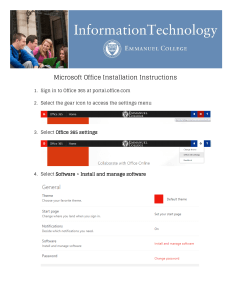
T.O. 2G-T62T-43 TECHNICAL MANUAL OVERHAUL INSTRUCTIONS DEPOT MAINTENANCE LEVEL ENGINE, QUICK START AUXILIARY POWER SYSTEM (QSAS) T-62T-40LC-2 PART NOS. 161331-135 AND 161331-135A (ATOS-HILL) SUNDSTRAND POWER SYSTEMS F33657-79-C-0439 F34601-91-C-1328 DISCLOSURE NOTICE: This information is furnished upon the condition that it will not be released to another nation without the specific authority of the Department of the Air Force of the United States, that it will be used for military purposes only, that individual or corporate rights originating in the information, whether patented or not, will be respected, that the recipient will report promptly to the United States, any known or suspected compromise, and that the information will be provided substantially the same degree of security afforded it by the Department of Defense of the United States. Also, regardless of any other markings on the document, it will not be downgraded or declassified without written approval of the originating United States agency. DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT C: Distribution authorized to U.S. Government agencies and their contractors, administrative and operational use, 15 January 1999. Refer other requests for this document to OO-ALC/417 SCMS, Hill AFB, Utah 84056-5826. WARNING: This document contains technical data whose export is restricted by the Arms Export Control Act (Title 22, U.S.C., Sec 2751 et seq) or the Export Administration Act of 1979, as amended (Title 50, U.S.C., App 2401 et seq). Violations of these export laws are subject to severe criminal penalties. Disseminate in accordance with provisions of DoD Directive 5230.25. HANDLING AND DESTRUCTION NOTICE: Comply with distribution statement and destroy by any method that will prevent disclosure of contents or reconstruction of the document. Basic and all changes have been merged to make this a complete publication Published under authority of the Secretary of the Air Force 15 MAY 1989 CHANGE 26 - 25 FEBRUARY 2013 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 INSERT LATEST CHANGED PAGES. DESTROY SUPERSEDED PAGES. LIST OF EFFECTIVE PAGES NOTE: The portion of the text affected by the changes is indicated by a vertical line in the outer margins of the page. Changes to illustrations are indicated by miniature pointing hands. Changes to wiring diagrams are indicated by shaded areas. Dates of issue for original and changed pages are: Original ........................... 0................ 15 May Change............................. 1............. 15 March Change............................. 2............... 15 June Change............................. 3...........31 October Change............................. 4............. 15 March Change............................. 5................. 1 June Change............................. 6............1 January Change............................. 7................. 1 June Change............................. 8......... 1 December Change............................. 9............15 August Change........................... 10....... 15 December Change........................... 11........ 15 February Change........................... 12..........30 January Change........................... 13............... 15 April Change........................... 14.......15 November 1989 1991 1991 1991 1992 1992 1993 1993 1993 1995 1995 1996 1997 1998 1998 Change........................... 15..........15 January Change........................... 16.........1 November Change........................... 17........ 15 February Change........................... 18............. 31 March Change........................... 19............... 17 April Change........................... 20............... 1 March Change........................... 21................ 28 May Change........................... 22.........4 November Change........................... 23............3 January Change........................... 24............... 21 June Change........................... 25............28 August Change........................... 26........ 25 February 1999 1999 2000 2000 2001 2006 2008 2011 2012 2012 2012 2013 TOTAL NUMBER OF PAGES IN THIS PUBLICATION IS 334, CONSISTING OF THE FOLLOWING: Page No. *Change No. Title ....................................... 26 A - B ...................................... 26 C Blank .................................20 i ..............................................23 ii - iii ......................................25 iv Blank .................................18 v - vi Deleted.........................18 vii .............................................0 viii - x ....................................24 xi Added ................................24 xii Blank................................24 1-1 ..........................................24 1-2 ............................................9 1-3 - 1-4 ...................................0 1-5 - 1-10 ...............................24 1-11 - 1-20 ...............................0 1-21 - 1-23 .............................22 1-24 ........................................16 1-25 ........................................23 1-26 Blank.............................10 2-1 - 2-2 ...................................0 2-3 ..........................................22 2-4 - 2-21 .................................0 2-22 Blank...............................0 3-1 - 3-8 .................................24 3-8A Added............................24 3-8B Blank ............................24 3-9 - 3-14 .................................0 3-15 ........................................20 3-16 ..........................................1 3-17 - 3-23 ...............................0 3-24 ..........................................9 Page No. *Change No. 3-25 - 3-28 ...............................0 3-29 - 3-30 .............................22 3-31 - 3-32 ...............................4 3-33 - 3-54 ...............................0 4-1 ..........................................10 4-2 - 4-4 .................................17 4-5 ..........................................24 4-6 ..........................................17 5-1 - 5-2 .................................23 5-3 - 5-4 .................................22 5-5 - 5-6 .................................11 5-7 - 5-8 .................................24 5-9 ..........................................22 5-10 ..........................................0 5-11 ..........................................6 5-12 - 5-14 .............................22 5-15 ........................................25 5-16 - 5-19 .............................22 5-20 ..........................................0 5-21 ........................................17 5-22 - 5-27 .............................22 5-28 ........................................25 5-29 - 5-33 .............................22 5-34 Blank.............................22 5-35 - 5-38 ...............................0 5-39 ........................................22 5-40 ........................................17 5-41 - 5-43 .............................22 5-44 ........................................16 5-45 - 5-46 ...............................0 5-47 ..........................................9 5-48 ..........................................3 Page No. *Change No. 5-49 - 5-58 ...............................0 5-58A - 5-58D ..........................9 5-59 ..........................................9 5-60 ........................................22 5-60A - 5-60B Added ............22 5-61 - 5-64 ...............................0 5-65 - 5-66 .............................22 5-66A Added..........................22 5-66B Blank ..........................22 5-67 - 5-69 .............................22 5-70 ........................................18 5-70A Added..........................22 5-70B Blank ..........................22 5-71 - 5-72 .............................22 5-72A - 5-72B ........................18 5-73 ........................................22 5-74 ........................................17 5-75 ........................................22 5-76 - 5-82 .............................25 5-83 - 5-85 Added..................25 5-86 Blank.............................25 6-1 ..........................................19 6-2 ..........................................22 6-2A........................................22 6-2B Blank ............................19 6-3 - 6-4 ...................................0 6-5 - 6-6 .................................22 6-7 - 6-8 ...................................0 6-9 - 6-12 ...............................22 6-13 - 6-16 ...............................0 6-17 ........................................22 6-18 ........................................13 *Zero in this column indicates an original page A Change 26 USAF T.O. 2G-T62T-43 LIST OF EFFECTIVE PAGES Page No. *Change No. Page No. *Change No. Page No. *Change No. 6-19 ........................................22 6-20 ..........................................0 6-21 ........................................25 6-22 - 6-33 .............................22 6-34 Blank.............................22 6-35 - 6-36 Deleted ...............22 6-37 ..........................................0 6-38 - 6-40 .............................22 6-41 - 6-44 ...............................0 6-45 - 6-49 .............................22 6-50 ........................................23 6-51 - 6-54 ...............................0 6-55 - 6-56 ...............................3 6-57 - 6-58 ...............................5 6-59 - 6-60 ...............................0 6-61 - 6-62 .............................24 6-62A Added..........................24 6-62B Blank ..........................24 6-63 Added ............................23 6-64 - 6-66 ............................ 26 7-1 - 7-2 ...................................0 7-3 - 7-4 .................................24 7-5 - 7-7 ...................................0 7-8 ............................................8 7-9 - 7-12 .................................0 7-13 ..........................................8 7-14 - 7-18 ...............................0 7-19 - 7-20 ...............................3 7-21 ........................................22 7-22 Blank...............................3 7-23 - 7-24 Deleted .................3 7-25 ..........................................0 7-26 ..........................................8 7-27 - 7-28 ...............................3 7-29 ........................................14 7-30 ........................................24 7-31 ..........................................1 7-32 - 7-34 ...............................8 7-35 - 7-38 ...............................0 7-39 - 7-40 .............................13 7-41 ..........................................8 7-42 ..........................................0 FO-1 .........................................0 FO-2 Blank..............................0 FO-3 .........................................0 FO-4 Blank..............................0 *Zero in this column indicates an original page Change 26 B/(C blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 TABLE OF CONTENTS Section Page LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS ....................................... ii LIST OF TABLES ...................................................... iii SAFETY SUMMARY ................................................ vii INTRODUCTION..................................................... viii I GENERAL INFORMATION ................................... 1-1 1-1 General .................................................. 1-1 1-2 Scope...................................................... 1-1 1-3 Description ............................................ 1-1 1-4 Turbine Assembly................................. 1-1 1-5 Reduction Drive Unit ........................... 1-3 1-6 Combustor Assembly ............................ 1-3 1-7 APU Accessories ................................... 1-6 1-8 Test Cell Adapter Kit ......................... 1-10 1-9 Leading Particulars ............................ 1-20 1-10 Consumable Materials ....................... 1-20 II SPECIAL TOOLS AND TEST EQUIPMENT ........................................................... 2-1 2-1 General .................................................. 2-1 2-2 Special Tools and Test Equipment.......................................... 2-1 III DISASSEMBLY........................................................ 3-1 3-1 General .................................................. 3-1 3-2 Unpacking ............................................. 3-1 3-3 General Disassembly Procedures.......................................... 3-1 3-4 Disassembly of APU ............................. 3-1 3-5 Disassembly of Turbine Assembly .......................................... 3-24 3-6 Disassembly of Reduction Drive Unit ....................................... 3-30 3-7 Disassembly of Combustor Assembly .......................................... 3-52 Section Page IV CLEANING............................................................... 4-1 4-1 General .................................................. 4-1 4-2 Solvent for General Use ....................... 4-1 4-3 Cleaning Procedures............................. 4-1 V INSPECTION, REPAIR, AND REPLACEMENT...................................................... 5-1 5-1 GENERAL............................................. 5-1 5-2 Inspection .............................................. 5-3 5-3 Repair and Replacement .................... 5-58 VI ASSEMBLY .............................................................. 6-1 6-1 General .................................................. 6-1 6-2 General Assembly Procedures.......................................... 6-1 6-3 Assembly of Combustor Assembly ............................................ 6-1 6-4 Assembly of Reduction Drive Unit ......................................... 6-2 6-5 Assembly of Turbine Assembly .......................................... 6-21 6-6 Assembly of APU ................................ 6-49 6-7 Preservation for Shipment and Storage ...................................... 6-61 6-8 General Part Marking....................... 6-62 6-9 UID Supplemental Information ...................................... 6-63 VII TESTING .................................................................. 7-1 7-1 General .................................................. 7-1 7-2 Calculations .......................................... 7-1 7-3 Test Procedures .................................... 7-1 7-4 Troubleshooting Procedures........................................ 7-30 Change 23 i TO 2G-T62T-43 LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS Figure 1 1-1 1-2 1-3 1-4 1-5 1-6 1-7 1-8 1-9 1-10 1-11 1-12 1-13 2-1 3-1 3-2 3-3 3-4 3-5 3-6 3-7 3-8 3-9 3-10 3-11 3-12 3-13 3-14 3-15 3-16 3-17 3-18 3-19 3-20 Title Page Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit ...................x Turbine Assembly and Combustor Housing Assembly................... 1-2 Cutaway View of Reduction Drive Unit ............................................................. 1-4 Lubrication System Schematic ..................... 1-5 Fuel System Schematic ................................. 1-7 QSAS -135 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) (-135A Not Pictured)....................... 1-8 Test Cell Adapter Kit .................................. 1-11 Load Compressor Subsystem Schematic .................................................. 1-13 APU Thermocouple Connections Schematic .................................................. 1-14 Hydraulic Start Subsystem Schematic .................................................. 1-15 Water Dynamometer Subsystem Schematic .................................................. 1-16 Vibration and Dynamometer Load Cell Subsystem Schematic ............. 1-17 Fuel Subsystem Schematic ......................... 1-18 Lubricating Subsystem Schematic .................................................. 1-19 Special Tools and Test Equipment .................................................. 2-6 Removal of APU from Shipping Container .................................................... 3-2 APU ............................................................... 3-4 Engine Hydraulic Starter, Oil Pressure Switch, Turbine Assembly, and Combustor Assembly ........ 3-9 Fuel Control Enclosure Base Assembly ................................................... 3-11 Surge Control Valve, Air Flow Sensor Assembly, and Turbine Ignition Exciter......................................... 3-15 Inlet Housing Manifold and Air Inlet Duct Assembly................................. 3-18 IGV Actuator................................................ 3-20 Hourmeter Junction Box Assembly ................................................... 3-21 Hourmeter Junction Box Assembly Wiring Diagram ...................... 3-23 Turbine Assembly........................................ 3-25 Installation of Turbine Assembly in Rotor Fixture....................... 3-28 Reduction Drive Unit .................................. 3-31 Removal of Bevel Gear Support and Zerol Bevel Gear ............................... 3-37 Removal of Locknut..................................... 3-38 Removal of Locknut..................................... 3-39 Removal of Carrier Assembly ..................... 3-40 Removal of Cover......................................... 3-41 Removal of Ring Gear ................................. 3-43 Removal of Housing Carrier ....................... 3-43 Removal of Locknut..................................... 3-44 ii Change 25 Figure 3-21 3-22 3-23 3-24 3-25 3-26 3-27 3-28 4-1 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 5-6 5-7 5-8 5-9 5-10 5-11 5-12 5-13 5-14 5-15 5-16 5-17 5-18 5-19 5-20 5-21 5-22 5-23 5-24 5-25 5-25.1 5-26 5-27 5-28 5-29 6-1 6-2 6-3 Title Page Removal of Locknut..................................... 3-45 Removal of Bearing ..................................... 3-46 Removal of Zerol Pinion.............................. 3-47 Removal of Accessory Pad Cover................ 3-48 Removal of Intermediate Gear Shaft .......................................................... 3-49 Removal of Ball Bearings ........................... 3-50 Removal of Ball Bearing ............................. 3-51 Combustor Assembly................................... 3-53 Cleaning Combustor Liner............................ 4-6 Inspection of Bearing Aft Carrier....................................................... 5-43 Inspection of Bearing Front Carrier....................................................... 5-44 Inspection of Diffuser Housing ................... 5-45 Inspection of Load Compressor Diffuser ..................................................... 5-46 Inspection of Rotor Shaft ............................ 5-47 Inspection of Seal Plate .............................. 5-47 Inspection of Turbine Nozzle ...................... 5-48 Inspection of Accessory Drive Pinion ........................................................ 5-49 Inspection of Accessory Gear ...................... 5-49 Inspection of Carrier Assembly .................. 5-50 Inspection of Cover...................................... 5-50 Inspection of Gear Planet Set..................... 5-51 Inspection of Hub Ring Gear ...................... 5-51 Inspection of Intermediate Gear ................ 5-52 Inspection of Oil Pump Housing Assembly ................................................... 5-53 Inspection of Pump Drive Gear .................. 5-55 Inspection of Zerol Pinion ........................... 5-55 Inspection of Combustor Housing ..................................................... 5-56 Inspection of Combustor Liner ................... 5-57 Repair of Diamond Knurl ........................... 5-61 Blade Tuning ............................................... 5-62 Repair of Reduction Drive Unit Housing Sleeves........................................ 5-67 Manufacture of Carrier Assembly Sleeves ..................................... 5-68 Manufacture of Housing Liner ................... 5-70 Manufacture of Bevel Gear Support Liners....................................... 5-70A Repair of Bevel Gear Support Housing ..................................................... 5-71 Inspection of Air Inlet Housing ................5-72A Inspection of Load Compressor Wheel Seal ............................................. 5-72B Metal Spray Repair; Diffuser Housing, Part No. 161625 ....................... 5-83 Oil Sump Leak Test Plate .......................... 5-84 Gear Shimming.............................................. 6-3 Determination of Shim Thickness................ 6-4 Installation of Shaft Seal .............................. 6-7 TO 2G-T62T-43 LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS - Continued Figure 6-4 6-5 6-6 6-7 6-8 6-9 6-10 6-11 6-12 6-13 6-14 6-15 6-16 6-17 6-18 6-19 6-20 6-21 6-22 6-23 6-24 6-25 Title Page Installation of Bearings on Straight Drive Shaft .................................. 6-8 Installation of Hub Ring Gear and Retainer ............................................. 6-10 Installation of Bearings on Zerol Bevel Gear ................................................ 6-11 Installation of Backlash Gage .................... 6-13 Backlash and Pattern Requirements............................................ 6-14 Installation of Adapter................................ 6-15 Installation of Shaft Seal ............................ 6-16 Installation of Bearings .............................. 6-17 Installation of Gear Planet Set and Bearings............................................. 6-18 Oil Pump Test Setup................................... 6-20 Balancer Setup (Ref) for Legacy Component-Balance Process.................... 6-26 Balancing Turbine Wheel ........................... 6-27 Balancing Engine Compressor Wheel......................................................... 6-28 Balancing Load Compressor Wheel......................................................... 6-29 Balancing Rotor Shaft................................. 6-30 Installation of Engine Compressor Wheel.................................... 6-31 Balancing Rotor Assembly .......................... 6-32 Balancing Rotor Assembly .......................... 6-32 Clearance Limits ......................................... 6-37 Determination of Shim Thickness .................................................. 6-40 Installation of Bridge Gage......................... 6-41 Determination of Depth .............................. 6-43 Figure 6-26 6-27 6-28 6-29 6-30 6-31 6-32 6-33 7-1 7-2 7-3 7-4 7-5 7-6 7-7 7-8 FO-1 Title Page Installation of Functional Assembly Gage ......................................... 6-44 Determination of Spacer Thickness .................................................. 6-48 Tolerance Specifications.............................. 