell. When a large number of sodium atoms lose these electrons, the result is many free electron NB:The metallic bond is the attraction between metal ions and free electrons. It is the same with all metals. The ions sit in a lattice, held together by their strong attraction to the free electrons. And because the ions are in a regular pattern, metals are crystalline METHODOLOGY TEACHER ACTIVITY LEARNER ACTIVITY The teacher will define metallic bonding. Learner will participat e orally. Techer will engage learner in comparing the forces attraction in metallic bond and forces of attractions in a covalent and ionic bond Learners will participat e by answering and asking question . NB:The copper ions are held together by their attraction to the free electrons between them. The strong forces of attraction are called metallic bonds. METALLIC PROPERTIES Metals usually have high melting points. That is because it takes a lot of heat energy to break up the lattice, with its strong metallic bonds. Copper melts at 1083 8C, and nickel at 1455 8C. (But there are exceptions. Sodium melts at only 98 8C, for example. And mercury melts at –39 8C, so it is a liquid at room temperature.) Metals are malleable and ductile. Malleable means they can be bent and pressed into shape. Ductile means they can be drawn out into wires. This is because the layers can slide over each other. Metals are good conductors of heat.That is because the free electrons take in heat energy, which makes them move faster. They quickly transfer the heat through the metal structure: Teacher will explain the diagrammatic representation of the metal. Use copper Learners will participat e by answering and asking question Teacher will explain the metallic properties due metallic bond. Learners will participat e by asking and answering questions Teacher will engage learners in comparing the characteristic of metallic bond, of ionic and covalent compound. Learners will participat e by answering and asking question . CONCLUSION: The teacher will conclude the lesson by running through the main points and giving an exercise. EVALUATION:…………………………………………………………………………………………………… ….…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………