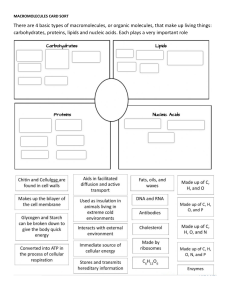
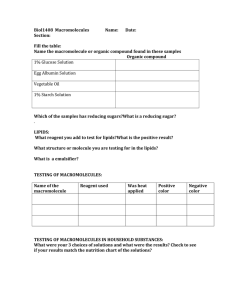
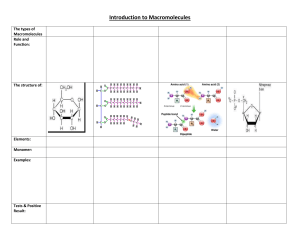
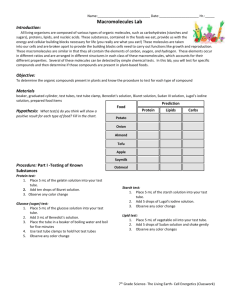
Introduction or purpose There are four macromolecules in living organisms which are proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. These are used by our cells and often obtained through foods we eat. The purpose of this laboratory is to determine the presence of key macromolecules in food and to relate these organic compounds to life processes. It is very important to realize because all of the organisms on earth use all of the biomolecules in our cell. In this lab, the hypothesis is if carbohydrates, protein, and lipids are present in the food slurry, then each will test positive in the presence of their respective reagents. Since McMush laboratory activity examines chemical tests for the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins found in food samples, we learn more about the existence of macromolecules in living organisms. So we can understand what macromolecules are and what macromolecules are in each organism. I would like to know why each solution is positive or negative. Seeing positive and negative responses to where the macromolecules exist can further enhance my understanding about macromolecules. Materials beaker, hot plate, well plate, tongs, test tubes, test tube rack, McMush food slurry, glucose control, starch control, protein control (egg solution), lipid control (oil), distilled water, Benedict’s Solution, Lugol’s Solution, Biuret’s Solution, Sudan Solution Methods or Procedure Monosaccharide test: 1.Place 3 ml each of glucose solution, distilled water, and the food slurry in seperate test tubes. 2.Add 5 drops of Benedict’s solution to each test tube and gently mix. 3.Leave the test tubes in the water bath for 5 minutes or until you start to see a color change. 4.Record color on the data table. Polysaccharide test: 1.Place 3 ml each of starch solution, distilled water, and the food slurry in seperate wells on the well plate. 2.Add 3 drops of Lugol’s Iodine Solution to each well. 3.Observe any color change and record the results in the data table. Protein test: 1.Place 3 ml each of egg solution, distilled water, and the food slurry in seperate wells on the well plate. 2.Add 10 drops of Biuret’s solution to each well and mix carefully. 3.Observe any color change and record the results in the data table. Lipid test: 1.Place 3 ml each of vegetable oil, distilled water, and the food slurry in seperate wells on the well plate. 2.Add 5 drops of Sudan III Solution to each well 3.Observe any color change and record the results in the data table. Data and Results Result of Test Performed on Known Substances Test Performed Substance Tested Positive Test Color Negative Test Color Monosaccharide Carbohydrates Benedict's solution Orange to brick-red color Blue Polysaccharide Carbohydrates Lygol’s solution Dark Blue Amber Proteins Biuret’s solution Violet Blue Lipids Sudan III solution Layers or Clumps No layers or no clumps Result of McMush Test Macromolecule Food Substance Result Water Result Food Slurry Result Monosaccharide Glucose solution: Negative No change Negative No change Negative No change Polysaccharide Starch solution: Positive Dark blue Negative Amber Negative Dark Amber Protein Egg solution: Positive Violet Negative Blue Negative No change Lipid Vegetable Oil: Positive Layer Negative Fat Positive Chunky layer The results of monosaccharide on Benedict’s solutions are negative of glucose, negative of water, and negative of food slurry. Because glucose, water, and food slurry has no change. The results of polysaccharide on Lygol’s solutions are positive of starch solution, negative of water, and negative of food slurry. Since Lygol’s positive color is dark blue and negative color is amber, the starch solution is positive because it changed to dark blue. And water and food slurry are changed to amber so both are negative. The results of protein on Biuret’s solutions are positive of egg solution, negative of water solution, and negative of food slurry. Since Biuret’s solution’s positive color is violet and the negative color is blue, the egg solution is positive because it changed to violet. Water changed to blue which is negative, and food slurry has no change which is also negative. The results of Lipid on Sudan’s solutions are positive of vegetable oil, negative of water, and positive of food slurry. Since Sudan’s positive result is layers or clumps and negative result is no layers or clumps, vegetable oil is positive because it is with layers. Water is negative because there is no layer. Food slurry has a chunky layer, so it is positive. Discussion or Analysis The hypothesis was if carbohydrates, protein, and lipids are present in the food slurry, then each will test positive in the presence of their respective reagents. Monosaccahride’s glucose solution and food slurry were both negative so it is accepted by the hypothesis. Lipid’s vegetable oil and food slurry were both positive so it is accepted by the hypothesis. However, when starch solution and egg solution were positive, their food slurries were present negative. It means that a happy meal has no protein and polysaccharide. But if I made a mistake, looking back on what I did, I am not sure that I put the right amount of solutions. Probably this is the reason for the wrong result if I made a mistake. Conclusion A happy meal at McDonald's does not have nutritional value because three biomolecules are not present in the meal. In the data, when the sudan’s solution was added into the McMush, it got a chunky layer. When other macromolecules were present negative in McMush, only lipids were present positive. It means only lipids are in a happy meal and it can not afford enough nutrients to people. Starch, protein, and lipids are three biomolecules essential for our nutrition. Therefore a happy meal does not have enough nutrition, so we should eat other food that has three biomolecules. Reference https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/biology/the-effect-of-indicat ors-on-the-presence-of-macromolecules-in-a-mcmush-slurry.html