6-52 QSAS Engine UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161331-135) (Not to Scale) ............................................ 6-64 Surge Control Valve UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161347-1) (Not to Scale)........................... 6-65 IGV Actuator UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161367-1) (Not to Scale) ............................................ 6-65 Fuel Control Assembly UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161676-203) (Not to Scale)....................... 6-66 Hydraulic Start Motor UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161794-1) (Not to Scale)........................... 6-66 APU Installation............................................ 7-2 Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup................. 7-5 Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators........................................... 7-15 Deleted Acceptance Run Test Data Sheet.......................................................... 7-25 APU Acceptance Test Performance .............................................. 7-31 APU Sequence Diagram.............................. 7-32 Decoded BITE Information ......................... 7-33 Electrical Subsystem .................................. FP-1 LIST OF TABLES Number 1-1 1-2 1-3 2-1 5-1 5-2 5-3 Title Page APU Leading Particulars............................ 1-20 Test Cell Adapter Kit Leading Particulars ................................................ 1-21 Consumable Materials ................................ 1-22 Special Tools and Test Equipment List........................................... 2-1 General Physical Conditions ........................ 5-1 Inspection Requirements (APU)................... 5-3 Oil Pump Housing Assembly Dimensional Limits.................................. 5-54 Number 5-4 5-5 5-6 6-1 6-2 7-1 7-2 7-3 Title Page Components Using Abrasive Crocus Cloth, P-C-458.............................. 5-58 Materials Application Table ....................... 5-79 Knurled Sleeve Data .................................. 5-80 Clearance Chart .......................................... 6-33 UID Label Requirements............................ 6-64 Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators........................................... 7-18 Calculations ................................................. 7-27 Troubleshooting ........................................... 7-34 Change 25 iii/(iv blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SAFETY SUMMARY DEFINITIONS. The following definitions apply to WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and NOTES found throughout this publication. warning An operating or maintenance procedure, practice, condition, statement, etc., which, if not strictly observed, could result in injury or death of personnel. caution An operating or maintenance procedure, practice, condition, statement, etc. which, if not strictly observed, could result in damage or destruction of equipment. NOTE An essential operating or maintenance procedure, condition, or statement which must be highlighted. GENERAL PRECAUTIONS. The following are gen- eral safety precautions that are not related to any specific procedure and therefore do not appear elsewhere in this publication. KEEP AWAY FROM LIVE CIRCUITS Operating personnel shall observe all safety regulations at all times. Do not replace components inside the equipment when potentially lethal voltages are present. Turn off system power before making/breaking electrical connections. Regard any exposed connector, terminal board, or circuit board as a possible shock hazard. To prevent electrical shock, make sure no voltage is being applied during removal or installation. If a test connection to energize equipment is required, make the test equipment ground connection before probing the voltage or signal to be tested. RESUSCITATION Personnel working with or near high voltages or hazardous material shall be familiar with modern methods of resuscitation. Such information may be obtained from the Office of Bioenvironmental Health. warning Before using any of the materials specified in this manual, be aware of all handling, storage, and disposal precautions recommended by the manufacturer or supplier. Failure to comply with manufacturer’s or supplier’s recommendations may result in personal injury or disease. Personnel must remain clear of dangerous areas such as intake area, exhaust area, and rotation of turbine blades. Extreme care must be exercised to be sure that all high voltage circuits are completely discharged. Wear eye protection when removing lockwire. Failure to comply may result in injury to personnel. When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. Failure to comply may result in injury to personnel. Voltages used can cause arcing which may result in severe burns. Remove watches, rings, and other jewelry. High/dangerous voltage may cause severe shock or death on contact during check-out of equipment. Use caution and avoid contact with energized components. DO NOT SERVICE OR ADJUST ALONE Personnel shall not under any circumstances reach into or enter any enclosure for the purpose of servicing or adjusting the equipment without immediate presence or assistance of another person capable of rendering aid. vii T.O. 2G-T62T-43 INTRODUCTION 1. PURPOSE OF MANUAL (Figure 1). This manual provides overhaul instructions for the Engine, Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit (QSAS), T-62T40LC-2, part number 161331-135 and 161331135A (herein referred to as APU). These instructions allow personnel to perform the various tasks necessary so that the repaired unit will meet standards for overhauled units. 2JA3-64-3 Hydraulic Starter Overhaul with IPB (Garrett) 33B-1-1 Nondestructive Inspection Methods 6J3-4-112-3 Fuel Control Assembly Overhaul with IPB 2. USE OF MANUAL. A table of contents indicates section and page numbers. Illustrations, tables, and diagrams are located throughout the publication to supplement the text material. A list of illustrations and tables indicates the number, title, and page number. 6J3-8-19-3 Inlet Guide Vane Actuator Overhaul with IPB 6J15-3-160-3 Surge Control Valve Overhaul with IPB 3. CHANGE RECOMMENDATIONS. Recommendations proposing changes to this manual shall be submitted per T.O. 00-5-1. 8D3-3-2-3 Electronic Sequence Control Unit (ESCU) Overhaul 8D3-3-2-4 Electronic Sequence Control Unit (ESCU) Illustrated Parts Breakdown ASTM E 1417 Standard Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination. No Number Assigned Hydraulic Dynamometer Instruction Manual (Kahn Companies) 4. RELATED PUBLICATIONS. The following publications are applicable to the overhaul of the APU and its components: List of Applicable Technical Manuals T.O. Number T.O. Title 00-5-1 AF Technical Order System 00-20-14 Air Force Metrology and Calibration Program 00-25-234 General Shop Practice Requirements for the Repair, Maintenance, and Test of Electronic Equipment 5. ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS. Abbreviations used in this manual conform to MIL-STD-12, except for the following: AFS Air flow sensor AFS. COEF Air flow sensor coefficient 00-85-3 Corrosion Control for Packaging AFS. COR 1-1A-1 General Manual for Structural Repair Air flow sensor correction coefficient CHP Corrected horsepower 1-1A-8 Engineering Manual Series for Aircraft and Missile Repair Structural Hardware CW. FUEL Fuel flow corrected ESCU 1-1A-9 Aerospace Metals-General Data and Usage Factors Electronic sequence control unit EWO Emergency war order 1-1A-14 Installation Practices Aircraft Electric and Electronic Wiring P. BARO Barometric pressure 2G-T62T-44 Engine, Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit System (QSAS) Illustrated Parts Breakdown P. EXDUCT Exhaust duct pressure P. EXIT AFS total pressure P. INLET Inlet pressure viii Change 24 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SMR Bleed air differential pressure at AFS Sourc, Maintenance, and Recoverability T. AFS AFS bleed temperature PB. COEF Bleed pressure coefficient T IN/AVG PB. CORR Bleed pressure corrected Compressor inlet temperature (average) PCD Pressure compressor discharge W FUEL Fuel flow corrected WB. AFS C AFS corrected bleed flow 5. ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS - Continued PASDIF PEX. COEF Pressure exhaust coefficient PIN. COEF Inlet pressure coefficient Change 24 ix T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1. x Change 24 Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit (Sheet 1 of 2) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1. Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit (Sheet 2 of 2) Change 24 xi/(xii blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SECTION I GENERAL INFORMATION 1-1. GENERAL. This manual provides overhaul instructions for the Quick Start Auxiliary Power Unit, T-62T-40LC-2, part number 161331-135 and 161331-135A, (hereafter referred to as APU) at the depot maintenance level. assembly and the aft end of the housing mates with the diffuser housing assembly. The air inlet duct assembly provides ducted air into the inlet. b. 1-3. DESCRIPTION. The APU provides compressed air and generates electrical power for starting aircraft main engines and running aircraft systems. The APU consists of three major assemblies: turbine assembly, reduction drive unit, and combustor assembly. Rotor Assembly. The rotor assembly is a balanced assembly, consisting of the rotor shaft, turbine wheel, engine compressor wheel, load compressor wheel, bearings, and seal plate. The engine compressor wheel and load compressor wheel are driven by the turbine wheel via the rotor shaft. The seal plate prevents leakage of air between the compressor and turbine sections of the APU. c. NOTE The electronic sequence and control unit (ESCU) is not a component of the APU (part number 161331-135 or 161331-135A), but is required for operation of the APU. Load Compressor Scroll. The load compressor scroll houses the load compressor wheel assembly and load compressor diffuser. The load compressor scroll directs compressed air from the load compressor wheel assembly blade tips, through the air flow sensor (AFS). d. Adapter Assembly. The adapter assembly is the structural interface between the turbine assembly and the reduction drive unit. e. Diffuser Housing Assembly. The circularcast diffuser housing assembly is secured to the aft end of the inlet housing assembly. The diffuser housing assembly is externally flanged to permit clamping to the combustor assembly. f. Load Compressor Diffuser. Mounted within the load compressor scroll, is the load compressor diffuser, which has vanes mounted on the forward face. The path formed between the load compressor diffuser and the load compressor scroll, directs the air, compressed by the compressor wheel, into the load compressor scroll. g. Pinion Assembly. The pinion assembly is the coupling between the turbine assembly rotor shaft and the reduction drive unit. 1-2. SCOPE. This manual enables personnel to perform repair and overhaul operations at the depot maintenance level. 1-4. TURBINE ASSEMBLY (FIGURE 1-1). The turbine assembly consists of a single-stage centrifugal load compressor, joined by a common shaft with an engine compressor wheel and turbine wheel. The major components of the turbine assembly consist of the inlet housing assembly, rotor assembly, load compressor scroll, adapter assembly, diffuser housing assembly, load compressor diffuser, pinion assembly, magnetic pickup, forward and aft bearing carriers, manifold assembly, turbine nozzle assembly, and inlet guide vanes: a. Inlet Housing Assembly. The inlet housing assembly is a contoured, cylindrical aluminum casting with dual radial inlets for air flow to the powerhead section (turbine wheel assembly, engine compressor wheel assembly, and combustor assembly) and to the load compressor section (load compressor wheel assembly, load compressor scroll, and inlet guide vanes). The flanged forward end of the housing mates with the adapter Change 24 1-1 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-1. 1-2 Turbine Assembly and Combustor Housing Assembly TO 2G-T62T-43 h. Magnetic Pickup. The magnetic pickup is mounted in the adapter assembly, to provide a speed sensing input to the ESCU. i. Bearing Carriers (forward and aft) (not shown). The forward bearing carrier provides an interface between the reduction drive unit adapter assembly, the front ball bearing, and the rotor assembly. The aft bearing carrier provides a similar interface for the air inlet housing, the aft ball bearing, and the rotor assembly. j. Manifold Assembly. The manifold assembly is mounted on the bottom of the inlet housing assembly. The manifold assembly provides a collection point for lubricating oil supplied to the aft bearing; returns the oil to the reduction drive unit engine oil sump; and supplies buffer air to the labyrinth seal and oil to the aft housing. k. Inlet Guide Vanes. Seventeen variable inlet guide vanes (IGV) are mounted in the inlet housing assembly on the load compressor side. The IGVs are modulated by the ESCU controlled IGV actuator. This system is used to prevent the APU exhaust gas temperature (EGT) from exceeding specified limits. Mounted with each IGV, is a sector gear which meshes with the IGV drive gear assembly. 1-5. REDUCTION DRIVE UNIT (Figure 1-2). The reduction drive unit reduces the output rotational speed (64,643 rpm) of the rotor assembly, to the speeds necessary to drive the APU accessories and APU-driven equipment. The reduction drive unit consists of the housing, engine oil sump assembly, gears, and bearings. a. Housing. The housing is a machined magnesium casting. The APU lubrication system (figure 1-3), consisting of an oil pump, oil filter, by-pass valve, and associated lubrication components, is located in the housing. The oil filter consists of a valve housing and an oil filter element. The by-pass valve housing assures lubrication of the APU if the oil filter element becomes clogged or the oil is extremely cold. The oil filter element is a 10-micron (nominal) throwaway type element. b. Engine Oil Sump Assembly. The engine oil sump assembly is attached with a quick release V-clamp to an external flange on the bottom of the reduction drive unit housing and is sealed with an O-ring. Mounted in the bottom of the engine oil sump assembly is the high oil temperature switch, which is a thermal switch that senses high oil temperature; provides an input to the ESCU; and shuts the APU down if oil temperature exceeds 275 ±5°F. Located at the bottom of the engine oil sump assembly is the magnetic-drain plug, which serves as a low point drain for the lubrication system and a collection point for ferrous (iron) particles that may be present in the lubrication system. c. Gears. The input pinion, splined to the rotor shaft, drives three planetary gears (gear planet sets) mounted in the stationary carrier assembly. The gear planet sets drive the ring gear. The ring gear is splined to a hub ring gear, which is keyed onto the aft end of the main drive shaft. A Zerol bevel pinion on the main drive shaft meshes with a Zerol bevel gear which is secured to the accessory drive pinion. The accessory drive pinion drives the pump drive gear and the intermediate gear, which in turn drives the accessory gear. d. Bearings (not shown). All gears and shafts, with the exception of the pump drive gear, are supported by ball bearings. Lubrication of the gears and bearings is by oil jets and air-oil mist. 1-6. COMBUSTOR ASSEMBLY (Figure 1-1). The combustor assembly consists of the combustor housing, combustor liner, and fuel system components. 1-3 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-2. Cutaway View of Reduction Drive Unit 1-4 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-3. Lubrication System Schematic Change 24 1-5 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 a. Combustor Housing and Combustor Liner. The combustor assembly is an annular, air atomizing type, consisting of the combustor housing and combustor liner. An external flange at the forward end of the combustor housing mates with an external flange on the aft end of the diffuser housing. The combustor assembly is secured to the diffuser housing by a V-band clamp that fits over the flanges. The outer wall of the combustor liner fits over the outer aft end of the turbine nozzle. The mating of the combustor housing inner wall with the inner aft end of the turbine nozzle, forms a conical exhaust duct for the flow of exhaust gases, as they leave the turbine portion of the rotor assembly and flow out of the APU. a. Fuel Control Assembly. The fuel control assembly, in conjunction with the ESCU, provides automatic control of acceleration and governing of APU fuel requirements. The fuel control assembly is a self-contained unit, consisting of a single-element, positivedisplacement, gear-type pump, and fuel control. The fuel control assembly includes an electronic servovalve, which meters fuel to the fuel manifold in direct proportion to a 0100 mA electrical input signal from the ESCU. Two solenoid valves are installed on the fuel control body. The fuel valve supplies fuel to the fuel nozzle during APU starting, while the main fuel valve supplies fuel to the fuel manifold once the APU has achieved 5 percent rated speed. b. Fuel System Components (Figure 1-4).After starting, fuel for the combustor assembly is supplied through an external circular fuel manifold assembly. A port located at the 6 o’clock position in the combustor housing provides a fuel drain. b. Ignition Cable. The ignition cable connects the turbine ignition exciter to the igniter plug. The ignition cable is a shielded high tension lead, that carries pulsating high voltage, low amperage current from the turbine ignition exciter to the igniter plug. c. Turbine Ignition Exciter. The turbine ignition exciter box is mounted at the 5 o’clock position on the combustor housing assembly, from aft looking forward. The turbine ignition exciter box provides a high energy spark through the igniter plug for fuel ignition. The turbine ignition exciter is a capacitive discharge type unit. Input voltage is 1430 Vdc. (1) Fuel Manifold Assembly (Figure 1-5). The combustor assembly provides six bosses for mounting the six fuel manifold nozzles, which are equally spaced at 60o intervals around the combustor housing. The fuel manifold assembly provides six streams of fuel into the venturi tubes that direct fuel into the aft end of the combustor liner. (2) Fuel Nozzle. The fuel nozzle is mounted at the 2 o’clock position on the combustor housing looking aft. The fuel nozzle provides a fine conical spray of atomized fuel for initial APU start. Fuel to the fuel nozzle is activated at 5 percent rated speed and cuts off at 70 percent rated speed. 1-7. APU ACCESSORIES (FIGURE 1-5). APU accessories, supplied with the APU, include the fuel control assembly, ignition cable, turbine ignition exciter, igniter plug, junction box hourmeter assembly, oil pressure switch, fuel purge valve, air filter, engine hydraulic starter, surge control valve, IGV actuator, air flow sensor, and oil cooler. 1-6 Change 24 Output voltage to the turbine igniter plug is 5 kilovolts. The turbine ignition exciter has an input connector for electrical power supply and an output connector for attaching the ignition cable. d. Igniter Plug. The igniter plug is mounted at the 10 o’clock position in the combustor housing assembly, looking forward. The igniter plug is a surface gap shielded type plug, that provides for initial fuel ignition during APU starting. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-4. Fuel System Schematic Change 24 1-7 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-5. 1-8 Change 24 QSAS -135 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) (-135A Not Pictured) (Sheet 1 of 2) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-5. QSAS -135 Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) (-135A Not Pictured) (Sheet 2 of 2) Change 24 1-9 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 e. Junction Box Hourmeter Assembly. The junction box hourmeter assembly is mounted on the right side of the fuel enclosure base assembly looking aft. The junction box contains two hourmeters (normal APU operating hours and emergency war order (EWO) operating hours), an events counter (APU starts), two terminal boards, and an electrical connector. f. Oil Pressure Switch. The oil pressure switch senses low APU oil pressure. It provides an input to the ESCU, which shuts the APU down if oil pressure drops below 6 (±1) psig after the APU reaches 65 percent rpm, or if the switch is closed (shorted) on start. g. Fuel Purge Valve. The fuel purge valve is an electrically operated solenoid valve. The fuel purge valve, in conjunction with the purge restrictor tee assembly, is connected via tube assembly to the fuel control assembly, fuel nozzle, and the fuel manifold assembly. When an APU stop is initiated, a signal from the ESCU opens the fuel purge valve, which allows pressure compressor discharge to purge fuel from the fuel manifold assembly. The purge restrictor tee assembly allows purging of the fuel nozzle after fuel shutoff. h. Air Filter. The 20-micron air filter is located on the left side of the APU looking aft. The air filter removes particulate matter from the control air used to operate the IGV actuator and surge control valve. i. Engine Hydraulic Starter. The engine hydraulic starter is mounted on the right side of the reduction drive unit looking aft. The engine hydraulic starter provides cranking torque for initial rotation of the APU. The engine hydraulic starter incorporates an overrun clutch to disengage the engine hydraulic starter, when APU rotational speed exceeds engine hydraulic starter rotational speed. The clutch case is internally drained, but maintained at 30 (±5) psig by means of a self-contained pressurizing valve. A drain port in the bottom of the case allows fluid to drain to the enclosure reservoir. A fill port on the top of the case is used to service the starter after installation. j. Surge Control Valve. The surge control valve is located above the right side of the combustor assembly looking aft. The valve is pneumatically actuated and electronically controlled. The surge control valve is activated 1-10 Change 24 by a 30-80 psi air supply, from the powerhead compressor and controlled by an electronic signal from the ESCU. The surge control valve prevents the APU from surging when no aircraft demand is present. The valve will open with loss of signal and/or loss of supply pressure. k. IGV Actuator. The IGV actuator is located on the load compressor scroll and is a pneumatically actuated, electronically controlled servomotor. The IGV actuator controls the opening and closing of the load compressor inlet guide vanes. The IGV actuator is powered by a 30-80 psi air supply from the powerhead compressor and controlled by an electronic signal from the ESCU. The IGV actuator is connected to the inlet guide vanes through a link which drives a ring gear. As the IGV actuator shaft extends, the ring gear rotates closing the inlet guide vanes. When the IGV actuator shaft is fully retracted, the inlet guide vanes are open. l. Air Flow Sensor. The Air Flow Sensor (AFS) is mounted on the outlet side of the load compressor scroll. Two pneumatic probes, P EXIT and P NOZZLE, are installed in the AFS housing. These probes provide pneumatic pressure to the P EXIT and P NOZZLE transducer on the ESCU. A remote temperature sensor, installed in the AFS, measures bleed air temperature and provides a signal to the ESCU. m. Oil Cooler. The oil cooler is mounted to the accessory drive housing and is used to eliminate ‘‘hot oil’’ shutdowns. 