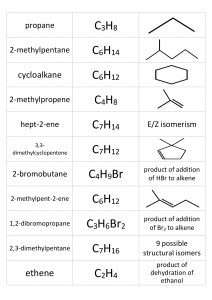
Cumulative Task Grade 12 Unit 1: Organic Chemistry: 1. Ethene (common name ethylene) is a commercially important organic compound. Millions of tons of ethene are produced by the chemical industry each year. Ethene is used in the manufacture of synthetic fibers for carpeting and clothing, and it is widely used in making polyethylene. Low-density polyethylene can be stretched into a clear, thin film that is used for wrapping food products and consumer goods. Highdensity polyethylene is molded into bottles for milk and other liquids. Ethene can also be oxidized to produce ethylene glycol, which is used in antifreeze for automobiles. The structural formula for ethylene glycol is: At standard atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of ethylene glycol is 198°C, compared to ethene that boils at –104°C. a. Identify the type of organic reaction by which ethene (ethylene) is made into polyethylene. _____________________________________________ b. According to the information in the reading passage, state two consumer products manufactured from ethene. ______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ c. Explain, in terms of bonding, why ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. In artificial apple flavour, the main ingredient is ethyl 2-methylbutanoate. (a) Draw a flow chart to show the synthesis of this compound, starting with simpler compounds. (b) Describe the steps in the procedure for this synthesis. Include experimental conditions and safety precautions in the handling and disposal of materials. 3. Classify and write structural formula equations for the following organic reactions. (a) ethene + water→ ethanol (b) 2 – butanol → 1 – butene + 2 – butene + water (c) ethoxyethane + oxygen → (d) ethene + hypochlorous acid (HOCl (aq)) →2 – chloroethanol (e) methanol + oxygen → 4. For each of the following particles, do the following: a) XeF4 b) SF6 a) Draw the structure/geometry as predicted by the VSEPR theory b) Name the shape of the geometry as predicted by the VSEPR theory c) Indicate the bond angle(s) found in the particle d) Indicate the polarity of the particle Unit 2: Structures and Properties of Matter (Quantum) 1. Draw and write the electron configuration for calcium and iron. (A: 4 marks) 2. Why is the ionization energy required to remove an outer electron from Na+ so much greater than that needed to remove the outer electron from Na? (HINT: if you’re stuck, draw the orbitals of Na and Na+ to help you visualize) 3. What types of bonds are in CN- (sigma vs pi) and what is the hybridization of carbon and nitrogen? Unit 3: Rates of Reaction 1. Ethanol, C2H5OH, and gasoline (approximately 100% octane, C8H18) are both used as fuel in cars. If gasoline sells for $1.15/L, what would the price of ethanol have to be in order to provide the same amount of heat per dollar? The density of octane is 0.7025 g/mL, and ∆H°f of octane is −249.9 kJ/mol. The density of ethanol is 0.7894 g/mL, and ∆H°f of ethanol is −277.6 kJ/mol. [ /9] 2. The forward activation energy of a reaction is 25 kJ/mol, and the heat of reaction is −286.4 kJ/mol. a) Sketch a potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the axes, the forward activation energy, the heat of reaction, the transition state, and the reactants and products. b) Indicate the numerical values of the forward activation energy and the enthalpy change on your diagram. c) Show and label the effect of a catalyst. 3. Unit 4: Equilibrium: 1. 2. Unit 5: Electrochemistry 1. 2. 3.