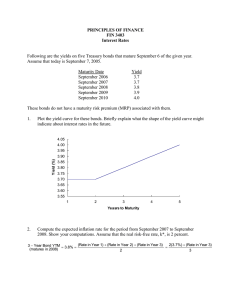
MIDTERM 1 SAMPLE TEST ____ 1. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. The cash flows for an ordinary annuity all occur at the beginning of the periods. b. If a series of unequal cash flows occurs at regular intervals, such as once per year, then the series is by definition an annuity. c. The cash flows for an annuity due must all occur at the beginning of the periods. d. The cash flows for an annuity may vary from period to period, but they must occur at regular intervals, such as once per year or once per month. e. If some cash flows occur at the beginning of the periods while others occur at the ends, then we have what the textbook defines as a variable annuity. ____ 2. You plan to analyze the value of a potential investment by calculating the sum of the present values of its expected cash flows. Which of the following would increase the calculated value of the investment? a. The total amount of cash flows remains the same, but more of the cash flows are received in the later years and less are received in the earlier years. b. The discount rate decreases. c. The cash flows are in the form of a deferred annuity, and they total to $100,000. You learn that the annuity lasts for 10 years rather than 5 years, hence that each payment is for $10,000 rather than for $20,000. d. The riskiness of the investment's cash flows increases. e. The discount rate increases. ____ 3. Which of the following statements is CORRECT, assuming positive interest rates and holding other things constant? a. Banks A and B offer the same nominal annual rate of interest, but A pays interest quarterly and B pays semiannually. Deposits in Bank B will provide the higher future value if you leave your funds on deposit. b. A 30-year, $150,000 amortized mortgage will have larger monthly payments than an otherwise similar 20-year mortgage. c. If an investment pays 10% interest, compounded annually, its effective annual rate will be less than 10%. d. The present value of a 5-year, $250 annuity due will be lower than the PV of a similar ordinary annuity. e. A bank loan's nominal interest rate will always be equal to or less than its effective annual rate. ____ 4. Suppose you have $2,000 and plan to purchase a 10-year certificate of deposit (CD) that pays 10.0% interest, compounded annually. How much will you have when the CD matures? a. b. c. d. e. $4,876.24 $5,187.48 $4,772.49 $5,291.23 $3,942.49 ____ 5. Suppose the U.S. Treasury offers to sell you a bond for $667.25. No payments will be made until the bond matures 5 years from now, at which time it will be redeemed for $1,000. What interest rate would you earn if you bought this bond at the offer price? a. b. c. d. e. ____ 6. Janice has money invested in a bank that pays 8.0% annually. How long will it take for her funds to triple? a. b. c. d. e. ____ $38,744.29 $40,294.06 $47,268.04 $46,105.71 $36,807.08 8. What's the rate of return you would earn if you paid $3,080 for a perpetuity that pays $85 per year? a. b. c. d. e. ____ 11.56 years 16.13 years 15.27 years 11.13 years 14.27 years 7. What is the PV of an annuity due with 5 annual payments of $8,600 at an interest rate of 5.5%? a. b. c. d. e. ____ 7.67% 6.83% 9.02% 8.43% 6.49% 2.07% 2.87% 2.76% 3.12% 2.68% 9. You sold a car and accepted a note with the following cash flow stream as your payment. What was the effective price you received for the car assuming an