1-8. TEST CELL ADAPTER KIT (FIGURE 1-6). The Test Cell Adapter Kit (hereafter called adapter kit), part number 164650-100, consists of those components necessary to facilitate starting, controlling, and monitoring the APU, when testing is being accomplished in the test cell facility. The adapter kit consists of the APU cart and the following subsystems: load compressor subsystem, engine subsystem, exhaust subsystem, hydraulic start subsystem, dyna- TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-6. Test Cell Adapter Kit 1-11 TO 2G-T62T-43 mometer subsystem, electrical subsystem, vibration measurement subsystem, fuel system subsystem, and lubricating subsystem. For installation procedures of the adapter kit, refer to Section VII - Testing. a. Load Compressor Subsystem (figure 1-7). The load compressor subsystem provides a means of exhausting the output air generated from the APU's load compressor section. There are two separate paths. One path exhausts bypass air when the by-pass valve is open. The adapter connects to the outlet port of the by-pass valve to the depot exhaust duct. The other path routes load compressor air to the facility ducting. The adapter simulates aircraft ducting volume and attaches to the APU duct assembly. The load compressor subsystem consists of four hose and transducer assemblies. Two assemblies mate the air flow sensor (AFS) at the P exit and P nozzle ports, to the transducer ports on the ESCU, located inside the cart. The pressure transducer on the P exit port has an operating range of 0-100 psig. The other pressure transducer on the P nozzle port has an operating range of 0-15 psid. The other two assemblies measure APU duct inlet and exit pressures. An accumulator tank (approximately 10 cubic feet volume) simulates aircraft pneumatic system volume. b. Engine Subsystem. The engine subsystem contains drain containers, container receptacles, and hardware to collect combustor, fuel control, hydraulic starter, and gearbox spent fluids. The subsystem also contains a 500 ml graduated cone to measure oil leakage or oil expended from the reduction drive unit vent. c. Exhaust Subsystem. The engine exhaust subsystem consists of the following four sections clamped together: (1) Adapter section mates with the APU combustor assembly. (2) Exhaust gas temperature (EGT) thermocouple assembly (figure 1-8) containing six individually read chromealumel EGT probes with connectors. 1-12 (3) Bellows assembly between the adapter and tailpipe sections to compensate for thermal expansion. (4) Tailpipe section connects to the exhaust stack. d. Hydraulic Start Subsystem (figure 1-9). The hydraulic start subsystem controls hydraulic fluid to the engine hydraulic starter. e. Dynamometer Subsystem (figure 1-10). The dynamometer subsystem is used to apply a shaft load to the APU reduction drive unit being tested. The dynamometer bolts to the output pad on the reduction drive unit and is required to absorb 0-50 hp. Facility water is provided to this subsystem at 50 ±2 psig. f. Electrical Subsystem (FO-1). The electrical subsystem contains an ESCU, three wiring harnesses, and junction box with annunciator indicators. The electrical subsystem interfaces with other subsystems. g. Vibration Subsystem (figure 1-11). The vibration subsystem provides for independent measurement of the vibration of the APU and of the reduction drive unit. The vibration subsystem consists of an engine accelerometer, gearbox accelerometer and mounts, and individual coaxial cables for connecting the accelerometers to the fluid panel connection point. h. Fuel Subsystem (figure 1-12). The fuel subsystem provides for switching from JP-4 type fuel to preservation oil, to facilitate APU preservation upon completion of testing. JP-4 type fuel is regulated by the facility to 5-40 psig and preservation oil is gravity fed from the wall mounted preservation oil box. i. Lubricating Subsystem (figure 1-13). The lubricating subsystem consists of a reduction drive unit temperature probe, which measures the APU oil sump temperature. An oil to water heat exchanger is provided for cooling the oil using facility cooling water. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-7. Load Compressor Subsystem Schematic 1-13 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-8. APU Thermocouple Connections Schematic 1-14 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-9. Hydraulic Start Subsystem Schematic 1-15 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-10. Water Dynamometer Subsystem Schematic 1-16 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-11. Vibration and Dynamometer Load Cell Subsystem Schematic 1-17 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-12. Fuel Subsystem Schematic 1-18 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 1-13. Lubricating Subsystem Schematic 1-19 TO 2G-T62T-43 1-9. LEADING PARTICULARS. Leading particulars for the APU are listed in Table 1-1. Leading particulars for the test cell adapter kit are listed in Table 1-2. 1-10. CONSUMABLE MATERIALS. Consumable materials required to accomplish prescribed maintenance are listed in table 1-3. c- Table 1-1. APU Leading Particulars Dimensions: 38.77 in. 24.00 in. 27.90 in. Length .................................................. Width .................................................. Height ................................................. Weight, .........,...,........,...,..,....... .,.., maximum Maximum 64,643 rpm ......................................... Rated engine speed ................................. shaft output power 190.0 lbsdry) 198.0 Ibs (wet) 40 Hp Rated axial output shaft speed ................................. 8,080. rpm Fuel MIL-T-5624, ...................................................... fuels ............................................. Lubricating oil .............................................. Lubrication system filtration Alternate Standard operating Operating Air delivery Maximum [59°F, day .............. ...... ...,.... Maximum specific fuel consumption for standard day conditions Speed variation at constant Speed variation during on/off load .......... ....... ....... ....,.................. ....... load transients Vibration at rotor frequency operating under pneumatic load and/or shaft load 1-20 10 micron disposable (nominal) type filter 14.696 psia (sea level)]: ........................................ EGT for standard JP-5 JP-7 JP-8 MIL-L-7808 ........ ,....................,.... temperatures rates MIL-T-5624L, MIL-T-38219, MIL-T-83133, ................................... conditions JP-4 .................... ................... ..... -40 to 120°F 42.5 lb/min. at 57.5 psia (ap 0.098 minimum) P Less than 1320°F for more than 10 sec. 252 lb/hr. rrected to sea level. 59°F Less than ±0.5% Less than ±2% Less than 5 Gs T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 1-1. APU Leading Particulars - Continued Vibration at rotor frequency when operating under no pneumatic load (IGV’s closed) no shaft load ......................................................... Less than 10Gs Oil pressure at 100% rotor speed........................................................ Greater than 18 psig Engine oil sump temperature.............................................................. Not to exceed 275oF Exhaust gas temperature .................................................................... Not to exceed 1375 (±12)oF APU oil consumption (measured at reduction drive unit oil vent by 500 ml graduated cylinder) ............................................................ Less than 20 cc/hr Compressor discharge pressure .......................................................... 45 psig (nominal) Table 1-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Leading Particulars Hydraulic fluid ..................................................................................... MIL-H-5606 Filtration: High pressure ................................................................................. Non-bypass, 3 micron, Beta (β) 3 filter = 200 Low pressure .................................................................................. Non-bypass, 3 micron, Beta (β) 2 filter = 200 Breather ................................................................................................ 3 Micron Hydraulic supply .................................................................................. 3000 +150, -300 psig Hydraulic pressure transducer (hydraulic and nitrogen) ................. 0-3000 psig Hydraulic accumulator, nitrogen precharge (no hydraulic charge) 500 (±5) psig AFS pressure transducer (differential)............................................... 0-15 psid AFS pressure transducer (total).......................................................... 0-100 psig Dynamometer: Water supply .................................................................................. Minimum flow rate 350 gal/hr at 50 (±2) psig Seal cooling water .......................................................................... Minimum flow rate to 0.1 gal/ min at 50 (±2) psig Load cell output.............................................................................. 0-300 pounds-force Fuel ....................................................................................................... MIL-T-5624, JP-4 MIL-DTL-83133, JP-8 Fuel boost pressure .............................................................................. 5-40 psig Fuel flow rate capacity ........................................................................ Minimum 350 pound/hr Preservation oil .................................................................................... MIL-L-6081, grade 1010 Oil cooler supply water ........................................................................ Minimum flow rate 20 (±10) psig, 7 gal/min Change 22 1-21 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 1-3. Consumable Materials Specification/ Manufacturer Nomenclature Use Acetone O-A-51 Cleaning braze repair Adhesive MIL-A-46106 Attach gaskets Adhesive MIL-A-46146, type III Attach ID plate Adhesive/sealant RTV-3145 Attach silicone pads Adhesive, silicone GE P/N PSA529/SRC18 or equiv (NSN 8040-00-097-6524 Adhesive, structural EC-1386 Install housing liner Alcohol, ethyl O-E-760, type III Freeze gear planet set Alloy, brazing AWS A5.8-62T BAU4 Repair fuel manifold Aluminum oxide, coarse-grit Metrolite, type C (FSCM 39918) Dry blasting Aqueous cleaner MIL-C-87937 Ultrasonic cleaning tank Bead, glass MIL-G-9954 Vapor blasting Blast medium MB-3, type IV, class 2, MIL-A21380B Vapor blasting Brush, soft-bristle MIL-B-15319, type I, class 2 Clean titanium and aluminum alloy parts Caps and plugs MS90376-8R, -10R, -12R, -14R, -16R, -16Y, -18Y, -20R, -20Y, -22R, -22Y, -24R, -24Y, -28Y Protect against dust and moisture Caps 1/8 SC, FSCM 95760 Protect fuel manifold tips Cheesecloth CCC-C-440 Clean aluminum parts Cleaner, alkaline TT-C-490C Clean steel parts Cleaner, alkaline MIL-C-87936 Clean titanium parts Cleaner, solvent P-D-680, type II or III Degrease turbine nozzle, seal plate, turbine wheel Cloth, abrasive crocus P-C-458 Remove nicks, burrs, scratches, surface blemishes, and scoring Cloth, lint-free MIL-C-85043, type II Dry components Coating, black oxide MIL-C-13924, class I Coat replacement sleeves Coating, chemical conversion MIL-C-81706, type III Treat exposed surfaces 1-22 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 1-3. Consumable Materials - Continued Specification/ Manufacturer Nomenclature Use Compound, aircraft surface cleaning MIL-C-43616 Clean steel parts Compound, alkaline cleaning P-C-436 Clean aluminum alloy parts Compound, antiseize MIL-A-907 Apply on components Compound, corrosion preventive MIL-C-16173, grade 4 Preserve steel parts Compound, gear marking No. 89 or Dykem Blue Mark teeth of accessory drive pinion Compound, sealing MIL-S-45180 Coat magnetic pickup threads Compound, thread-locking MIL-S-46163A Apply to screw threads Corrosion inhibitor Rustlick 606 Corrosion prevention of rotor assembly Cushioning, cellulosic PPP-C-843 Wrap APU Desiccant MIL-D-3464 Absorb moisture in container Fluid, assembly RT-403A, No. 1 (FSCM 77988) Lubricate parts Change 22 1-23 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 1-3. Consumable Materials - Continued Specification/ Manufacturer Nomenclature Use Fluid, calibrating MIL-C-7024, type II Test fuel nozzle and fuel manifold Fluid, hydraulic MIL-H-5606 Precharge accumulator Fuel MIL-T-5624, JP-4, MIL-T-5624L, JP-5, MIL-T-38219, JP-7, MIL-T-8133, JP-8, Operate APU Gloves, thermally insulated MIL-G-440, type II (HH-G-450D) Handle components Grain, sof t abrasive MIL-G-5634 Vapor blasting Ice, dry BB-C-104 Freeze components Indicator, humidity MIL-I-8835A6 Check humidity in shipping container Lockwire MS20995C20, MS20995C32 Safety wire components Lubricant, solid MIL-L-8937 Coat threads of shaf t Mat, non-metallic MIL-A-9962 Clean aluminum alloy parts Material, barrier MIL-B-131, class III Wrap APU Material, braze f iller BNI-2, AMS 4777 Cover braze cracks Material, titanium bar 6A1-4V, AMS 4996-84 Manufacture sleeve Nitrogen, liquid MIL-P-27401 Freeze components Nitrogen, technical BB-N-411, type I, class 1, grade B Precharge accumulator Oil Grade S 150 Flow test oil jet cartridges Oil, lubricating MIL-L-7808, MIL-L-23699 Lubricate components Oil, non-carbon penetrating VV-P-216 Loosen igniter plug grommet Oil, preservation MIL-L-6081, grade 1010 (NSN 9150-00-273-2388) Test and preserve components Paint, epoxy polyamide MIL-C-22750, class I, type I Paint component Powder, welding Metco 601 NS (FSCM 78253) Apply abradable coat and plasma spray Powder, welding Metco 450 Apply abradable coat and plasma spray. Primer, epoxy MIL-P-23377, type I, class C or N Restore f inish Primer, water borne epoxy MIL-P-85582, type I, class 2 Restore f inish Rod, welding MIL-R-5031, class 7 Weld cracks or holes 1-24 Change 16 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 1-3. Consumable Materials - Continued Specification/ Manufacturer Nomenclature Use Sealant MIL-C-81733, type III (NSN 9Q8030-00-008-7196) Treat repair areas Sealant MIL-S-22473, grade A Apply to sleeve Shot AB Glass shot peening Soap, silicate MIL-M-7752 (NSN 8520-00-228-0598) Clean aluminum and magnesium parts Solder QQ-S-571, type Sn63 Solder/unsolder wires Stone, abrasive SS-S-736 Polish surface Stop-off Nicrobraze green Prevent excess flow of braze material Tape, masking MIL-T-21595 Mask surfaces for vapor blasting Tape, pressure sensitive MIL-T-22085, type II Mask ports, outlets, and fittings Water, deionized Local purchase Mix alkaline cleaning solution Water, distilled Local purchase Mix alkaline cleaning solution Tape, Tesa Tesa Secure 6973 PV6 Change 23 1-25/(1-26 Blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 SECTION II SPECIAL TOOLS AND TEST EQUIPMENT 2-1. GENERAL. Special tools and test equipment required for maintenance of the APU are presented in this section. Equivalent items may be used if the recommended tool/test equipment is not available. 2-2. SPECIAL TOOLS AND TEST EQUIPMENT. Special tools and test equipment required for maintenance of the APU are listed in table 2-1 and illustrated in figure 2-1. Table 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment List Tool/Equipment Figure/Index Number Number FD-100 2-1-1 Nomenclature Use and Application Eddy current tester Detect flaws in components HBH-003 -2 Balancer Balance rotor assembly M93 -3 Accelerometer Used with vibration analysis tool, ST63939 (see index no. 13) APU service cart Mount APU build stand MIL-T-16549G Not illus. SD340 -4 Spectrum analyzer Used with vibration analysis tool, ST63939 (see index, no. 13) ST60051 -5 Bridge gage Measure dimension ST60811 -6 Backlash gage Check backlash gears ST60880 -7 Wire gage Measure load compressor wheel ST61186-06 -8 Ring gage Check clearance between diffuser and engine compressor wheel ST61404 -9 Inspection fixture Inspect and qualify final assembly of combustor assembly ST62880 -10 Inspection fixture Check alignment and critical details ST63929 -11 Assembly function gage Determine shim thickness ST63931 -12 Functional gage assembly Pre-gage stacking height of load compressor wheel ST63939 -13 Vibration analysis tool Blade tuning ST64016 -14 Rotor assembly inspection fixture Inspect run-out of rotor assembly ST64037 -15 Eddy current holder Hold component 2-1 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment List - Continued Tool/Equipment Number Figure/Index Number Nomenclature Use and Application ST64038 or LKG 05 -16 Tension tester Test movement of gears ST70137 -17 Rotor fixture Hold turbine assembly ST70170 -18 Puller Removal of support and gear ST70234 -19 Puller Removal of accessory pad cover ST70235 -20 Puller Removal of shaft ST70236 -21 Arbor plate Installation/removal of components ST70237 -22 Bushing Removal of pinion and ring ST70238 -23 Bushing Removal of bearings ST70241 -24 Spanner wrench Installation/removal of locknuts ST70242 -25 Adapter Torquing nuts ST70243 -26 Spanner wrench Torquing ST70254 -27 Holding bar Used with backlash gage, ST6081 1 ST70266 -28 Holding fixture Hold component to torque ST70267 -29 Holding fixture Hold gear to torque ST70277 -30 Bearing remover holder Removal of bearings ST70278 -31 Holding fixture Support reduction drive unit housing ST70281 -32 Driver Installation of bearings ST70282 -33 Driver installation of bearings ST70283 -34 Driver installation of hub ST70284 -35 Disassembling tool Compress retaining ring ST70286 -36 Arbor plate and driver Installation/removal of bearings ST70370 -37 Assembly fixture Hold reduction drive unit for assembly 2-2 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 2-1. Tool/Equipment Number Special Tools and Test Equipment List - Continued Figure/Index Number Nomenclature Use and Application ST70414 -38 Driver set Installation of bearings ST70433 -39 Oil filter cap assembly fixture Installation of spring and pin ST71078 -40 Stretch tool Stretch shaft ST71186 -41 Turbine wheel puller Remove turbine wheel ST71191 -42 Wrench Torquing ST71201 -43 Combustor puller Installation/removal of combustor assembly ST71206 -44 Assembly build stand Hold APU for assembly/disassembly ST71207 -45 Arbor press guide Installation/removal of labyrinth seal ST71209 -46 Pinion installation and disassembly tool Installation/removal of pinion ST71214 -47 Assembly check gage plate Check dimensions ST71217 -48 Assembly check gage plate Use with bridge gage, ST60051 ST71219 -49 Load compressor rotor assembly tooling Press load compressor wheel onto rotor shaft ST71231 -50 Bearing bevel gear removal tool Remove bearings ST71232 or local manufacture -51 Containment ring Hold dry ice ST71234 -52 Rotor assembly tool Assist in rotor assembly ST71235 -53 Assembly clearance gage Measure dimensions ST71236 -54 Load compressor wheel assembly Support load compressor to shoulder -55 Turbine stud torque wrench Remove and torque stud 18D8325-1 (Alt to ST71236) ST71238 Change 22 2-3 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 2-1. Tool/Equipment Special Tools and Test Equipment List - Continued -. Figure/Index Number Nomenclature ST71 240 or TM 70017 -56 Bearing installation ST80043 -57 Balancing ST8021 1 -58 Oil filter cap removal tool Remove by-pass ST80472 -59 Balancing Hold rotor shaft for balancing ST80608 -60 Balance arbor Assist in balancing parts ST8061 6 -61 Balance arbor Assist in balancing parts ST8061 7 -62 Balance arbor Assist in balancing parts ST90030 or TM 90027 -63 Adapter Installation of oil pump on flow bench ST901 33 -64 Driver Press bearing on gear planet set ST90 142 -65 Driver Installation of bearing and gear planet set ST90288 -66 Puller Removal of carrier assembly cover ST94270 -67 Support fixture Balance rotor assembly ST90671 -68 Bearing assembly ST90682 -69 Mounting ST90684 -70 Retaining plate Removal of carrier assembly cover ST90889-01 -71 Guide tool set Installation of shaft seals ST90889-04 -72 Guide tool set Installation of shaft seals ST91 061 -73 Bearing puller Provide pressure surface for removal of bearings from shaft Number Use and Application tool of pinion Used with balancing ST80472 cradle tool cradle block Installation tool Installation tool cradle, housing valve of bearings Hold shim ST9 1064 -74 Flaring fixture Flaring igniter plug grommet ST92300 -75 Flow check fixture Check spray flow of fuel nozzle 2-4 -. w TO Table 2-1. Tool/Equipment Number Figure/lndex Number Special Tools and Test Equipment 2G-T62T-43 List - Continued Use and Application Nomenclature Remove shaft seal ST93057 -76 Seal puller ST93950 -77 Load compressor tool clearance Check for axial load compressor to scroll clearance ST93951 -04 -78 Load compressor restrainer wheel Hold load compressor ST93975 -79 Spanner ST94276 -80 Balancing support Support part while balancing ST9428 1 -81 Balancing support Support balancing ST94409 -82 Lifting fixture ST94426 -83 Carrier bearing 163000 -84 Eddy current master inspection Detect flaws in components 164101-100 -85 Fuel manifold flow bench Test fuel nozzle and fuel manifold 164650-l 7-2 Test cell adapter 166471-100 -86 Shipping 166819-100 -87 Engine support 167147-l -88 APU cart Hold engine in test cell Local manufacture or ST78602 -89 Driver Press seal on load compressor wheel Local manufacture or ST78603 -90 Holder Hold load compressor wheel during seal installation Local manufacture -91 Bushing Support rotor shaft during balancing Layout table Making measurements 00 00 No part no. Not illus. wheel Torquing wrench Lift APU engine puller kit container kit Remove bearing Test APU in test cell Store or ship APU Install APU on test cell cart on APU 2-5 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 1 of 16) 2-6 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 2 of 16) 2-7 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 3 of 16) 2-8 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 4 of 16) 2-9 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 5 of 16) 2-10 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 6 of 16) 2-11 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 7 of 16) 2-12 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 8 of 16) 2-13 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 9 of 16) 2-14 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 10 of 16) 2-15 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 11 of 16) 2-16 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 12 of 16) 2-17 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 13 of 16) 2-18 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 14 of 16) 2-19 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 15 of 16) 2-20 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 2-1. Special Tools and Test Equipment (Sheet 16 of 16) 2-21/(2-22 blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SECTION III DISASSEMBLY 3-1. GENERAL. This section contains information necessary to disassemble the APU, including the turbine assembly, the reduction drive unit, and the combustor assembly. The extent of disassembly should be determined by preliminary visual inspection and test. No part should be disassembled unless it requires servicing, or unless it must be removed to allow access to other parts requiring replacement or servicing. 