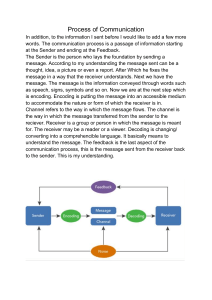
lOMoARcPSD|18009790 1 Functions, Nature and Process of Communication Speech and Oral Communication (University of Southeastern Philippines) StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|18009790 Grade 11: Oral Communication in Context QUARTER 1 WEEK 1 Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competencies The learner understands the nature and elements of oral communication in context. The learner designs and performs effective controlled and uncontrolled oral communication activities based on context. Explains the functions, nature and process of communication. EN11/12OC-Ia-2 Topic 1: Functions, Nature and Process of Communication WHAT IS COMMUNICATION? Webster defines communication as a process by which information is exchanged between individuals through a common system of symbols, signs or behavior. Communication is a process of sharing and conveying messages or information from one person to another using different means, medium, context, media, and cultures. There are different ways and terms in which communication can be manifested. It can be through face-to-face, a phone conversation, a group discussion, a meeting or interview, a letter correspondence, a class recitation, and many others. In other words, the basic functions of communication are to achieve understanding or shared meaning and to persuade, inform, entertain and manage relationships. ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION Communication is divided into elements which help us better understand its mechanics or process. These elements are the following: 1. Speaker – the source of information or message 2. Message – the information, ideas, or thoughts conveyed by the speaker in words or in actions 3. Encoding – the process of converting the message into words, actions, or other forms that the speaker understands 4. Channel – the medium or the means, such as personal or non-personal, verbal or nonverbal, in which the encoded message is conveyed 5. Decoding – the process of interpreting the encoded message of the speaker by the receiver 6. Receiver – the recipient of the message, or someone who decodes the message 7. Feedback – the reactions, responses, or information provided by the receiver 8. Context – the environment where communication takes place 9. Barrier – the factors that affect the flow of communication FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNICATION Basically, there are five functions of communication. These are control, social interaction, motivation, emotional expression, and information dissemination. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Control – Communication functions to control behavior. Social Interaction – Communication allows individuals to interact with others. Motivation – Communication motivates or encourages people to live better. Emotional expression – Communication facilitates people’s expression of their feelings and emotions. Information dissemination – Communication functions to convey information. 1|Page Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|18009790 Grade 11: Oral Communication in Context NATURE OF COMMUNICATION 1. Communication is a process. Communication as a process means it is a step by step activity and it is essentially a two-way process that involves the active participation of both the sender and receiver. It is the act or process of using words, sounds, signs, or behaviors to express or exchange information or to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings, etc., to someone else. 2. Communication is much more of an ART than a science. There is no right or wrong way to communicate – no set of absolute rules to be followed but there are underlying principles to guide us into an effective communication. 3. Communication has a sender and receiver. Communication occurs between two or more people acting as the speaker or the receiver of the message. 4. Communication is verbal or non-verbal. Communication can be expressed through written or spoken words (verbal) or actions (non-verbal) of both spoken words and nonverbal actions at the same time. It does involve ideas and emotions that are expressed through signs, symbols and gestures. 5. Communication is inevitable. Inevitability means communication is taking place even when someone does not want or intend to communicate. This “does not want to communicate” feeling of someone actually does communicate something. You cannot avoid communicating even when you do not want to communicate, you are communicating. You are sending a message by the way you smile, or frown, sit or move or by the way you walk or dress up yourself and by your actions. And even when you are sleeping in class, you are communicating that you are either bored or sick or whatever your reasons be! 6. Communication is irreversible. This means that what you have said can never be unsaid. Irreversibility happens the very minute you click the “OK” button for a comment or post on your social media and that it would be too late to take it back when a lot of people have already reacted, and commented to it. The same thing when you perhaps throw a hurting or offensive word to your enemy because of your anger so we must be careful and choose the appropriate words to say before saying them. 7. Communication is Unrepeatable. Unrepeatability means that an act of communication can never be duplicated. We may say the same thing over and over again but the effect of what you said the second or third or fourth time will not be the same as the first time you said it. This time let’s take a closer look at the illustration on how the communication process takes place in any given situation. Diagram 1. The Natural Flow of Communication Process TheSp e a k e rge n e r a t e sa n i de a Thes pe a k e re nc ode sa nd i de aorc on v e r t st h ei de a i nt owo r d sora c t i ons Ther e c e i v e rge t st he me s s a ge Ther e c e i v e rd e c ode sor i nt e r pr e t st heme s s a ge ba s e dont h ec ont e x t Thes pe a k e rt r a ns mi t sor s e nd sout ame s s a ge . Ther e c e i v