interest rate of 6.0%? Yr: CFs: a. b. c. d. e. $5,987 $4,730 $5,209 $6,166 $5,628 0 $0 1 $1,000 2 $2,000 3 $2,000 4 $2,000 ____ 10. You agree to make 24 deposits of $500 at the beginning of each month into a bank account. At the end of the 24th month, you will have $12,850 in your account. If the bank compounds interest monthly, what nominal annual interest rate will you be earning? a. b. c. d. e. 6.85% 5.28% 5.67% 6.65% 6.52% ____ 11. Master Card and other credit card issuers must by law print the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) on their monthly statements. If the APR is stated to be 18.00%, with interest paid monthly, what is the card's effective annual rate (EFF%)? a. b. c. d. e. 18.78% 17.02% 19.56% 24.45% 23.67% ____ 12. Your company has just taken out a 1-year installment loan for $72,500 at a nominal rate of 9.0% but with equal end-of-month payments. What percentage of the 2nd monthly payment will go toward the repayment of principal? a. b. c. d. e. 113.29% 92.11% 78.29% 77.37% 99.48% ____ 13. Assume that interest rates on 20-year Treasury and corporate bonds are as follows: T-bond = 7.72% AAA = 8.72% A = 9.64% BBB = 10.18% The differences in these rates were probably caused primarily by: a. Real risk-free rate differences. b. Maturity risk differences. c. Default and liquidity risk differences. d. Inflation differences. e. Tax effects. ____ 14. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. If inflation is expected to increase in the future and the maturity risk premium (MRP) is greater than zero, the Treasury bond yield curve must be upward sloping. b. Because long-term bonds are riskier than short-term bonds, yields on long-term Treasury bonds will always be higher than yields on short-term T-bonds. c. If the maturity risk premium (MRP) is greater than zero, the Treasury bond yield curve must be upward sloping. d. The Treasury bond yield curve will never be downward sloping. e. If the maturity risk premium (MRP) equals zero, the Treasury bond yield curve must be flat. ____ 15. The real risk-free rate is 3.05%, inflation is expected to be 4.25% this year, and the maturity risk premium is zero. Ignoring any cross-product terms, what is the equilibrium rate of return on a 1-year Treasury bond? a. b. c. d. e. 7.23% 7.30% 6.06% 6.13% 8.32% ____ 16. Suppose 10-year T-bonds have a yield of 5.30% and 10-year corporate bonds yield 8.75%. Also, corporate bonds have a 0.25% liquidity premium versus a zero liquidity premium for T-bonds, and the maturity risk premium on both Treasury and corporate 10-year bonds is 1.15%. What is the default risk premium on corporate bonds? a. b. c. d. e. 3.30% 3.33% 3.20% 2.59% 2.82% ____ 17. Which of the following events would make it more likely that a company would call its outstanding callable bonds? a. b. c. d. e. The company's financial situation deteriorates significantly. Market interest rates rise sharply. The company’s bonds are downgraded. Inflation increases significantly. Market interest rates decline sharply. ____ 18. Which of the following statements is CORRECT? a. b. c. d. e. All else equal, high-coupon bonds have less reinvestment risk than low-coupon bonds. All else equal, low-coupon bonds have less price risk than high-coupon bonds. All else equal, long-term bonds have less reinvestment risk than short-term bonds. All else equal, short-term bonds have less reinvestment risk than long-term bonds. All else