3-2. UNPACKING. This section contains procedures for removing the APU from the shipping container, SPI NO. F01-345-3402 (86, Figure 2-1). Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to Figure 3-1. WARNING Two maintenance personnel are required to remove APU from shipping container. Failure to comply could result in injury to personnel. a. Remove lag screws (1) and washers (2) securing cover (3) to skid (4). b. Remove cover (3) from skid (4). c. Remove masking tape and cellulosic cushioning from around APU. d. Remove barrier material from around APU. e. Install lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, Figure 21), in forward and aft eye bolts on APU. f. Hook suitable hoist (minimum 2,000 lbs lifting capacity) to lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, Figure 2-1), and take up slack. g. Remove bolts (5, Figure 3-1), nuts (6), and washers (7) securing APU to supports on skid (4). h. Lift APU from skid (4). 3-3. GENERAL DISASSEMBLY PROCEDURES. The following general disassembly procedures shall be observed during disassembly. a. Clean all parts per Section IV - Cleaning. b. Place all parts in order of disassembly on a flat, clean surface to avoid loss or disarrangement. Place small parts in suitable containers. c. Carefully observe any specific instructions given. d. Never apply force during removal and installation of parts. If a part is not easily removed, investigate the cause (i.e. alignment or some attaching part being overlooked). e. Always use the proper tool for an operation. f. Do not mix parts from several APUs. 3-4. DISASSEMBLY OF APU. This section contains procedures for removal of accessory parts, tubing, and wiring mounted on the APU. It also covers breaking down the APU into three main subassemblies for individual disassembly outlined in following paragraphs. a. Place assembly build stand, ST71206 (44, Figure 2-1), on APU service cart, Specification MIL-T-16549G. b. Install APU in assembly build stand, ST71206 (44, Figure 2-1), then remove lifting fixture, ST94409 (82). . . NOTE If APU is not being completely disassembled, perform only those steps necessary to accomplish the required maintenance. With the APU mounted on assembly build stand fixture, the APU can be rotated to either the vertical or horizontal position. To facilitate disassembly, rotate APU whenever necessary. c. Tilt APU into a vertical position and remove lockwire from magnetic-drain plug (1, Figure 3-2, detail G). Return APU to horizontal position. d. Place suitable container under fuel lines and oil lines to catch oil and spilled fluid. Change 24 3-1 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-1. 3-2 Change 24 Removal of APU from Shipping Container T.O. 2G-T62T-43 e. e1. f. Remove magnetic-drain plug (1) and selfclosing valve (2), and drain oil from engine oil sump assembly (71). Reinstall self-closing valve (2) and magnetic-drain plug (1). assembly (75, Figure 3-2, detail B). Remove support clamps (7). (5) Remove bolt (1, Figure 3-5, detail A), nut (2), and washer (3), securing support clamps (4) to ignition cable (27) and thermocouple harness (40). Remove support clamps (4). (6) Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail C), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6 and 8) to engine control harness (13, Figure 3-2, detail B), and thermocouple harness (14). Remove two sets of support clamps (6 and 8, Figure 3-2, detail C). (7) Remove bolts (3), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6 and 9) to start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16, Figure 3-2, detail B) and purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19) and to engine control harness (13). Remove support clamps (6 and 9, Figure 3-2, detail C). (8) Remove bolts (10, Figure 3-2, detail C), nuts (4), washers (5), and spacers (11), securing support clamps (6 and 7) to engine control harness (13, Figure 3-2, detail B), purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19), and APU. Remove support clamps (6 and 7). (9) Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail H), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6) to tee to gearbox adapter tube assembly (54, Figure 3-2, detail G), oil pressure manifold housing to reduction drive tube assembly (66), and engine control harness (13). Remove six sets of support clamps (6, Figure 3-2, detail H). (10) Remove bolts (3), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6) to filter to tee PCD air tube assembly (36, Figure 3-2, detail F) and engine control harness (13). Remove support clamps (6, Figure 3-2, detail H). If applicable (-135A APU) remove oil cooler (76, Figure 3-2, detail I), as follows: (1) Disconnect hose assembly, (82, Figure 3-2, detail I), from the ‘‘oil in’’ fitting of the oil cooler. (2) Disconnect hose assembly, (81, Figure 3-2, detail I), from the ‘‘oil out’’ fitting of the oil cooler. (3) Disconnect hose assembly, (82, Figure 3-2, detail I), from the ‘‘oil out’’ fitting of the APU gearbox. (4) Disconnect hose assembly, (81, Figure 3-2, detail I), from the ‘‘oil in’’ fitting on the APU gearbox. (5) Remove left bracket, (86, Figure 3-2, detail I), (cooler end) by removing nut, (92, Figure 3-2, index 1) and bolt (91, Figure 3-2, detail I), and nut (gearbox end) (93, Figure 3-2, index 1). (6) Remove right bracket (85, Figure 3-2, detail I), (cooler end) by removing bolt (91, Figure 3-2, detail I), and nut (92, Figure 3-2, detail I), and nut (gearbox end) (93, Figure 3-2, detail I). (7) Remove top bracket (84, Figure 3-2, detail I) by removing two bolts (90, Figure 3-2, detail I) from oil breather pad of APU gearbox. Remove support clamps as follows: (1) (2) (3) (4) Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail H), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6) to purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19, Figure 3-2, detail B) and engine control harness (13). Remove support clamps (6). Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail H), nuts (4), and washers (5) securing support clamps (6) to purge valve to tee tube assembly (24, Figure 3-2, detail B) and thermocouple harness (14). Remove support clamps (6). Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail E), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (6) to fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20, Figure 3-2, detail B), thermocouple harness (14) and ignition cable (67, Figure 3-2, detail E). Remove support clamps (6). Remove bolts (3, Figure 3-2, detail D), nuts (4), and washers (5), securing support clamps (7) to engine control harness (13) at fuel control enclosure base g. Remove bolt (1, Figure 3-3), self-locking nut (2), and washer (3), securing support clamp (4) to connector mounting bracket (23) and engine control harness. Remove support clamp (4). h. Remove bolts (5, Figure 3-3), nuts (6), and washers (7), securing connector mounting bracket (23) to engine control harness (13, Figure 3-2, detail A). i. Remove tiedown strap (12) from engine control harness (13). Change 24 3-3 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-2. 3-4 Change 24 APU (Sheet 1 of 5) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-2. APU (Sheet 2 of 5) Change 24 3-5 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-2. 3-6 Change 24 APU (Sheet 3 of 5) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-2. APU (Sheet 4 of 5) Change 24 3-7 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-2. 3-8 Change 24 APU (Sheet 5 of 5) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 j. Remove lockwire from all connectors and disconnect connectors on engine control harness (13) and thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15) as follows: (1) Connector mounting bracket, J1. (2) Fuel control enclosure spacer, P2. (3) Hourmeter junction box, P3. (4) Fuel purge valve, P4. (5) Turbine ignition exciter, P302. (6) Low oil pressure switch, P303. (7) Magnetic pickup, P304. (8) High-oil temperature switch, P305. (9) Surge control valve, P306. (10) Ambient temperature, P307. (11) IGV actuator, P308. (12) Air flow sensor, P309. k. Remove engine control harness (13) and thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15). l. Separate thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15) from engine control harness (13) at connectors P8 and P9. m. Install protective plugs on all fuel oil lines and caps on all electrical connectors on engine control harness (13). n. Remove fuel control enclosure base (44, Figure 3-4) and fuel electronic control assembly (33) as follows: (1) Loosen studs (1), springs (2), and washers (3 and 4) securing fuel control enclosure cover (5) to enclosure spacer assembly (18). Remove fuel control enclosure cover. NOTE Do not remove gasket (6) unless loose or damaged. (2) If necessary, remove gasket (6) from fuel control enclosure cover (5). (3) Remove screws (7), self-locking nuts (8), and washers (9), securing fuel electronic harness (16) and gasket (17) to enclosure spacer assembly (18). (4) Remove bolt (10), washer (11), and nut (12), securing support clamp (13) and bracket (14) to fuel electronic harness (16). Remove clamp (13) and bracket (14). (5) Remove tiedown straps (15) from fuel electronic harness (16). (6) Disconnect connectors of fuel electronic harness (16) from fuel electronic control assembly (33). (7) Remove fuel electronic harness (16) and gasket (17) from enclosure spacer assembly (18). (8) Install protective caps on all connectors of fuel electronic harness (16). (9) Loosen studs securing enclosure spacer assembly (18) to fuel control enclosure base (44). Remove enclosure spacer assembly (18) and hourmeter junction box (18, Figure 3-8) as an assembled unit. NOTE Do not remove gasket (19) unless loose or damaged. (10) If necessary, remove gasket (19, Figure 3-4) from enclosure spacer assembly (18) and discard. (11) Remove bolts (20), nuts (21), and washers (22), securing support clamps (23) to enclosure elbow to fuel pump tube assembly (24). Remove support clamps (23). (12) Remove enclosure elbow to fuel pump tube assembly (24) from elbows (25 and 41). (13) Remove elbow (25) and O-ring (26) from fuel electronic control assembly (33). Discard O-ring (26). Install protective cap. (14) Remove tube elbow (27) and main fuel control to elbow tube assembly (28) from nipple (29) in fuel electronic control assembly (33). Install protective caps on main fuel control to elbow tube assembly (28). Change 24 3-8A/(3-8B blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-3. Engine Hydraulic Starter, Oil Pressure Switch, Turbine Assembly, and Combustor Assembly (Sheet 1 of 2) 3-9 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-3: 1. Bolt 2. Self-locking nut 3. Washer 4. Support clamp 5. Bolt (4) 6. Nut 7. Washer (4) 8. Self-locking nut (6) 9. Washer (6) 10. Engine hydraulic starter 11. Gasket 12. Nipple 13. O-ring 14. Self-locking nut (6) 15. Washer (6) 16. Reduction drive cover 17. Gasket 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. Oil pressure switch O-ring Eye bolt Bolt (4) Washer (4) Connector mounting bracket Clamp Check valve (-114 only) O-ring (-114 only) Combustor assembly Seal ring Bolt (6) Turbine assembly O-ring Adapter gasket Reduction drive unit Figure 3-3. Engine Hydraulic Starter, Oil Pressure Switch, Turbine Assembly, and Combustor Assembly (Sheet 2 of 2) 3-10 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-4. Fuel Control Enclosure Base Assembly (Sheet 1 of 2) 3-11 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-4: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Enclosure elbow to fuel pump tube assembly 25. Elbow Stud (22) Spring (22) Washer (22) Washer (22) Fuel control enclosure cover Gasket Screw (4) Self-locking nut (4) Washer (4) Bolt (2) Washer (2) Nut (2) Support clamp Bracket Tiedown strap (4) Fuel electronic harness Gasket Enclosure spacer assembly Gasket Bolt Nut Washer Support clamp Figure 3-4. 3-12 26, 27. 28. 29. 30. 31, 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. Fuel Control Enclosure O-ring Tube elbow Main fuel control to elbow tube assembly Nipple O-ring Bolt (4) Washer (4) Fuel electronic control assembly Engine accessory drive gasket Locknut Elbow O-ring Locknut Washer (2) Washer Elbow Bolt (4) Washer (4) Fuel control enclosure base Gasket Base Assembly (Sheet 2 of 2) TO 2G-T62T-43 (15) Remove nipple (29) and O-ring (30) from fuel electronic control assembly (33). Discard O-ring (30). Install protective cap. (16) Disconnect start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16, figure 3-2, detail B) from elbow (36, figure 3-4). (17) Remove bolts (31, figure 3-4) and washers (32) securing fuel electronic control assembly (33) to fuel control enclosure base (44) and reduction drive unit (33, figure 3-3). Remove fuel electronic control assembly (33, figure 3-4). Install protective plugs on fuel electronic control assembly (33) and spline-shaft protective cover (part number 164416, TO 6J3-4-112-3) on fuel pump spline. (18) Remove engine accessory drive gasket (34) and discard. (19) Loosen locknut (35) and remove elbow (36) and O-ring (37) from fuel electronic control assembly (33). Discard O-ring (37). (20) Remove locknut (38) and washers (39 and 40) securing elbow (41) to fuel control enclosure base (44). Remove elbow (41). caution Start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) and purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19, figure 3-2, detail B) are held tightly in enclosure base (44, figure 3-4). Be careful to avoid damaging when removing. (23) Remove O-ring (17) from purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19) and discard. (24) Remove O-ring (18) from start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) and discard. NOTE Do not remove gasket (45) unless loose or damaged. (25) Remove bolts (42) and washers (43) securing fuel control enclosure base (44) and gasket (45) to reduction drive unit (33, figure 3-3). Remove fuel control enclosure base (44, figure 3-4) and if necessary, gasket (45). Discard gasket (45) if removed. (26) Temporarily install bolts (42) and washers (43) into reduction drive unit (33, figure 3-3). (27) Install protective cover on accessory pad cover (108, figure 3-12) and secure. o. Remove fuel purge valve and tubing as follows: (1) Remove fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20, figure 3-2, detail B), connecting tee (28) on fuel purge valve (25) and fuel manifold on combustor assembly (74). Install protective caps. (2) Remove start fuel to start nozzle fuel tube assembly (21) from fuel nozzle (22) and bulkhead tee (35). Install protective caps. NOTE Do not remove fuel nozzle (22) and fitting (23) from combustor assembly (74) at this time. (21) Remove start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16, figure 3-2, detail B) from bulkhead tee (35). (3) Remove purge valve to tee tube assembly (24), connecting fuel purge valve (25) to tee tube (30). Remove fuel purge valve (25). (22) Remove purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19) from tee (28). Install protective caps. (4) Remove straight adapter (26) and Oring (27) from fuel purge valve (25). Discard O-ring (27). 3-13 TO 2G-T62T-43 Remove tee (28) and O-ring (29) from fuel purge valve (25). Discard O-ring (29). reduction drive unit (73) to elbow (59) on inlet housing manifold (72). Install protective plugs. (6) Remove tee tube (30) from orifice jet restrictor (31). z. Remove elbow (55) and O-ring (56) from reduction drive unit (73), Discard O-ring (56). aa. Remove lockwire, then remove high-oil temperature switch (57), and O-ring (58) from engine oil sump assembly (71). Discard Oring (58). Install protective cap. (5) (7) Remove orifice jet restrictor (31) and O-ring (32). Discard O-ring (32). (8) Remove locknut (33), washer (34) and bulkhead tee (35). p. Remove filter to tee PCD air tube assembly (36, figure 3-2, detail F) from air filter (37) and tee (45) on IGV actuator (70). Remove air filter (37). Install protective caps on air filter (37), and plugs on filter to tee PCD air tube assembly (36). q. Remove diffuser to filter PCD air tube assembly (38) from elbow (39). Install protective plugs. r. Remove elbow (39) from straight adapter (40) on PCD air outlet on turbine assembly (68, figure 3-2, detail G). ab. Remove surge control valve (9, figure 3-5) as follows: (1) Remove V-band clamp (5), securing duct assembly (6) to duct assembly (17). (2) Remove duct assembly (6) and O-ring (7). Discard O-ring (7). (3) (4) s. Remove straight adapter (40, figure 3-2, detail F) and O-ring (41). Discard O-ring (41). t. Remove tee to surge valve PCD air tube assembly (42). connecting PCD air to surge control valve (69) and tee (45) on IGV actuator (70). Install protective plugs. u. Remove reducer (43) and O-ring (44) from surge control valve (69). Discard O-ring (44). (2) v. Remove tee (45), reducer (43). and O-ring (46) from IGV actuator (70). Discard Oring (46). (3) w. Remove oil hose assembly (47, figure 3-2, detail G), connecting engine oil sump assembly (71) to straight adapter (63) on inlet housing manifold (72). Install protective plugs on oil hose assembly (47). x. y. 3-14 Remove straight adapter (48) and O-ring (49) from engine oil sump assembly (7.1). Discard O-ring (49). Install protective cap in engine oil sump assembly (71). Remove oil pressure-manifold housing to reduction drive tube assembly (54), connecting (5) Remove V-band clamp (8), securing surge control valve (9) to duct assembly (17). Remove surge control valve (9) and Oring (10). Discard O-ring (10). Loosen band clamp (11), but do not remove. ac. Remove air flow sensor (25) as follows: (1) Remove nuts (13), washers (14), and bolts (15). securing duct support bracket (16) to containment ring (37). Remove duct support bracket (16). (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) Remove V-band clamp (12), securing duct assembly (17) to air flow sensor (25). Remove duct assembly (17) and O-ring (18). Discard O-ring (18). Remove temperature sensor (19) and O-ring (20) from air flow sensor (25). Discard O-ring (20). Remove bolt (21), securing fitting assembly (22) to air flow sensor (25). Remove fitting (22) and O-rings (23). Discard O-rings (23). Remove V-band clamp (24) from air flow sensor (25). Remove air flow sensor (25) and Oring (26) from load compressor scroll (38). Discard O-ring (26). T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-5. Surge Control Valve, Air Flow Sensor Assembly, and Turbine Ignition Exciter (Sheet 1 of 2) Change 20 3-15 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Legend or figure 3-5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Bolt Nut Washer Support clamp (2) V-band clamp Duct assembly O-ring V-band clamp Surge control valve O-ring Band clamp V-band clamp Nut (2) Washer (2) Bolt Duct support bracket Duct assembly O-ring Temperature sensor O-ring 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Bolt (2) Fitting O-ring (2) V band clamp Air flow sensor O-ring Ignition cable Nut (4) Bolt (4) Washer (4) Turbine ignition exciter Bolt (2) Bushing Engine mounting adapter (2) Locking ring (2) Identification plate (2) Containment ring Load compressor scroll Igniter plug Thermocouple harness P9100234 Figure 3-5. Surge Control Valve, Air Flow Sensor Assembly, and Turbine Ignition Exciter (Sheet 2 of 2) 3-16 Change 1 TO 2G-T62T-43 ad. Remove turbine ignition exciter (31, figure 3-5) as follows: warning NOTE Do not remove spring pin (7) unless loose or damaged. (6) Remove O-rings (5, 6, and 15, figure 3-6) and if necessary, spring pin (7) from inlet manifold assembly (3) and manifold assembly (4). Discard Orings (5, 6, and 15). (7) Remove elbow (59, figure 3-2, detail G) and O-ring (60) from inlet housing manifold (72). Discard O-ring (60). (8) Remove orifice fitting (61) and O-ring (62) from inlet housing manifold (72). Discard O-ring (62). (9) Remove straight adapter (63) and Oring (64) from inlet housing manifold (72). Discard O-ring (64). Be sure ignition cable and turbine ignition exciter are cool before handling. Do not touch end of turbine ignition cable when removing cable. Always remove cable from igniter plug end. Ground end of ignition cable to combustor to discharge turbine ignition exciter. Failure to do so could cause injury. (1) (2) Remove lockwire, disconnect, and remove ignition cable (27) from igniter plug (39) end and turbine ignition exciter (31). Do not remove igniter plug (39) at this time. Install protective caps. Remove nuts (28), bolts (29), washers (30) and turbine ignition exciter (31) from containment ring (37). Install protective caps. ae. Remove inlet housing manifold (3, figure 3-6) as follows: af. Remove air inlet duct (13, figure 3-6) as follows: (1) Remove lockwire from straps (8). (2) Loosen nuts (16) and separate straps (8). (3) Remove temperature sensor (14) from air inlet duct (13). (4) Remove top half of air inlet duct (13). (1) Remove tee to gearbox adapter tube assembly (66, figure 3-2, detail G), connecting orifice fitting (61) on inlet housing manifold (72). Install protective plugs. (5) Remove diffuser to tee PCD air tube assembly (65, figure 3-2, detail G), connecting combustor assembly (74) to orifice fitting (61) on inlet housing manifold (72). (2) Remove straight adapter (52) and Oring (53) from turbine assembly (68). Discard O-ring (53). (6) Remove bottom half of air inlet duct (13, figure 3-6) and O-ring (15). Discard O-ring (15). (3) Disconnect diffuser to tee PCD air tube assembly (65) from orifice fitting (61). (4) Remove bolts (1, figure 3-6) and washers (2), securing inlet housing manifold (3) to manifold assembly (4). (5) Remove inlet housing manifold (3) from manifold assembly (4). NOTE Top and bottom half of air inlet duct (13) should be kept together as a matched set, per serial number. (7) Assemble top and bottom half of air inlet duct (13) and secure with straps (8). 