e rs e nd sor p r o v i d e sf e e dba c k 2|Page Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|18009790 Grade 11: Oral Communication in Context Diagram 2. Sheena and Nicko Friendship and Love Story Th eSp e a k e rg e n e r a t e sa ni d e a Sh e e n al o v e sNi c k o , h e r s u i t o r , a saf r i e n d . Th es p e a k e re n c o d e sa n di d e ao rc o n v e r t st h ei d e ai n t o wo r d so ra c t i o n s Sh et h i n k so f h o wt ot e l l h i mu s i n gt h e i rn a t i v el a n g u a g e . Th es p e a k e rt r a n s mi t so rs e n d so u t ame s s a g e . Sh et e l l sh i m, “ Ni c k o , Ma h a l k i t ab i l a n gk a i b i g a n . ” Th er e c e i v e rg e t st h eme s s a g e Ni c k oh e a r swh a t Sh e e n as a y s . Th er e c e i v e rd e c o d e so ri n t e r p r e t st h eme s s a g eb a s e do n t h ec o n t e x t Het r i e st oa n a l y z ewh a t s h eme a n sb a s e do nt h ec o n t e x t a n d t h e i r r e l a t i o n s h i pa n dh ei sh e a r t b r o k e n . Th er e c e i v e rs e n d so rp r o v i d e sf e e d b a c k Hef r o wn sa n dd o e sn o t s a ya n y t h i n gb e c a u s eh ei sh u r t . The table showed the communication process and the communication flow between Nicko and Sheena. Sheena, being the sender, expresses her feelings for Nicko, her suitor, but only as a friend. Nicko, the receiver was hurt upon receiving Sheena’s message. See, this is how simple communication process goes. We actually do this everyday, right? Diagram 3. The Communication Process As you can see in Diagram 3, communication goes through a certain process involving the sender, who is the source of the message, the message, which is the shared information, the receiver, whose function is to decode the meaning of what was received and of course, the feedback, referring to the receiver’s reply to the message. LEARNING TASK 1: Write True if the statement is true. If not, write False. __________________1. Communication is a process. __________________2. The sender decodes the message to be transmitted. __________________3. Channel is a medium of communication. __________________4. Talking to the self can develop one’s self-confidence. __________________5. The receiver interprets the message received. __________________6. Communication can either be written or spoken words. __________________7. The receiver is the source of the message. 3|Page Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|18009790 Grade 11: Oral Communication in Context __________________8. Man cannot survive without communication. __________________9. Communication is a one-way process. __________________10. To seek for clarification, channel is needed. LEARNING TASK 2: Read each item carefully then choose the letter that corresponds to your answer. 1. It is the exchange of thoughts, messages, or information as by speech, signals, writing or behavior. a. communication b. feedback c. language d. message 2. These are considered forms of communication. I. talking clearly II. chewing gum III. sending emails IV. looking bored a. I, II, III, IV b. I, III, IV only c. III, IV, II only d. I only 3. This body language shows that one is listening. a. nodding and making eye contact b. looking out of the window c. turning away from the speaker d. whistling while biting nails 4. It is the sender of the message. a. barrier b. originator c. receiver d. sender 6. It is shown when there is an understanding in the communication. a. Each gets a chance to be the sender and the receiver. b. Each party is able to provide feedback. c. Each party is able to say what they want to without the other person interrupting. d. Each party has different languages. 7. It is the content of the communication. a. jargon b. media c. message d. noise 8. This communication type is characterized by a certain look or gaze. a. non-verbal Communication b. oral Communication c. verbal Communication d. written Communication 9. It is an indication that communication really takes place. a. when the message enters the channel b. when the message leaves the channel c. when the receiver understands the message d. when the sender transmits the message 5. It is a good indication that good communication occurs. a. destructed b. confused c. unreceived d. shared 10. This is to be avoided for effective communication. a. ambiguity b. listening c. politeness d. sharing of activity LEARNING TASK 3: Explain the function, nature and process of communication and list down real example that occurs around you. Write at least a minimum of 20 sentences. Rubrics for the Essay Writing Cr i t e r i a Me c h a n i c s Co n t e n t 5 Out s t a ndi ng Ru l e so f g r a mma r , u s a g e , a n d p u n c t u a t i o na r e f o l l o we d ; s p e l l i n g i sa l l c o r r e c t . Th e r e a r en o t y p o g r a p h i c a l e r r o r s . Al l i d e a sa r e r e l e v a n t t ot h e t o p i c . 4 Ve r ySa t i s f a c t or y F e we r r o r si n g r a mma r , u s a g e , a n dp u n c t u a t i o n ma r k s ; s p e l l i n gi s c o r r e c t . 3 Ad e qua t e So mee r r o r si n g r a mma r , u s a g e , p u n c t u a t i o nma r k s a n ds p e l l i n g . 2 Sa t i s f a c t or y Er r o r si ng r a mma r , u s a g e , p u n c t u a t i o n ma r k sa n ds p e l l i n g . Di s p r o p o r t i o n a t et o l e n g t ha n d c o mp l e x i t yo f p i e c e . F e wi d e a sa r en o t So mei d e a sa r e Mo s t l yo f t h ei d e a s r e l e v a n t t ot h e n o t r e l e v a n t t ot h e a r en o t r e l e v a n t t o t o p i c . t o p i c . t h et o p i c . 1 Uns a t i s f a c t or y Ra t i ng Er r o r si ng r a mma r , u s a g e , p u n c t u a t i o n ma r k sa n ds p e l l i n g ma k ewr i t i n g u n c l e a r . Al l i d e a sa r en o t r e l e v a n t t ot h e t o p i c . T o t a l 4|Page Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|18009790 Grade 11: Oral Communication in Context 1 0 Reference: Oral Communication in Context ADM Sabay, K.G. & Salipande, F.P. (2016). Oral Communication in Context (1st ed.). Philippines: C & E Publishing, Inc. 5|Page Downloaded by Tarik Ibn Ziad (tarikhighschool@gmail.com)