equal, long-term bonds have less price risk than short-term bonds. ____ 19. Morin Company's bonds mature in 8 years, have a par value of $1,000, and make an annual coupon interest payment of $65. The market requires an interest rate of 7.3% on these bonds. What is the bond's price? a. b. c. d. e. $1,000.42 $952.78 $876.56 $914.67 $809.86 ____ 20. Adams Enterprises’ noncallable bonds currently sell for $1,110. They have a 15-year maturity, an annual coupon of $85, and a par value of $1,000. What is their yield to maturity? a. b. c. d. e. 7.34% 8.65% 7.49% 7.71% 7.27% ____ 21. Sadik Inc.'s bonds currently sell for $1,030 and have a par value of $1,000. They pay a $105 annual coupon and have a 15-year maturity, but they can be called in 5 years at $1,100. What is their yield to call (YTC)? a. b. c. d. e. 10.83% 11.28% 11.50% 9.47% 10.72% ____ 22. At time 0, Malko Enterprises’ bonds sell for $1,150. The bonds have a 10 year maturity, an annual coupon of $100, and a par value of $1,000. What is their expected current yield in the first year? a. b. c. d. e. 7.14% 7.50% 7.88% 8.70% 10.00% ____ 23. Assume that you are considering the purchase of a 20-year, noncallable bond with an annual coupon rate of 9.5%. The bond has a face value of $1,000, and it makes semiannual interest payments. If you require an 9.6% nominal yield to maturity on this investment, what is the maximum price you should be willing to pay for the bond? a. b. c. d. e. $852.41 $1,199.33 $1,169.59 $911.89 $991.18 ____ 24. XYZ Inc.'s bonds currently sell for $1,275. They pay a $90 annual coupon, have a 25-year maturity, and a $1,000 par value, but they can be called in 5 years at $1,050. Assume that no costs other than the call premium would be incurred to call and refund the bonds, and also assume that the yield curve is horizontal, with rates expected to remain at current levels on into the future. What is the difference between this bond's YTM and its YTC? (i.e. Subtract the YTC from the YTM) a. b. c. d. e. 3.00% 3.30% 2.92% 3.32% 2.60% ____ 25. O'Brien Ltd.'s outstanding bonds have a $1,000 par value, and they mature in 25 years. Their nominal yield to maturity is 9.25%, they pay interest semiannually, and they sell at a price of $925. What is the bond's nominal coupon interest rate? a. b. c. d. e. 7.46% 10.09% 8.48% 7.80% 6.36% Formula Sheet – Midterm 1 CH5: FVN = PV (1 + I)N 𝑭𝑽 PV = (𝟏+𝑰)𝑵 𝑵 (𝟏 + 𝑰)𝑵 − 𝟏 𝑭𝑽𝑵 = 𝑷𝑴𝑻[ ] 𝑰 𝑭𝑽𝒅𝒖𝒆 = 𝑭𝑽𝒐𝒓𝒅𝒊𝒏𝒂𝒓𝒚 (𝟏 + 𝑰) 𝑷𝑽𝑶𝑹𝑫 = 𝑷𝑴𝑻 𝟏 [𝟏 − ] 𝑰 (𝟏+𝑰)𝑵 𝑷𝑽𝒅𝒖𝒆 = 𝑷𝑽𝒐𝒓𝒅𝒊𝒏𝒂𝒓𝒚 (𝟏 + 𝑰) 𝑷𝑽𝑷𝑬𝑹𝑷 = 𝑰𝑷𝑬𝑹 = 𝑷𝑴𝑻 𝑰 𝑺𝒕𝒂𝒕𝒆𝒅 𝒂𝒏𝒏𝒖𝒂𝒍 𝒓𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒑𝒂𝒚𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒔 𝒑𝒆𝒓 𝒚𝒆𝒂𝒓 = 𝑰 𝑴 𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒅𝒔 = (𝑵𝒖𝒎𝒃𝒆𝒓 𝒐𝒇 𝒚𝒆𝒂𝒓𝒔) ∗ (𝑷𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒅𝒔 𝒑𝒆𝒓 𝒚𝒆𝒂𝒓) = 𝑵𝑴 𝑰 FVN = PV (1+ 𝑴)NM EFF% = (1+ 𝑵 𝑷𝑽 = ∑ 𝒕=𝟏 𝑰𝑵𝑶𝑴 M ) 𝑴 -1 𝑪𝑭𝒕 (𝟏 + 𝑰)𝒕 CH6: r = r* + IP + DRP + LP + MRP CH7: 𝑵 𝑽𝑩 = ∑ 𝒕=𝟏 𝑰𝑵𝑻 𝑴 + 𝒕 (𝟏 + 𝒓𝒅 ) (𝟏 + 𝒓𝒅 )𝑵 𝑪𝒖𝒓𝒓𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝒀𝒊𝒆𝒍𝒅 (𝑪𝒀) = 𝒄𝒐𝒖𝒑𝒐𝒏 𝒑𝒂𝒚𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕 𝑩𝒆𝒈𝒊𝒏𝒏𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝑪𝒂𝒑𝒊𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒈𝒂𝒊𝒏𝒔 𝒚𝒊𝒆𝒍𝒅 (𝑪𝑮𝒀) = 𝑪𝒉𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒆 𝒊𝒏 𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝑩𝒆𝒈𝒊𝒏𝒏𝒊𝒏𝒈 𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