3-17 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-6. Inlet Housing Manifold and Air Inlet Duct Assembly 3-18 TO 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Do not remove straps (8) unless damaged. (8) If straps (8) are damaged, remove nuts (9), washers (10), bolts (11), and bushings (12), securing straps (8) to air inlet duct (13). ag. Remove IGV actuator (6, figure 3-7) as follows: (1) Remove nut (1) securing IGV drive link (8) to turbine assembly. (2) Remove self-locking nuts (2), bolts (3), washers (4), and insulation actuator bushings (5), securing IGV actuator (6) to turbine assembly. Remove IGV actuator (6). (3) Remove nut (1) and bolt (7) securing IGV drive link (8) to IGV actuator (6). Remove IGV drive link (8). (4) Remove IGV actuator stop (9) from IGV actuator (6). ah. Remove and disassemble hourmeter junction box (18, figure 3-8) as follows: (1) Remove screws (1), lockwashers (2), washers (3), cover (4), and gasket (5) from hourmeter junction box (18). (2) Disconnect terminal lugs (6 and 7) from hourmeters (11). (3) Remove screws (8), nuts (9), and lockwashers (10), securing hourmeters (11) Remove hourmeters to cover (4). (11). warning Soldering fumes are toxic. Do not breathe fumes. Solder in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection. (5) Remove screws (12), self-locking nuts (13), and washers (14) from event counter ( 15). Remove event counter (15. (6) Remove screws (16) and washers (17), securing hourmeter junction box (18) to enclosure spacer assembly (31). Remove hourmeter junction box (18). (7) Remove screws (19), nuts (20), and washers (21) securing connector (22) to hourmeter junction box (18). Remove connector (22). (8) Remove screws (23), nuts (24), and lockwashers (25), securing terminal boards (26) and terminal board strips (27) to hourmeter junction box (18). Remove terminal boards (26) and terminal board strips (27). NOTE Wiring will be labeled according to its termination. (9) (10) Remove nuts (28, figure 3-8), lockwashers (29), and washers (30), securing terminal lugs (7) to studs on terminal boards (26). Remove terminal lugs (7) from terminal boards (26). ai. Remove engine hydraulic starter (10, figure 3-3) as follows: (1) Remove self-locking nuts (8) and washers (9), securing engine hydraulic starter (10) to reduction drive unit (33). Remove engine hydraulic starter (10). (2) Remove gasket (11) and discard. (3) Remove nipple (12) and O-ring (13) from engine hydraulic starter (10). Discard O-ring ( 13). caution Be careful not to break wires on event counter. Use a minimum of heat when unsoldering components. Use a heat sink to prevent damage. (4) Unsolder wires from event counter (15). Tag and disconnect wiring from components to be replaced (see figure 3-9 for wiring diagram). 3-19 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-7. IGV Actuator 3-20 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-8. Hourmeter Junction Box Assembly (Sheet 1 of 2) 3-21 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-8: 1, 2, 3, Screw (4) Lockwasher (4) Washer (4) 17, Washer (3) 18. Hourmeter junction box 19. Screw (4) 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. cover Gasket Terminal lug (14) Terminal lug (4) Screw (6) Nut (6) Lockwasher (6) Hourmeter (2) Screw (2) Self-locking nut (2) Washer (2) Event counter Screw (3) 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Nut (4) Washer (4) Connector Screw (4) Nut (4) Lockwasher (4) Terminal board (2) Terminal board strip (2) Nut (8) Lockwasher (8) Washer (6) Enclosure spacer assembly C”- Figure 3-8. 3-22 Hourmeter Junction Box Assembly (Sheet 2 of 2) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-9. Hourmeter Junction Box Assembly Wiring Diagram 3-23 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 aj. Remove self-locking nuts (14) and washers (15), securing cover (16) to reduction drive unit (33). Remove cover (16). (4) Using combustor puller, ST71201 (43, figure 2-1), remove combustor assembly (27, figure 3-3). ak. Remove gasket (17). al. Remove oil pressure switch (18) as follows: (1) (2) Record information on identification plate before removing. Remove lockwire from oil pressure switch (18). ap. Remove oil pressure switch (18) and Oring (19) from reduction drive unit (33). Discard O-ring (19). Install protective cap on oil pressure switch (18). If damaged, remove identification plate (36, figure 3-5) from containment ring (37). aq. ar. Remove containment ring (37). as. Remove turbine assembly (30, figure 3-3) as follows: am. Remove eye bolt (20). an. Remove bolts (21) and washers (22) securing connector mounting bracket (23) to reduction drive unit (33). Remove connector mounting bracket (23). ao. NOTE Remove combustor assembly (27) as follows: (1) Remove lockwire, bolts (32, figure 3-5), and bushing (33) from containment ring (37). NOTE Do not remove engine mounting adapter (34) on right hand side looking from aft end unless removing diffuser housing. (2) Unstake locking ring (35) and, using spanner wrench, ST93975 (79, figure 2-1), remove engine mounting adapter (34, figure 3-5) and locking ring (35) from left side of containment ring (37) looking from aft end. If necessary, remove engine mounting adapter (34) and locking ring (35) from right side. (3) Remove clamp (24, figure 3-3) from combustor assembly (27). 3-24 Change 9 (1) Remove seal ring (28) and discard. (2) Remove lockwire, loosen bolts (1, figure 3-10), and remove turbine nozzle (2). (3) Remove bolts (29) securing turbine assembly (30) to reduction drive unit (33). (4) Separate turbine assembly (30) from reduction drive unit (33). caution Locking ring (35, figure 3-5) is staked. Be sure to unstake prior to removing engine mounting adapter (34) to prevent damage to adapters or special tools. Remove elbow (50, figure 3-2, detail G) and O-ring (51) from turbine assembly (74). Discard O-ring (51). (5) 3-5. Remove O-ring (31) and adapter gasket (32) from reduction drive unit (33). Discard O-ring (31). DISASSEMBLY OF TURBINE ASSEMBLY. This section contains procedures for disassembly of the turbine assembly after it has been removed from the APU. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to figure 3-10. NOTE Make sure slots in turbine fit into slots of rotor fixture, ST70137 (figure 3-11). a. Install turbine assembly (turbine end) in rotor fixture, ST70137 (figure 3-11). b. Remove lockwire from magnetic pickup (3), then remove magnetic pickup. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-10. Turbine Assembly (Sheet 1 of 3) 3-25 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-10. Turbine Assembly (Sheet 2 of 3) 3-26 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-10: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11, 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. Bolt (6) Turbine nozzle Magnetic pickup Nut Pinion assembly Steel ball (3) Bearing front carrier Spring (6) Spacer (A/R) O-ring. (3) Forward bearing Pin’ Nut (19) Washer (40) Stud Bolt (18) Adapter assembly Load compressor diffuser O-ring Load compressor wheel Load compressor seal Rotor assembly Load compressor scroll Shim (AIR) Bolt (17) Lockring (19) Insert (19) Pin (2) Pin Support housing Inlet housing Figure 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 3-10. Turbine Assembly Bolt (2) Pin-drive flange IGV drive gear IGV drive gear bearing Insert (2) Locknut (17) IGV sector gear (17) Inlet guide vane (17) IGV bushing (34) Diffuser O-ring (2) Bolt (12) Washer (12) Diffuser housing Lockring (18) Insert (12) Lockring (4) Insert (4) Insert (6) Shim (A/R) Labyrinth seal Bearing aft carrier Nut Turbine wheel Pin (3) Seal plate Stud Rotor shaft Engine compressor Aft bearing (Sheet 3 of 3) 3-27 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-11. 3-28 Installation of Turbine Assembly in Rotor Fixture T.O. 2G-T62T-43 c. Install pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 (Figure 3-11), on to top of adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17). Tighten screws on tool and press down on toggle clamps until it is secure on bearing aft carrier (53). d. Using wrench, ST71191 (Figure 2-1, 42), remove nut (Figure 3-10, 4), pinion assembly (5), and steel balls (6). Discard steel balls (6). n. Install turbine assembly in load compressor wheel restrainer, ST 93951-04 (Figure 2-1, 78) and place in hydraulic press. o. Using an assembly aid (4 inches long x 0.437 inches diameter steel dowel), press off load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20) and rotor assembly (22) from turbine assembly. NOTE Do not remove load compressor seal (21) unless loose or damaged. WARNING Ensure nut (4) is reinstalled and clamps loosened slowly to prevent personnel injury when releasing compressed bearing aft carrier (53). e. Reinstall nut (4) finger tight. f. Slowly loosen toggle clamps of pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 (Figure 3-11), and back off nut (Figure 3-10, 4) until pre-load on bearing aft carrier (53) is removed. Remove pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 and nut (4) using wrench, ST71191 (Figure 2-1, 42). p. If necessary, remove load compressor seal (21) by machining off from load compressor wheel (20). q. Remove load compressor scroll (23) with rubber mallet. r. Remove shim (24) from inlet housing (31). s. Remove bolts (25) and washers (14) securing support housing (30) to inlet housing (31). g. Using carrier bearing puller, ST94426 (Figure 2-1, 83), lift and remove bearing front carrier (Figure 3-10, 7). NOTE Do not remove lockrings (26), inserts (27 and 36), and pins (28 and 29) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. h. Remove springs (8), O-rings (10), and spacer (9). Discard O-rings (10). t. Separate support housing (30) from inlet housing (31). i. Remove forward bearing (11) from bearing front carrier (7) and discard. u. Remove bolts (32), pin drive-flange (33), IGV drive gear (34), and IGV drive gear bearing (35). Discard IGV drive gear bearing (35). NOTE Do not remove pin (12) from bearing front carrier (7) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. v. Remove locknuts (37) securing IGV sector gears (38) to inlet guide vanes (39). w. Remove IGV sector gears (38) from inlet guide vanes (39). j. Remove nut (13), washers (14), and stud (15) from adapter assembly (17). x. Remove inlet guide vanes (39) and IGV bushings (40). k. Remove bolts (16), washers (14), and nuts (13), securing adapter assembly (17) to load compressor scroll (23). NOTE Support housing and inlet housing are a matched set and must be kept together. l. Using puller, ST70170 (Figure 2-1, 18), remove adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17). m. Remove load compressor diffuser (18) and Oring (19). Discard O-ring (19). y. Reinstall support housing (30) on inlet housing (31) and secure loosely with four bolts (25). Change 22 3-29 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 WARNING WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and local Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations for additional information. When handling titanium parts, be sure to wear clean, white, cotton gloves. ah. Remove turbine wheel (55) using turbine wheel puller, ST71186 (Figure 2-1, 41). NOTE Do not remove pins (Figure 3-10, 56) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. z. Remove diffuser (Figure 3-10, 41) from diffuser housing (45) by first heating the assembly to 400-450oF. Remove from oven. Install containment ring, ST71232 (Figure 2-1, 51), or local manufacture, in diffuser (41) and place dry ice, CGA-G6.2, in containment ring. aj. Install turbine wheel (55) in rotor fixture, ST70137 (Figure 2-1, 17), and using turbine stud torque wrench, ST71238 (55), or equivalent, remove stud (Figure 3-10, 58). aa. (45). Remove diffuser (41) from diffuser housing ak. Remove engine compressor wheel (60) from rotor shaft (59) as follows: ab. Remove O-rings (42) from inlet housing (31) and discard. (1) If engine compressor wheel (60) is to be reused, match-mark engine compressor wheel (60) to rotor assembly (22). ac. Remove bolts (43) and washers (44), securing diffuser housing (45) to inlet housing (31). ad. Place diffuser housing (45) in arbor press with locally manufactured wooden ring, and press off diffuser housing (45) from inlet housing (31). NOTE Do not remove inserts (47, 49, and 50) or lockrings (46 and 48) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. ae. Remove shim (51). af. Using arbor press guide, ST71207 (Figure 21, 45), and arbor press, remove labyrinth seal (Figure 3-10, 52) and bearing aft carrier (53). ag. Install rotor assembly (22) in load compressor rotor assembly tooling, ST71219 (Figure 2-1, 49), and using stretch tool, ST71078 (40), remove nut (Figure 3-10, 54). 3-30 Change 22 ai. Remove seal plate (57). (2) Using load compressor rotor assembly tooling, ST71219 (Figure 2-1, 49), and hydraulic press, press rotor shaft (Figure 3-10, 59) away from engine compressor wheel (60). al. Remove aft bearing (61) using load compressor rotor assembly tooling, ST71219 (Figure 2-1, 49), an assembly aid, and hydraulic press. Discard aft bearing (61). 3-6. DISASSEMBLY OF REDUCTION DRIVE UNIT. This section contains procedures for disassembly of the reduction drive unit after it has been removed from the APU. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to Figure 3-12. a. Remove engine oil sump (22) as follows: (1) Place suitable container under engine oil sump drain to catch any excess oil. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-12. Reduction Drive Unit (Sheet 1 of 5) Change 4 3-31 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-12. Reduction Drive Unit (Sheet 2 of 5) 3-32 Change 4 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-12. Reduction Drive Unit (Sheet 3 of 5) 3-33 to 2g-t62t-43 legend for figure 3-12 44. Insert (5) 45. Zerol bevel gear 46. Shim 47. O-ring 48. Screw (5) 49. Retainer 50. Locknut 51. Locknut 52. Accessory drive pinion 53. Ball (2) 54. Ball bearing 55. Ball bearing 56. Spacer 57. Shaft seal 58. Bolt (8) 59. Washer (8) 60. Carrier assembly 61. Bolt (3) 62. Washer (3) 63. Cover 64. Bearing (6) 65. Gear planet set 66. Retaining ring (3) 67. Dowel (3) 68. Retaining ring 69. Ring gear 70. Gasket 71. Lube oil elbow 72. Insert (9) 73. Sleeve (3) 74. Sleeve (3) 75. Oil jet cartridge pin 76. Spring-slotted 77. Housing carrier 78. Straight drive shaft 79. O-ring 80. O-ring 81. Pipe plug (2) 82 Cover 83. Locknut 84. Retainer 85. Hub ring gear 86. Screw (3) 1. Caplug 2. Plug (3) 3. O-ring (3) 4. Nameplate 5. Retaining ring 6. By-pass valve housing 7. O-ring 8. Spring pin 9. Valve spring 10. Bali bearing (2) 11. Oil filter element 12. Bolt 13. Accessory pad cover 14. Accessory drive gasket plug 15. Magnetic-drain 16. O-ring valve 17. Self-closing O-ring 18. 19. Caplug 20. Clamp 21. O-ring 22. Engine oil sump 23. Screw 24. Screw 25. Dowel pin 26. Oil pump housing 27. Gasket 28. Cap screw 29. Oil suction tube 30. O-ring nut 31. Self-locking 32. Washer 33. Pump drive gear 34. Dowel pin (3) 35. Cover 36. Pump element gear (2) 37. Driver shaft 38. Driven shaft 39. Cap screw (2) 40. Bevel gear support 41. Pin 42. Liner 43. Liner Figure 3-34 3-12. Reduction Drive Unit (Sheet 4 of 5) TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-12 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. 99. 100. 101. 102. 103. 104. 105. 106. 107. 108. 109. 110. 111. 112. 113. 114. 115. 116. Continued: 117. 118. 119. 120. 121, 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. Lockwasher (3) Shim Locknut Bearing Zerol pinion Bearing Retainer bearing ring Key Key Housing liner Shaft seal Insert (4) Screw (2) Washer (2) Washer (6) Vent plate Valve housing Bail Relief valve spring Screw (4) Washer (4) Accessory pad cover O-ring Lockring Insert (4) Retaining ring Intermediate gear shaft O-ring O-ring Bearing spacer Figure 3-12. Reduction Intermediate gear Ball bearing Oil shield Accessory gear Oil/air separator Oil/air separator Ball bearing (2) Plug Dowel pin Shaft seal Retaining ring (2) Insert Insert (12) Insert (8) Insert (4) Lockring (12) Stud (5) Stud Stud (6) Pin Sleeve Lockring Insert Oil/air separator sleeve Spring-slotted pin (2) Housing Drive Unit (Sheet 5 of 5) 3-35 TO 2G-T62T-43 (2) (3) Remove magnetic-drain plug (15) and O-ring (16) from self-closing valve (17). Discard O-ring (16). Remove self-closing valve (17) and Oring (18) from engine oil sump (22). Discard O-ring (18). (4) Unscrew caplug (19). (5) Remove clamp (20) and O-ring (21) from engine oil sump (22). Discard Oring (21). (6) Remove engine oil sump (22). (7) Remove cap screw (28), oil suction tube (29), and O-ring (30). Discard O-ring (30). b. Remove oil pump housing (26) as follows: NOTE NOTE Record information on nameplate before removing. f. g. Remove oil filter element (11) as follows: Remove screws (23 and 24), oil pump housing (26), and gasket (27). Discard gasket (27). (2) Remove self-locking washer (32). (3) Remove pump drive gear (33) from driver shaft (27). Remove one dowel pin (34). (4) Separate oil pump housing (26) from cover (35). nut (31) and (5) Remove pump element gears (36) from driver shaft (37) and driven shaft (38). (6) Remove remaining dowel pins (34) from driver shaft (37) and driven shaft (38). c. Remove reduction drive unit from assembly build stand, ST71206 (44, figure 2-1), and place on assembly fixture, ST70370 (37, figure 2-1). (1) Remove retaining ring (5). (2) Place suitable container under by-pass valve housing (6) to catch oil. (3) Using oil filter cap removal tool, ST80211 (58, figure 2-1), remove bypass valve housing (6, figure 3-12) from housing (142). NOTE Do not remove spring pin (8). valve spring (9), or ball bearings (19) from by-pass valve housing (6). Do not remove dowel pin (25) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. (1) If damaged, remove nameplate (4). (4) Remove and discard O-ring (7). (5) Remove oil filter element (11). card oil filter element. h. Remove bolts (12), accessory pad cover (13), and accessory drive gasket (14) from housing (142). i. Remove bevel gear support (40) and Zerol bevel gear (45) as follows: (1) 3-36 Remove cap screws (39) attaching bevel gear support (40) to housing (142). NOTE Do not remove pin (41), liners (42 and 43). or inserts (44) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove inserts (44), refer to Section V for procedure. (2) If necessary, remove pin (41) and liners (42 and 43). (3) Using puller, ST70170 (figure 3-13), remove bevel gear support (40) and Zerol bevel gear (45, figure 3-12) as an assembled unit from housing (142). (4) Remove shim (46) and O-ring (47). Discard O-ring (47). (5) Remove screws (48) (49). d. Remove caplug (1, figure 3-12). e. Cut lockwire and remove plugs (2) and Orings (3). Discard O-rings (3). Dis- from retainer TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-13. Removal of Bevel Gear Support and Zerol Bevel Gear (6) Remove retainer (49) and Zerol bevel gear (45) as an assembled unit. (10) Using common gear puller, remove accessory drive pinion (52, figure 3-12) and balls (53). (7) Install holding fixture, ST70267 (figure 3-14), on face of Zerol bevel gear (45). (8) Using spanner wrench, ST70243 (figure 3-14), remove locknut (50). (11) Using arbor plate, ST70236 (21, figure 2-1), bushing, ST70238 (23), and bearing bevel gear removal tool, ST71231 (50), remove ball bearings (54 and 55, figure 3-12) and spacer (56) from Zerol bevel gear (45). Discard ball bearings (54 and 55). (9) Using holding fixture, ST70267, and spanner wrench, ST70241 (figure 3-15). remove locknut (51). (12) Using sealer puller, ST93057 (76, figure 2-1), remove shaft seal (57, figure 3-12) from bevel gear support (40). 3-37 TO 2G-T62T-43 . Figure 3-14. Removal of Locknut 3-38 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-15. Removal of Locknut j. Remove carrier assembly (60) as follows: (1) (2) Remove bolts (58) and washers (59) securing carrier assembly (60) to housing (142). (6) Using puller, ST70170 (figure 3-16), remove carrier assembly (60) from housing (142). Remove bearings (64, figure 3-12) and gear planet set (65) as an assembled unit from carrier assembly (60). (7) Using bearing puller, ST91061 (73, figure 2-1), and an arbor press, push gear planet set (65, figure 3-12) off bearings (64). Discard bearings (64). (3) Remove lube oil elbow (71) from carrier assembly (60) and discard. (4) Remove bolts (61) and washers (62) securing cover (63) to carrier assembly (60). (5) puller until cover (63) is free from carrier assembly. Remove retaining plate, ST90684, from carrier assembly (60). Using retaining plate, ST90684, and puller, ST90288 (figure 3-17), place three fingers of puller around edge of cover (63). With three guide pins on flange of carrier assembly (60), rotate NOTE Carrier assembly and cover are a matched set and must remain together. (8) Reinstall cover (63) on carrier assembly (60) and secure loosely with bolts (61). (9) Remove retaining ring (66) from carrier assembly (60). 3-39 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-16. Removal of Carrier Assembly 3-40 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-17. Removal of Cover 3-41 TO 2G-T62T-43 Remove O-rings (79 and 80) from housing carrier (77) and discard. NOTE Do not remove dowels (67) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. k. Remove ring gear (69) as follows: (1) Remove cover (82) from housing carrier (77). (2) Install disassembling tool, ST70284 (figure 3-18); inserting each leg of tool in equally spaced access slots inside ring gear (69, figure 3-12) [the slots are recessed around edge of teeth that mate with splines on hub ring gear (85)]. Turn knurled knob of tool and compress retaining ring (68) into groove on hub ring gear (85). (3) Tip ring gear (69) to hold retaining ring (68) in place, and continue working retaining ring into groove until ring gear slips forward. Remove and discard retaining ring (68). (4) Remove ring gear (69) from carrier assembly (60). (5) Remove and discard gasket (70). NOTE Do not remove inserts (72), sleeves (73 and 74), oil jet cartridge (75). and springslotted pin (76) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove inserts or sleeves, refer to Section V for procedure. (6) If necessary, remove oil jet cartridge (75) by grinding around spring-slotted pin (76) sufficiently to grasp springslotted pin (76) with small needle-nose pliers. Remove and discard springslotted pin (76) and oil jet cartridge (75). l. Remove housing carrier (77) and straight drive shaft (78) as follows: (1) Using adapter, ST70242 (figure 3-19), and rubber mallet, remove housing carrier (77) and straight drive shaft (78, figure 3-12) as an assembled unit from housing (142). 3-42 NOTE Do not remove pipe plugs (81) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. (3) Using holding fixture, ST70266, and wrench, ST70243 (figure 3-20), remove locknut (83) from straight drive shaft (78, figure 3-12). spanner (4) Remove retainer (84). (5) Using common gear puller, remove hub ring gear (85) from straight drive shaft (78). (6) Straighten tab on lockwashers (87); then remove screws (86) and lockwashers (87). (7) Separate housing carrier (77) from straight drive shaft (78). (8) Remove shim (88) and tie to housing carrier (77) to prevent loss. (9) Using holding fixture, ST70266, and spanner wrench, ST70241 (figure 3-21), remove locknut (89) from straight drive shaft (78). (10) Using arbor plate, ST70236, bushing, ST70238, and an arbor press (figure 3-22), remove bearing (90) from straight drive shaft (78). Discard bearing (90). (11) Using arbor plate, ST70236, bushing, ST70237, and an arbor press (figure 3-23), remove Zerol pinion (91), bearing (92), retainer bearing ring (93), and key (94, figure 3-12) as an assembled unit from straight drive shaft (78). NOTE Do not remove key (95) or housing liner (96) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. (12) Remove shaft seal (97, figure 3-12) from housing (142). TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-18. Removal of Ring Gear Figure 3-19. Removal of Housing Carrier 3-43 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-20. Removal of Locknut 3-44 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-21. Removal of Locknut 3-45 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-22. Removal of Bearing 3-46 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-23. Removal of Zerol Pinion 3-47 TO 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Do not remove inserts (98) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. m. Remove valve housing (103) as follows: (1) Remove screws (99) and washers (100 and 101) securing valve housing (103) and vent plate (102) to housing (142). (2) Remove vent plate (102). (3) Remove valve housing (103), ball (104), and relief valve spring (105) from housing (142). n. Remove intermediate gear (117) and accessory gear (120) as follows: (1) Remove screws (106) and washers (107) securing accessory pad cover (108) to housing (142). (2) Using puller, ST70234 (figure 3-24), remove accessory pad cover (108). (3) Remove O-ring (109, figure 3-12) from accessory pad cover (108) and discard. (4) Remove accessory gear (120), oil/air separators (121 and 122), ball bearings (123), plug (124), and dowel pin (125) from housing (142) as an assembled unit. Figure 3-24. Removal of Accessory Pad Cover 3-48 TO 2G-T62T-43 remove intermediate gear shaft (113) from housing (142). NOTE Do not remove lockrings (110) or inserts (111) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. (5) Remove retaining ring (112) securing intermediate gear shaft (113) to housing (142). (7) Remove O-rings (114 and 115) from intermediate gear shaft (113) and discard. (8) Remove bearing spacer (116), intermediate gear (117), ball bearing (118), oil shield (119), and retaining rings (127) from housing (142). (9) holder, removal bearing Using ST70277, a piece of brass stock (0.467 in. approximately), and arbor press (figure 3-26), remove ball bearings (123, figure 3-12) from accessory gear (120). Discard ball bearings (123). caution To prevent damage, support intermediate gear (117) during removal of intermediate gear shaft (113). Do not allow intermediate gear to drop. (6) Using puller, ST70235 (figure 3-25), Figure 3-25. Removal of Intermediate Gear Shaft 3-49 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-26. Removal of Ball Bearings 3-50 TO 2G-T62T-43 (10) Remove oil/air separators (121 and 122) from accessory gear (120). NOTE Do not remove plug (124) and dowel pin (125) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove dowel pin (124), refer to Section V for procedure. (11) Using arbor press and a piece of brass stock (0.725-0.750 in.), remove shaft seal (126) from accessory pad cover (108). (12) Remove retaining rings (127) securing ball bearing (118) in intermediate gear (117). (13) Using arbor plate and driver, ST70286 (figure 3-27). remove ball bearing (118, figure 3-12) from intermediate gear (117). Discard ball bearing (118). Figure 3-27. Removal of Ball Bearing 3-51 TO 2G-T62T-43 fold from tube fittings on combustor housing (17). NOTE Do not remove pin (136), sleeve (137), oil/air separator sleeve (140), or springslotted pins (141) unless loose, damaged on inside diameter surface, or not in proper position. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. Do not remove inserts (128, 129, 130, 131, or 139), lockrings (132 or 138), or studs (133, 134, or 135) unless loose or damaged. If necessary to remove, refer to Section V for procedure. 3-7. DISASSEMBLY OF COMBUSTOR ASSEMBLY. This section contains procedures for disassembly of the combustor assembly after it has been removed from the APU. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to figure 3-28. a. Remove igniter plug (1) from combustor housing ( 17). b. Remove fuel nozzle (3) and fitting (2) from combustor housing ( 17). c. Remove fuel manifold (9) as follows: (1) (2) Remove filter fitting (4) and O-ring (5) from fuel manifold (9). Discard Oring (5). Remove bolts (6), nuts (7), and washers (8) securing fuel manifold (9) to combustor housing (17). (4) Install protective caps on tips of fuel manifold (9). d. If necessary, remove bolts (10), nuts (11), and washers (8) securing loop clamps (12) and loop clamp cushions (13) to fuel manifold (9). e. Remove lockwire and pins (14) from combustor housing ( 17). f. Remove combustor liner assembly (15) from combustor housing (17). g. Remove O-rings (16) from atomizer fittings in combustor liner (15). Discard O-rings (16). NOTE Do not remove igniter plug grommet (18), washers (19), and spring (20) unless loose or damaged. h. If necessary, remove igniter plug grommet (18) as follows: (1) If igniter plug grommet (18) is frozen, apply a few drops of non-carbon penetrating oil, VV-P-216, to igniter plug grommet and remove. (2) If igniter plug grommet (18) still remains frozen, use a pair of pliers, or equivalent tool, and collapse igniter plug grommet. (3) Using a soft-ended drift (copper or wood), carefully remove igniter plug grommet (18) from liner assembly (16). Discard igniter plug grommet (18), washers (19), and spring (20). caution To prevent damage to fuel outlet tips of fuel manifold (9), do not bend tubes during removal of fuel manifold. (3) 3-52 Loosen six coupling nuts on fuel manifold (9) and carefully slide fuel mani- TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 3-28. Combustor Assembly (Sheet 1 of 2) 3-53 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 3-28: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Igniter plug Fitting Fuel nozzle Filter fitting O-ring Bolt (2) Nut (2) Washer (4) Fuel manifold Bolt (2) 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Nut (2) Loop clamp (2) Loop clamp cushion (4) Pin (4) Combustor liner O-ring (6) Combustor housing Igniter plug grommet Washer (2) Spring Figure 3-28. Combustor Assembly (Sheet 2 of 2) 3-54 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SECTION IV CLEANING 4-1. GENERAL. Cleaning instructions for the APU are provided in this section. To ensure satisfactory results, each cleaning procedure must be performed exactly as described. All dust, dirt, corrosion, rust, and moisture must be removed, as these destructive agents will eventually cause operational failure. 4-2. SOLVENT FOR GENERAL USE. Only the solvent specified in this section should be used for cleaning purposes. Any part not specifically mentioned in the text should be cleaned in the same general manner as a similar part. Whenever refinishing is required, adherence to the procedure given in this section or in Section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement will ensure satisfactory results. 4-3. CLEANING PROCEDURES. This section con- tains cleaning procedures for the APU and its components. a. Solvent Cleaning of Painted Aluminum Alloy Parts. b. Aqueous Cleaning of Aluminum Alloy Parts. warning compound, Alkaline cleaning PP-C-436, is toxic, irritating to the skin, and harmful to the eyes. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. caution Aluminum alloy parts having protective coatings, either anodized or chemical film treatment, must be cleaned using non-etching alkaline cleaner, unless otherwise specified. (1) Prepare cleaning solution using 6-10 oz. of non-etching alkaline cleaning compound, P-C-436, per gallon of water, maintained at a temperature of 160-180 °F. (2) Immerse parts in cleaning solution for 5-15 minutes. (3) Remove parts from cleaning solution and immerse in clear, agitated water within 15 seconds. Leave component in water for 1-2 minutes. (4) Remove parts and spray rinse with fresh water. warning Cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II, is toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear goggles and solvent-resistant gloves. caution Aluminum alloy parts having protective coating, either anodized or chemical film treatment, must be cleaned using non-etching alkaline cleaner, unless otherwise specified. (1) Wipe parts with clean, cheesecloth, CCC-C-440, saturated with cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II or III. (2) Scrub parts with abrasive crocus cloth, P-C-458, or non-metallic mat, MIL-A-9962. (3) Wipe parts again with clean, cheesecloth, CCC-C-440, saturated with cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II or III. (4) (5) Allow parts to air dry. c. Cleaning of Steel and Corrosion-Resistant Alloy Parts. warning Alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490, and aircraft surface cleaning compound, MIL-C-43616, are toxic, irritating to the skin, and harmful to the eyes. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. Allow parts to air dry. Change 10 4-1 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 13. Blasting shall be to the extent required to remove foreign material and oxidation, but not to the extent to distort or remove metal, and shall be followed by thorough cleaning of blasting debris from blasting area. Surface treat part by Type VIII chromate treatment per MIL-M-3171. CAUTION Steel-plated parts having protective coatings, either cadmium, chromium, nickel, or zinc, must be cleaned using alkaline cleaner solution only. d. (1) Prepare alkaline cleaning solution using 6-8 oz. of alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490C, per nine gallons of water. (2) As an alternate solution, use one part aircraf t surface cleaning compound, MIL-C-43616, per nine parts of water. Maintain solution at a temperature of 160-180oF. (3) Immerse parts in cleaning solution for 5-20 minutes. (4) Remove parts from cleaning solution and immerse in clear, agitated water within 15 seconds or spray rinse with fresh water. (5) Pressure-wash parts with fresh water. (6) Dry parts with clean, lint-free cloth, MIL-C-85043, type II. (7) If part is a low-alloy steel, preserve immediately af ter rinsing as follows: (a) Dip or spray with corrosion preventive compound, MIL-C-16173, grade 4. (b) Allow parts to air dry. Cleaning Magnesium Parts. (1) Soak parts in silicate soap solution, MIL-M-7752, maintained at 190-200 oF for 10-15 minutes, (2) Rinse parts water. (3) Dry parts with clean, lint-free cloth, MIL-C-85043, type II. thoroughly with fresh e. Cleaning Titanium Parts. WARNING Methyl-ethyl-ketone, TT-M-261, and cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II, are toxic and f lammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. CAUTION Titanium parts must not come in contact with chlorinated solvents, chloride salts (including perspiration), methyl alcohol, silver and silver compounds, and cadmium. (1) WARNING Alkaline cleaner, MIL-C-87936, is toxic, irritating to the skin, and harmful to the eyes. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. (2) Prepare alkaline cleaning solution consisting of one part alkaline cleaner, MIL-C-87936, to nine parts of distilled or deionized water. Heat solution to 160-180oF in an air-agitated tank. (3) Immerse parts in alkaline cleaning solution for 3-5 minutes minimum. (4) Scrub surface of parts with a sof t-bristle brush, MIL-B-15319, type I, class 2, to remove surface contamination. (5) Rinse parts with fresh water. (6) Allow parts to air dry to remove excess water, then place parts in an oven set at 160-250oF for 1 hour. WARNING Dichromate Solution, MIL-M-3171, is toxic and harmful to the exposed skin. Avoid breathing vapors and avoid skin contact. PPE: Gloves, goggles/ faceshield, apron and adequate ventilation. (4) 4-2 Small or localized areas may be blasted with glass beads per MIL-G-9954, size Change 17 Remove excessive oils with cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II or III. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 f. Vapor Blasting Turbine Nozzle (2, f igure 3-10), Seal Plate (57), and Turbine Wheel (55). (1) Using masking tape, MIL-T-21595, mask any surface that can be damaged by blasting. (2) Ensure all open ports are closed with protective caps. (6) Glass bead, MIL-G-9954, peen corroded areas to remove corrosion. (7) Rinse surface free of glass beads with fresh water at 50-90oF. WARNING When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. WARNING (8) Cleaning solvent, P-D-680, type II, is toxic and f lammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. (3) g. Cleaning Reduction Drive Unit. (1) Remove all oil and grease from parts prior to vapor blasting by degreasing with P-D-680, type II or III. WARNING When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. (4) Dry parts with lint-free cloth, MIL-C-85043, type II, or dry with compressed air. WARNING . . Corrosion inhibitor, Rustlick 606, is toxic and f lammable. Do not breathe vapor. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. Dry parts with compressed air or in an oven at 250oF for 2 hours. Clean reduction drive unit housing (142, f igure 3-12) and accessory pad cover (108) as follows: (a) Soak parts in silicate soap solution, MIL-M-7752, at 190oF - 200oF for 1015 minutes. (b) Rinse thoroughly with fresh water. (c) Dry part with clean lint-free cloth, MIL-C-85043, Type II. WARNING Dichromate Solution, MIL-M-3171, is toxic and harmful to the exposed skin. Avoid breathing vapors and avoid skin contact. PPE: Gloves, goggles/ faceshield, apron and adequate ventilation. (d) Perform vapor blasting only in a suitable enclosure with protective doors and shields in place. Do not direct blasting nozzle at any part of the body. CAUTION Regulate nozzle air pressure to 70-90 psi to keep erosion of base metal to a minimum. Keep nozzle in motion to prevent blast from eroding any one spot. (5) Vapor blast using water containing 1/4-1/2 percent corrosion inhibitor, Rustlick 606. (2) Small or localized areas may be blasted with glass beads per MIL-G9954, size 13. Blasting shall be to the extent required to remove foreign material and oxidation, but not to the extent to distort or remove metal, and shall be followed by thorough cleaning of blasting debris from blasting area. Surface treat part by Type VIII chromate treatment per MIL-M-3171. Ultrasonically degrease reduction drive unit parts as follows: (a) Prepare ultrasonic cleaner using aqueous cleaner, MIL-C-87937, diluted to manufacturer specifications. Change 17 4-3 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (b) (c) WARNING Remove parts and rinse with fresh water. When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. WARNING (6) When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. Using compressed air, blow out residue of blasting material and carbon from external and internal surfaces. (7) Visually check internal passages to verify all material has been removed. (d) h. Immerse parts in ultrasonic cleaner until contamination has been removed. Dry parts with clean, lint-free cloth, MIL-C-85043, type II, or compressed air. WARNING Cleaning Combustor Housing. (1) Prepare ultrasonic cleaner using aqueous cleaner, MIL-C-87937, diluted to manufacturer specif ications. (2) Immerse combustor housing in ultrasonic cleaner until all traces of contamination have been removed. (3) Remove combustor housing and rinse with fresh water. (4) Cover all threaded bosses, inserts, and f ittings with pressure sensitive tape, MIL-T-22085, type II, or protective caps. Alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490, is toxic, irritating to the skin, and harmful to the eyes. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. CAUTION Steel-plated parts having protective coating, either cadmium, chromium, nickel, or zinc, must be cleaned using alkaline cleaner solution only. (8) Prepare alkaline cleaning solution per MIL-D-26549, using 6-8 oz. of alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490C, or equivalent, per nine gallons of water. Maintain solution at a temperature of 160-180oF. (9) Immerse combustor housing in alkaline cleaning solution for 3-5 minutes minimum. (10) Remove combustor housing and rinse with fresh water. WARNING Perform dry blasting only in a suitable enclosed area with protective doors and shields in place. Wear protective face shield and clothing. CAUTION WARNING Use care to avoid thinning of metal during blasting operation. When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. NOTE Clean bare metal indicates an acceptable degree of cleanliness. (5) 4-4 Using sof t abrasive grain, MIL-G-5634, or equivalent, vapor blast at 30-50 psig to remove all oxides and carbon deposits. Change 17 (11) i. Allow combustor housing to air dry or dry with compressed air. Cleaning Combustor Liner. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (7) Rinse combustor liner with fresh water. CAUTION To prevent damage to venturi throat and U-tubes, use care in cleaning combustor liner. (1) WARNING When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. Clean venturi throat (figure 4-1) using soft-bristle brush, MIL-B-15319, type I, class 2. Rotate brush to remove carbon deposits. (2) Prepare ultrasonic cleaner using aqueous cleaner, MIL-C-87937, diluted to manufacturer specifications. (3) Immerse combustor liner in ultrasonic cleaner until all traces of contamination have been removed. (4) Remove combustor liner and rinse with fresh water. WARNING Alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490, is toxic, irritating to the skin, and harmful to the eyes. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. CAUTION (8) j. Cleaning Oil Cooler. WARNING MIL-PRF-680 type 2/3 Dry Cleaning Solvent may cause eye and skin irritation. Over exposure may cause dizziness and other central nervous system effects. Wear nitrile gloves and chemical protective goggles. Dry cleaning solvent is manufactured by several companies, and its composition varies. Therefore, it is very important that you consult the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and local Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations for additional information. (1) Steel-plated parts having protective coatings, either cadmium, chromium, nickel, or zinc, must be cleaned using alkaline cleaner solution only. (5) (6) Prepare alkaline cleaning solution per MlL-D-26549, using 6-8 oz. of alkaline cleaner, TT-C-490C, or equivalent, one part per nine gallons of water. Maintain solution at a temperature of 160-180oF. Immerse combustor liner in alkaline cleaning solution for 3-5 minutes minimum. Allow combustor liner to air dry or dry with compressed air. Flush clean oil cooler with dry cleaning solvent until solvent flow is clear and particle free. WARNING When using air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. (2) Remove excess cleaning solvent from the oil cooler using clean compressed air. Change 24 4-5 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 4-1. 4-6 Change 17 Cleaning Combustor Liner T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SECTION V INSPECTION, REPAIR, AND REPLACEMENT 5-1. GENERAL This section covers inspection, repair, and replacement of all worn or damaged parts of the APU. Perform a visual inspection of all parts, checking for signs of wear, damage, cracks, and evidence of erosion, corrosion or pitting. Nondestructive inspection techniques will be accomplished per TO 33B-1-1, unless otherwise specified. a. Magnetic particle inspection is used to reveal near surface cracks in parts made of magnetic material. Table 5-1. Term b. Fluorescent penetrant (black light) inspection is used to detect surface cracks in parts made of non-magnetic material. c. Description terms used to describe the condition of parts are defined in Table 5-1. d. For replacement procedures, refer to Section III - Disassembly and Section VI - Assembly. e. Check that Unique Identification (UID) label on part number(s) identified in paragraphs 6-8 to 6-9 is present and readable. Manufacture or replace as required. Reference paragraphs 6-8 to 6-9 of this technical manual for supporting information. General Physical Conditions Definition Probable Cause Abrasion A roughened area, light to heavy, dependent upon amount of rework necessary to restore surface Foreign particles between moving parts Blistering Raised areas indicating separation of the surface from the base: usually found on plated or painted surfaces Imperfect bond with base, usually aggravated by presence of moisture, gas, heat, or pressure Break Complete separation by force into two or more pieces Fatigue, shock, or overload Brinelling Indentions occasionally found on surfaces of ball or roller bearing parts/shaft surfaces Improper assembly or disassembly technique Burning Injury to surface by excessive heat: evidence by discoloration or by flow or loss of metal Improper clearance or lack of lubrication due to plugged oil passages or other lubrication malfunctions Burr A sharp projection or rough edge Excessive wear; careless handling Chafing A rubbed action between two parts having limited motion Improper assembly techniques; improper fits Chipping Breaking out of small particles of metal Careless handling of parts; concentration of stresses due to shock, nicks, scratches, etc. Corrosion Breakdown or pitting of surfaces by chemical action Improper surface treatment, wear or damage on treated surfaces Crack A break in material Excessive stress due to shock, overloading or faulty processing: extension of a nick or scratch; damaged material or overheating Change 23 5-1 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-1. Term General Physical Conditions - Continued Definition Probable Cause Dent Small, smoothly rounded, hollow in surface Careless handling of parts Distortion A change from original shape Application of severe heat Erosion Wearing away of metal by the flow of hot gases, grit or chemical Flow of corrosive liquids, hot gases or grit-laden oil Fatigue failure Progressive damage as the stress on a piece is repeatedly applied and removed Stress at a surface nick or scratch Flaking Breaking away of pieces of a plated/painted surface Incomplete bond, excessive load or blistering Grooving Smooth, rounded furrows whose sharp edges have been polished off Concentrated wear: parts out of alignment Heat oxidizing (discoloration) Characterized by discoloring film. Color varies from yellow to brown and blue to purple. High temperature operation Nick A sharp indentation Careless handling or foreign particles in unit during operation Pitting Small indentions in a surface Breakdown of surface by chemical action (corrosion); or pressure of foreign material (mechanical) Scoring Deep scratches Presence of foreign particles between loaded surfaces having motion Scratch Narrow, shallow marks on surface Careless handling: foreign particles in unit during operation Stripped Part of thread is torn away Improper installation or thread size 5-2 Change 23 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-1. Term General Physical Conditions - Continued Definition Probable Cause Tear Parting of parent material Excess tension, caused by an external force Wear Slow removal of parent material Result of abrasive substances contacting rolling surfaces, and acting as a lapping compound 5-2. INSPECTION. A careful inspection to reveal any evidence of excessive temperature, deterioration or other damage, which may lead to eventual malfunction or failure, shall be made. Inspection procedures for the APU are covered in Table 5-2. Refer to Figure 3-2 through Figure 3-10, Figure 312, and Figure 3-28 for part identification. Inspection procedures for the fuel control and fuel pump Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. can be found in T.O. 6J3-4-112-3, for the starter in T.O. 2JA3-64-3, the IGV actuator in T.O. 6J3-8-193, and the surge control valve in T.O. 6J15-3-160-3. All parts listed in Table 5-2 with less than ten percent of painted surface flaked or chipped shall not be stripped and repainted. Inspection Requirements (APU) Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Air filter (Figure 3-2, 37, detail F) Check for contamination and obstructions No contamination or obstructions permitted None Replace air filter Check for leakage No leakage permitted None Pressure test air filter at 75 psig per AMS 2606. Replace air filter if leaking Visually inspect for cracks No cracks permitted None Weld cracks or holes in fusion zone only per Specification MILW-8611, using CRES welding rod Check screen for loose or broken wires No loose or damaged wires permitted Loose wires may be welded Weld loose wires at joints per ES9-63, class B. If wires are broken, replace screen Check sealing flanges for distortion of duct assembly No distortion permitted Sealing flanges may be straightened. No distortion permitted after straightening Straighten sealing flanges per T.O. 1-1A-1 Check for deterioration of cushion No deterioration permitted None Replace support clamps Check for cracks or distortion No cracks or distortion permitted None Replace support clamps. Air inlet duct (Figure 3-6, 13) Clamps, support (Figure 3-2) Change 22 5-3 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Containment ring (Figure 3-5, 37) Visually inspect pads on the containment ring extension for cracks and degradation None None Replace pads per Para. 5-3w(1)(6). Visually inspect. If damage is evident, check for cracks by fluorescent-penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, method A Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Weld cracks or holes in fusion zone only per MIL-STD-2219 using AWS 5.9, ER308L, ER316L or ER347 welding rods. Visually inspect mounting brackets for distortion No distortion permitted Distorted mounting brackets may be straightened. No distortion permitted after straightening Cold straighten mounting brackets. Check for cracks by fluorescent-penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, method A Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Braze repair cracks or holes in brazed joints using braze alloy per AMS 4777. Visually inspect for dents Dents are allowed up to an area of 4.00 square inches and less than 0.100 inch deep. Dents that exhibit a sharp crease are not allowable. The total number of dents is not limited; however, there must be a minimum separation of 1.00 inch between dents. Dents that are accessible may be cold worked. No creases permitted after cold working. Straighten and/or remove dents with a soft-faced mallet or replace duct as required. Duct assembly (Figure 3-5, 6 and 17) 5-4 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Duct assembly (6 and 17, figure 3-5) - continued Check for leakage No leakage permitted None Static pressure test duct assembly at 60-70 psig per AMS 2606. Replace duct assembly if leaking Check sealing flanges for distortion Maximum distortion permitted is 0.20 in. None Replace duct assembly if out of limits Check for wrinkles or dents in tubing of duct assembly (6) Wrinkles or dents shall not exceed 0.030 in. deep None Replace duct assembly (6) if out of limits Check for wrinkles or dents in tubing of duct assembly (17) Wrinkles or dents shall not exceed 0.150 in. deep None Replace duct assembly (17) if out of limits Check for deterioration No deterioration permitted Minor deterioration can be repaired Repair engine control harness per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check cable terminals for looseness Cable lugs must be secure None Tighten, repair, or replace cable lugs No corrosion None Replace connectors per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check connectors for bent or broken pins No bent or broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Repair connectors per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check for stripped or damaged threads No stripped or damaged threads permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase connector threads or replace connector if length allows per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check cover for dents and warpage No warpage permitted. Dents shall not exceed 0.040 in. deep Dents greater than 0.040 in. deep may be peened out Peen dents that exceed limits or replace fuel control enclosure cover Check for damaged or missing fasteners in cover No damaged or missing fasteners permitted None Replace damaged or missing fasteners No damaged gasket permitted None Replace damaged gasket Engine control harness (13, figure 3-2, detail A) Check connectors for corrosion permitted Fuel control enclosure cover (5, figure 3-4) Check for damaged gasket Change 11 5-5 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Check for cracks in cover No cracks permitted None Replace fuel control enclosure cover Check sealing flanges for distortion No distortion permitted Sealing flanges may be straightened. No distortion is permitted after straightening Straighten sealing flanges per T.O. 1-1A-1 Check for deterioration No deterioration permitted Minor deterioration may be repaired Repair fuel electronic harness per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check cable terminals for looseness Cable lugs must be secure None Tighten or replace connectors per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check connectors for corrosion No corrosion permitted None Replace connectors per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check connectors for bent or broken pins No bent or broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Repair fuel electronic harness per T.O. 1-1A-14 Check for stripped or damaged threads No stripped or damaged threads permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase threads per T.O. 1-1A-14 or replace connector if length allows No Obstruction None Clean per Section IV, Paragraph 4.3.b. No Obstructions None Clean per Section IV, Paragraph 4.3.c. Fuel electronic harness (16, figure 3-4) Air Flow Sensor Housing (25, figure 3-5) Visually inspect holes for obstructions Air Flow Sensor Fitting (22, figure 3-5) Visually inspect holes for obstructions 5-6 Change 11 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Fuel purge valve (25, Figure 3-2, detail B) Check connectors for bent or broken pins No broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Straighten bent pins per TO 11A-14 or replace fuel purge valve Check connector and valve body for corrosion Corrosion permitted if operation not affected None Remove corrosion per Section IV - Cleaning Check valve body for nicks, burrs, or scratches Nicks, burrs, or scratches repairable None Blend nicks, burrs, or scratches per Section 5-3a Check for cracks No cracks permitted None Replace fuel purge valve Check electrical connector for stripped or damaged threads No more than 4% of thread damage permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase threads or replace fuel purge valve Check for dents in valve body Dents that do not affect valve operation are permitted None Replace fuel purge valve if dents affect valve operation Check connectors for bent or broken pins No broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Straighten bent pins per TO 11A-14 or replace high-oil temperature switch Check for corrosion Corrosion permitted if operation not affected Check for stripped or damaged No more than 4% of thread damage permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase threads per TO 1-1A-14 or replace high-oil temperature switch Check for nicks, burrs, or scratches Nicks, burrs, or scratches repairable None Lend nicks, burrs, or scratches per Section 5-3a Damage shall not exceed 3% of total core face area or 1.5 linear inch fin damage on core face None Contact Engineering for disposition instructions High-oil temperature switch (57, Figure 3-2, detail G) Remove corrosion per Section IV - Cleaning Oil cooler (76, Figure 3-2, detail I) Check cooler for fin damage Change 24 5-7 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Oil cooler (76, Figure 3-2, detail I) Continued Threaded surfaces and fittings for crossed, stripped, galled or worn threads None -- Contact Engineering for disposition instructions Brackets (84, 85, and 86, Figure 3-2, detail I) None None Contact Engineering for disposition instructions Hoses (81 and 82, Figure 3-2, detail I) None None Contact Engineering for disposition instructions Check hourmeters and event counter for broken or cracked glass No broken or cracked glass permitted None Replace hourmeters or event counter Check for dents and deformation of hourmeter junction box Dents or deformation permitted if operation not affected None Replace hourmeter junction box Check for nicks and scratches on hourmeter junction box Nicks and scratches permitted if operation not affected None Treat per Specification MIL-C5541 Check for wear Ensure that no tinnickel plating is worn through None Replace IGV drive link Check for movement of each ball Each ball must move freely None Replace IGV drive link Check for misalignment of link bearings Angle of misalignment shall not exceed 20o None Replace IGV drive link if out of nits Hourmeter junction box assembly (18, Figure 3-8) IGV drive link (8, Figure 3-7) 5-8 Change 24 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Ignition cable (Figure 3-5, 27) Check for frayed braiding No frayed braiding permitted None Replace ignition cable Check for stripped threads No stripped threads permitted None Replace ignition cable Check insulator or terminals for damage No damage permitted None Replace ignition cable Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, Type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace inlet housing manifold Check for leakage in internal passages No leakage permitted None Hydrostatic pressure test internal passages at 40-50 psi per AMS 2606. If leakage occurs, impregnate per MIL-STD-276. Check connector for bent or broken pins No broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Straighten bent pins per T.O. 11A-14 or replace oil pressure switch Check connector and switch body for corrosion Corrosion permitted on switch body if operation not affected None Remove corrosion per Section IV - Cleaning and anodize treat per Specification MIL-A-8625, type II, class 1. Replace oil pressure switch if operation affected Perform functional check None None Functional check per Section 53e. Replace oil pressure switch if operation affected Inlet housing manifold (Figure 3-6, 3) Oil pressure switch (Figure 3-3, 18) Change 22 5-9 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued lnspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Oil pressure switch (18, figure 3-3) - continued Check oil pressure connection for damaged or stripped threads No more than 4% of thread damage permitted Damaged threads nay be chased Chase threads per TO 1-1A-14 or replace oil pressure switch Check switch body for nicks, burrs, or scratches Nicks, burrs, or scratches permitted if operation not affected None Remove nicks, burrs, or scratches per Section 5-3a. Replace oil pressure switch if operation affected Check for dents, distortion, or cracks Dents and distortion permitted if Operation not affected. No cracks permitted None Replace oil pressure switch if operation affected Check for nicks and scratches Nicks and scratches permitted None Treat per MIL-C-5541 Visually check for cracks No cracks permitted Cracks less than 1 in. may be welded. Cracks in excess of 1 in. shall be cause for rejection Weld aluminum alloy cracks as required per TO 1-1A-9 and grind to return to original contour. Treat per MIL-C-5541 No broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Straighten bent pins per TO 1-1A-14 or replace temperature sensor Reduction drive cover (16, figure 3-3) Temperature sensor (13, figure 3-6) Check connectors for bent or broken pins 5-10 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) -Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) Check for damage or distortion No damage or distortion permitted None Replace thermocouple harness Check B-nut for stripped threads No stripped threads permitted None Replace thermocouple harness Check tubing for chafing, kinks, cracks, twisting or distortion No chafing, kinks, cracks, twisting or distortion permitted None Replace tube assembly Check for obstructions No obstructions permitted None Remove any obstructions with low pressure air (30 psig) Check for corrosion No corrosion permitted None Remove corrosion per Section IV Cleaning Check B-nuts for cracks or stripped threads No cracks or stripped threads permitted None Replace tube assembly Visually check flared tubing for cracks No cracks permitted None Replace tube assembly Check for nicks, burrs or scratches Nicks, burrs or scratches permitted Nicks, burrs or scratches shall not exceed 0.030 in. long Blend nicks, burrs or scratches per Section 5-3a Check for dents, distortion or cracks Minor dents and distortion permitted if operation not affected. No cracks permitted None Replace turbine ignition exciter if operation affected Tube assemblies (figure 3-2) Turbine ignition exciter (31, figure 3-5) Change 6 5-11 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Turbine ignition exciter (Figure 3-5, 31) - continued Check connectors for corrosion No corrosion permitted None Remove corrosion per Section IV - Cleaning Check connectors for bent or broken pins No bent or broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Straighten pins per T.O. 1-1A-14 or replace turbine ignition exciter Check for stripped or damaged No stripped or damaged threads permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase threads per T.O. 1-1A-14 or replace turbine ignition exciter Perform functional check for spars per Section 5-3m Spark rate shall be a minimum of 2.7/ second at 28 Vdc and maximum input current is 1.0 A None Replace turbine ignition exciter if out of limits Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method D, Sensitivity Level 4 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace adapter assembly if out of limits Visually check for obstructions in passages No obstructions permitted None Remove any obstructions with low pressure air (30 psig) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method D, Sensitivity Level 4 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace adapter assembly if out of limits Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on machined surfaces Minor nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks, burrs, and scratches less than 0.020 inch, may be repaired Blend nicks, burrs, and scratches per Section 5-3a and treat per Specification MIL-C-5541 Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on nonmachined surfaces Minor nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks, burrs, and scratches less than 0.020 inch may be repaired Treat per Specification MIL-C5541 TURBINE ASSEMBLY (Figure 3-10) Adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17) 5-12 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Bearing aft carrier (Figure 3-10, 53) Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, class B No cracks permitted None Replace bearing aft carrier Check oil passages for obstructions No obstructions permitted None Remove any obstructions with low pressure air (30 psig) Visually check bearing bore diameter for signs of race rotation Make sure diameter and flatness meet original dimensions Maximum diameter is 1.5751 inch (Figure 5-1, dimension A). Runout shall not exceed 0.0002 inch (Figure 5-1, area B) Electroless nickel plate per AMS 2404 to original dimensions Check sleeve of bearing aft carrier assembly for wear, scoring, scratches, nicks, and burrs Minor wear, scoring, scratches, nicks or burrs permitted Maximum inside diameter is 1.6038 inch, installed in inlet housing (Figure 5-1, dimension C) Sleeve of bearing aft carrier is non-separable. Replace bearing aft carrier Check housing for nicks, burrs, scratches, and corrosion Nicks, burrs, scratches, and corrosion repairable None Blend nicks, burrs, scratches, and corrosion per Section 5-3a Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade B No cracks permitted None Replace bearing front carrier Check oil passages for obstructions No obstructions permitted None Pressure wash passages to remove any obstructions Check for nicks and scratches Minor nicks and scratches repairable Nicks and scratches shall not exceed 0.200 inch long, 0.050 inch wide, and 0.020 inch deep Electroless nickel plate per AMS 2404 to original dimensions Check pin for looseness No looseness permitted None Replace pin if loose per T.O. 11A-1 Bearing front carrier (Figure 3-10, 7) Change 22 5-13 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Bearing front carrier (Figure 3-10, 7) - continued Check that inside diameter of bearing front carrier is within limits Inside diameter shall not exceed 1.344 inch (Figure 5-2, dimension A) Coating thickness shall not exceed 0.070 inch after machining. Drill 12 holes 0.075-0.080 inch through abradable coating (Figure 5-2, area F) Abradable coat using Metco 601 NS powder per AMS 2437 to restore to original dimensions. Repair per paragraph 5-3aa. Visually check plating for corrosion (Figure 5-2, dimensions B, C, D, and E) Minor corrosion repairable None Electroless nickel plate per AMS 2404 to restore to original dimensions Visually check bearing bore diameters for signs of race rotation Make sure diameter and flatness meet original dimensions Maximum diameter is 1.5751 inch (Figure 5-2, dimension C). Runout shall not exceed 0.0002 inch Electroless nickel plate per AMS 2404 to restore to original dimensions Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace diffuser if out of limits Check for nicks and scratches on vane leading edges Minor nicks and scratches permitted Nicks and scratches shall not exceed 0.016 inch deep or 0.125 inch long Replace diffuser if out of limits Check vane throat diameters (17 places) Vane throat area average diameter shall not exceed 0.463 inch. Measure diameter 0.16 −0.190 inch from root of vane None Replace diffuser if out of limits Check for roundness of outside diameter Outside diameter may have a free state variation of 0.04 inch roundness on diameter None Replace diffuser if out of limits Diffuser (Figure 3-10, 41) 5-14 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Diffuser housing (Figure 3-10, 45) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection per ASTM E1417; using type I, Method A, B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials. No cracks allowed None Replace diffuser if out of limits Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on machined surfaces Nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable None Blend nicks, burrs, and scratches per paragraph 5-3a. Treat reworked surfaces per paragraph 5-3p. Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on nonmachined surfaces Nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable None Treat surfaces per paragraph 53p. Check for loose thread inserts No loose thread inserts permitted Inserts must be flush with housing surface Replace inserts Check for local compressor rub on profile Minor rub repairable on surface A, Figure 5-3 Not to exceed 0.005 inch in depth Remove burrs and raised edges with abrasive cloth. (Federal Specification PC-458). Do not blend. Touch up exposed surfaces per paragraph 5-3p Check for rub damage on profile and scoring on throat are due to contact with inducer Major rub repairable, surface A, Figure 5-3 Not to exceed 0.033 inch in depth Plasma spray using Metco 450 to restore to original dimensions. See paragraph 5-3z. Check for damage/ out-of-roundness on the 11.100-11.104 inch diameter Damage/out-ofroundness repairable Not to exceed 11.185 inches diameter Plasma spray using Metco 450 to restore to original dimensions. See paragraph 5-3z. Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace engine compressor wheel if out of limits Diffuser housing (Figure 3-10, 45) Engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method A, B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Change 25 5-15 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Check for nicks or scratches on blades and air passages Minor nicks and scratches repairable Nicks or scratches shall not exceed 0.030 inch long or 0.005 inch deep Blend nicks and scratches per Section 5-3a and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check for broken or missing blades No broken or missing blades permitted None Replace engine compressor wheel Check diamond knurl for wear. Measure outer diameter (OD) of the knurl No wear permitted. Diameter shall be 1.5985 - 1.5990 inches See paragraph 53f(1) Repair diamond knurl per Section 5-3f(1) as required Check blade tuning First mode frequencies of all long blades shall be 1950-2500 Hz. Second mode shall not fall between 59006600 Hz None Blade tune engine compressor wheel per Section 5-3f(3) and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check for rub marks Minor rub marks acceptable if balanced, finished, machined surfaces, and tuning within limits None Remove minor rub marks per Section 5-3a and balance per Section VI - Assembly Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace inlet guide vane if out of limits Corrective Action Engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60) - continued Inlet guide vane (Figure 3-10, 39) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials. Only vane airfoil needs to be inspected. Items 37-40 (Figure 3-10) do not need to be disassembled to NDI IGV airfoil section 5-16 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Inlet guide vane (Figure 3-10, 39) - continued Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches Nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks shall not exceed 0.030 inch on vane edges Blend nicks, burrs, and scratches per Section 5-3a No damage permitted None Replace labyrinth seal Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials for all non-rotating parts Acceptance criteria per Specification MIL-P-47158, Table III, Method C None Replace load compressor diffuser Check for bent or broken vanes Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace load compressor diffuser Check for nicks and scratches on vane leading edge Minor nicks and scratches permitted Nicks and scratches shall not exceed 0.016 inch deep or 0.125 inch long (Figure 5-4, dimension A) Replace load compressor diffuser if out of limits Check vane throat area diameter (19 places) Vane throat area average diameter shall not exceed 0.307 inch at 0.190 inch from vane root (Figure 5-4, dimension B) None Replace load compressor diffuser if out of limits Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace load compressor scroll if out of limits Labyrinth seal (Figure 3-10, 52) Check for nicks, scratches, wear or other damage Load compressor diffuser (Figure 3-10, 18) Load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Change 22 5-17 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23) - continued Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on machined surfaces Nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable None Blend nicks, burrs or scratches per Section 5-3a and treat per Specification MIL-C-5541 Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches on nonmachined surfaces Nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable None Treat per Specification MIL-C5541 Check for broken or missing blades No broken or missing blades permitted None Replace load compressor wheel Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method D, Sensitivity Level 4 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace load compressor wheel if out of limits Check for nicks or scratches on vanes and air passages Minor nicks and scratches repairable Nicks or scratches shall not exceed 0.030 inch long or 0.005 inch deep Blend nicks and scratches per Section 5-3a, shotpeen per Section 5-3f(2), and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check for rub marks Minor rub marks on blade ends acceptable if balance, finished, machined surfaces, and tuning within limits None Blend rub marks in a radial direction per Section 5-3a and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check blade tuning All blades must have a first mode frequency of 43504600 Hz None Blade tune load compressor wheel per Section 5-3f(3) and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check seal (21) for wear, nicks or damage No wear, nicks or damage permitted. Inspection criteria per Figure 5-27 None Replace seal (21). Install new seal per paragraph 6-5e(1) No damaged threads or broken pins permitted Bent pins may be straightened Chase damaged threads and straighten bent pins per T.O. 11A-14 Load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20) Magnetic pickup (Figure 3-10, 3) Check connector for damaged threads and broken or bent pins 5-18 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Magnetic pickup (Figure 3-10, 3) - continued Check for cracks or dents in pole piece No cracks or dents permitted None Replace magnetic pickup Check resistance between J304 pins A to B 1190-1450 ohms None Replace magnetic pickup Change 22 5-19 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Pinion assembly (5, figure 3-10) Check gear teeth for wear No wear permitted None Replace pinion assembly Check for chips or cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M-47230, grade A No chips or cracks permitted None Replace pinion assembly Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace pinion assembly if out of limits Check for pitting on gear teeth Pitting on tooth contact area shall not exceed 0.010 in. deep and 4% of tooth contact pattern None Replace pinion assembly if out of limits Check for loose or missing oil retainer Loose or missing oil retainer not permitted None Replace pinion assembly Check measurement of external involute spline Minimum pinion diameter is 0.5517 in. None Measure external involute spline between two pins of 0.060 in. diameter. Ensure pins are flush to surface of splines. Replace pinion assembly if out of limits Check for wear on external spur gear Minimum pinion diameter is 0.7543 in. None Measure external spur gear spline wear between two pins of 0.0657 in. diameter. Ensure pins are flush on surface of spline. Replace pinion assembly if out of limits 5-20 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Rotor shaft (59, figure 3-10) Check for worn, damaged, or stripped threads No more than 4% of thread damage permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase damaged threads per T.O. 1-1A-14 or replace rotor shaf t Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MILSTD-1907, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace rotor shaf t Check for nicks and scratches Nicks and scratches repairable None Blend nicks and scratches per Section 5-3a and balance per Section VI - Assembly Visually check nickel-plated surfaces for pitting, erosion, or scoring No pitting, erosion, or scoring permitted at bearing, load compressor, or labyrinth seal journals Minimum plating thickness is 0.002 in. Finish shall be 16 microinches Repair minor damage by hand polishing while maintaining minimum diameter limits. If minimum diameter limits cannot be maintained, repair per Section 5-3s, 5-3t, or 5-3u as applicable Check surface for corrosion, pitting, or erosion Corrosion, pitting or erosion shall not exceed 0.020 in. deep None Replace seal plate if out of limits Visually check spot welds and diaphragms for cracks No cracks permitted None Replace seal plate Check for signs of compressor wheel rub at inside diameter Minimum inside diameter is 1.6761.674 in., and up to 0.020 in. deviation in diameter roundness is permitted (f igure 5-6, dimension A) None Replace seal plate Check for warpage Maximum diaphragm protrusion from seal plate is 0.025 in. None Seal plate (57, Figure 3-10) Replace seal plate Change 17 5-21 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Stud (Figure 3-10, 15) Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace stud Check for damaged threads No damaged threads permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase damaged threads per T.O. 1-1A-14 or replace stud Check for damaged threads None allowed None Replace stud Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials No cracks permitted None Replace Stud Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace inlet housing and support housing as a matched set Check for nicks, burrs, and scratches Minor nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks, burrs, and scratches shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep, 0.015 inch wide, or 0.250 inch long Blend nicks, burrs, and scratches per Section 5-3a Check helical coil inserts for looseness Inserts shall not be less than 3/4 turn below flange surface None Replace inserts per T.O. 1-1A-8 Dimensionally inspect 1.800 inch bore area (Figure 5-26) 1.7997 to 1.8003 1.804 Restore to original dimensions in accordance with Section 5-3r Stud (Figure 3-10, 58) Support housing and inlet housing, matched set (Figure 3-10, 30 and 31) 5-22 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Turbine nozzle (Figure 3-10, 2) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace turbine nozzle if out of limits Check vane passages for nicks, scratches, and erosion Minor nicks, scratches, and erosion repairable Nicks, scratches or erosion shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 0.015 inch wide (Figure 5-7, dimension E) Repair per Section 5-3h Check vane throat area diameter (17 places) Vane throat area average diameter shall not exceed 0.464 inch diameter over 17 places None Replace turbine nozzle if out of limits Check radial runout for surface deviations Radial runout of any surface deviations shall not exceed 0.010 inch total in any two inch circumferential increment. Minimum diameter is 10.048 inch (Figure 5-7, dimension D) A coating thickness of 0.020 - 0.060 inch is acceptable Restore to original dimensions per Section 5-3h Check that inside profile is within contour Inside profile to be within 0.0035 inch from basic contour of 0.765 radius (Figure 5-7, dimension A) and inside diameter of 4.975 inch (Figure 5-7, dimension C) None Replace turbine nozzle if out of limits Check for signs of turbine wheel rub Minor rub marks removable. No more than 3 rub marks permitted Rub marks shall not exceed 0.020 inch deep (Figure 5-7, dimension B) Repair per section 5-3h. Replace turbine nozzle if out of limits Change 22 5-23 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Turbine wheel (Figure 3-10, 55) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method D, Sensitivity Level 4 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace turbine wheel if out of limit Check for bore cracks using eddy current method per Section 5-3g No cracks permitted None Replace turbine wheel Check for broken or missing blades No broken or missing blades permitted None Replace turbine wheel Check for nicks and scratches Minor nicks and scratches permitted Nicks and scratches shall not exceed 0.015 inch wide or 0.075 inch long Blend nicks and scratches per Section 5-3a and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check for erosion Minor erosion permitted Overall diameter shall not be less than 6.416 inch Replace turbine wheel Check blade tuning All blades must have a first mode frequency of 34003650 Hz None Blade tune turbine wheel per Section 5-3f(3) and balance per Section VI - Assembly Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace accessory drive pinion Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped gear teeth permitted None Replace accessory drive pinion Check for scoring Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace accessory drive pinion if out of limits REDUCTION DRIVE UNIT (Figure 3-12) Accessory drive pinion (Figure 3-12, 52) 5-24 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Accessory drive pinion (Figure 3-12, 52) - continued Check for pitting Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact pattern None Replace accessory drive pinion if out of limits Check bore for wear Maximum diameter shall not exceed 0.5886 inch (Figure 5-8, dimension A) None Replace accessory drive pinion if out of limits Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace accessory gear Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace accessory gear Check for wear of shaft (2 places) Minimum diameter is 0.4723 inch (Figure 5-9, dimension A) None Replace accessory gear if out of limits Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace accessory gear if out of limits Check for scoring on shaft Scoring shall not exceed 0.005 inch deep and must not affect bearing fit 0.438 inch diameter, 0.405 inch length on internally-splined end Repair accessory gear per Section 5-3x. Replace accessory gear if out of limits Check for pitting on gear teeth Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact pattern None Replace accessory gear if out of limits Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace bevel gear support if out of limits Accessory gear (Figure 3-12, 120) Bevel gear support (Figure 3-12, 40) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Change 22 5-25 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Check housing for nicks, burrs, and scratches Minor nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks and scratches shall not exceed 0.10 inch deep or 0.1 inch wide Blend nicks, burrs or scratches per Section 5-3a Check bearing bores for signs of bearing race rotation No race rotation permitted None Replace bevel gear support liners per Section 5-3l Check for loose helical coil inserts Inserts shall not be less than 3/4 turn below flange surface None Replace loose inserts per T.O. 11A-8 Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace bypass valve housing if out of limits Check for nicks and scratches Nicks and scratches repairable None Blend nicks and scratches per Section 5-3a and treat with Specification MIL-C-83286 or Specification MIL-C-85285 Check passages for obstructions No obstructions permitted None Remove any obstructions with low pressure air (30 psig) Check for cracks and through porosity by fluorescent penetrant inspection ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace carrier assembly and cover as a matched set if out of limits Check for nicks or scratches Minor nicks or scratches repairable Nicks or scratches or erosion shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 0.01 inch long Blend nicks or scratches per Section 5-3a Corrective Action Bevel gear support (Figure 3-12, 40) - continued Bypass valve housing (Figure 3-12, 6) Carrier assembly (Figure 3-12, 60) (Matched set with cover, Figure 3-12, 63) 5-26 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Carrier assembly (Figure 3-12, 60) (Matched set with cover, Figure 3-12, 63) - continued Check for obstructions in holes and passages No obstructions permitted None Pressure wash to remove any obstructions Check for wear in bearing sleeves and shaft bore Maximum sleeve diameter shall not exceed 1.3788 inch in 3 places (Figure 5-10, dimension A) None Replace sleeve per Section 5-3j Flow check oil jet cartridge per ASTM 2422 All four jets of cartridge must flow freely. Total flow is 0.3-0.5 gpm at 20 psi None Flow test oil jet cartridge per Section 5-3d(3) Check oil jet cartridge and spring pin for looseness or damage No looseness or damage permitted None Replace oil jet cartridge and spring pin per Section 5-3j(1) Check for cracks and through porosity by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace cover and carrier assembly as a matched set if out of limits Check for scratches and scoring Minor scratches and scoring repairable Scratches and scoring shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep or 0.250 inch long Blend scratches and scoring per Section 5-3a and dichromate treat per Specification MIL-M3171, type I or VI Check for obstructions in holes and passages No obstructions permitted None Pressure wash to remove any obstructions Check bearing sleeve and inside diameter Maximum inside diameter shall not exceed 1.3788 inch in 3 places (Figure 5-11, dimension A) None Replace sleeve per Section 5-3j Cover (Figure 3-12, 63) (Matched set with carrier assembly, Figure 3-12, 60) Change 22 5-27 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Cover (Figure 3-12, 63) (Matched set with carrier assembly, Figure 3-12, 60) - continued Check bearing bore inside diameter Maximum inside diameter shall not exceed 1.2604 inch (Figure 5-11, dimension B) None Replace cover and carrier assembly as a matched set if out of limits Minor wear permitted. No elongated pin holes permitted Wear limits shall not exceed those specified in Table 5-3 Replace driver/driven shaft if out of limits Inspect for silver braze repairs Silver braze shall be removed None Passivate oil sump as required to remove silver braze in accordance with AMS 2700, Method 1, type 6. Replace oil sump if silver braze has not been removed after two attempts. Furnace braze as required in accordance with AWS C3.6 Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Weld cracks or holes in fusion zone only per Specification MILW-8611, using Specification MIL-R-5031, class 7 welding rod Check for leakage using Figure 5-29 diagram and instructions No leakage permitted None Hydrostatic pressure test at 5 psi per AMS 2615. Replace engine oil sump if leaking Check lockwire tab holes for tears No tears permitted None Weld repair or replace tabs per Specification MIL-W-8611, using Specification MIL-R-5031, class 7, welding rod Check sealing flanges for warpage No warpage permitted Warped flanges may be straightened Straighten warped flanges per T.O. 1-1A-1 Check enging oil sump for dents Dents shall not exceed 0.20 inch long and 0.040 inch deep None Straighten dents per T.O. 1-1A-1 Driver/driven shaft (Figure 3-12, 37 and 38) Check shaft diameter and for elongated pin holes Engine oil sump (Figure 3-12, 22) 5-28 Change 25 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Gear planet set (Figure 3-12, 65) Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace gear planet set (all 3) Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace gear planet set (all 3) if out of limits Check for scoring on shaft Scoring shall not exceed 0.005 inch deep and must not affect bearing fits None Replace gear planet set (all 3) if out limits Check for wear of shaft (2 places) Minimum diameter is 0.5905 inch (Figure 5-12, dimension A) None Replace gear planet set (all 3) if out of limits Check for wear on external spur gear Minimum diameter of gear is 2.3055 inch None Measure diameter of gear over 0.06565 inch diameter pins. Ensure measurement pins reflect true diameter by being flush to surface of gear teeth. Replace gear planet set (all 3) if out of limits Check for pitting on gear teeth Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact pattern None Replace gear planet set (all 3) if out of limits Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace gear planet set (all 3) Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace housing if out of limits Housing (Figure 3-12, 142) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B, C or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials. Inspect all non-painted areas including bearing seats, bolt holes, and web Change 22 5-29 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Housing (Figure 3-12, 142) - continued Visually check bearing bores for bearing race rotation Make sure diameter and flatness meet original dimensions None Replace housing sleeves per Section 5-3i Check housing for nicks, burrs or scratches Nicks, burrs or scratches are repairable Nicks, burrs or scratches shall not exceed 0.100 inch long or 0.030 inch deep Blend nicks, burrs or scratches and treat per Section 5-3a Check for wear on main output pad bearing sleeve Inside diameter of output pad bearing sleeve shall be 2.1665 - 2.1653 inch None Replace sleeve per Section 5-3i if out of limits Check for loose helical coil inserts Inserts shall not be less than 3/4 turn below flange surface None Replace inserts that are loose or out of limits per T.O. 1-1A-8 Check for wear, corrosion, scratches, out-ofroundness, out-ofconcentricity of 6.000 - 6.002 inch diameter Wear spots are permitted except within 0.500 inch around oil passage hole. Corrosion pits are acceptable up to 0.010 inch deep by 0.125 inch diameter. Scratches deeper than 0.010 inch deep and up to 0.250 inch in length are acceptable in other areas. Out of roundness or out of concentricity greater than 0.0005 TIR are not acceptable except in local wear spots. None Repair housing per paragraph 53v Inspect air oil separator sleeve (Figure 3-12, 140) retaining pins for looseness or protrusion from sleeve No looseness or protrusion of pin None Repair per paragraph 5-3y 5-30 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Housing (Figure 3-12, 142) - continued Inspect for sealant between air-oil separator sleeve (Figure 3-12, 140) and reduction drive housing (Figure 312, 142), denoted by an ‘‘R’’ etched on the sleeve Presence of sealant NA Apply sealant as required per paragraph 5-3y Check for cracks or through porosity by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace housing carrier Check housing for nicks, burrs, and scratches Minor nicks, burrs, and scratches repairable Nicks, burrs or scratches shall not exceed 0.1 inch long or 0.01 inch deep Blend nicks, burrs or scratches and treat per Section 5-3a Check bearing bores for bearing race rotation No race rotation permitted None If indication of race rotation, replace liner per Section 5-3k Check for loose helical coil inserts Inserts shall not be less than 3/4 turn below flange surface None Replace inserts that are loose or out of limits per T.O. 1-1A-8 Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace hub ring gear Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace hub ring gear Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace hub ring gear if out of limits Housing carrier (Figure 3-12, 77) Hub ring gear (Figure 3-12, 85) Change 22 5-31 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Hub ring gear (Figure 3-12, 85) - continued Check for pitting on gear teeth Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact pattern None Replace hub ring gear if out of limits Check for wear on external splines Minimun diameter of gear is 1.8585 inch None Measure diameter of gear over 0.0864 inch diameter pins. Ensure measurement pins reflect true diameter by being flush to surface of gear teeth. Replace hub ring gear if out of limits Check for wear in bore of gear Maximum diameter is 0.9694 inch (Figure 5-13, dimension A) None Replace hub ring gear if out of limits Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, Specification MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace intermediate gear Check for pitting on gear teeth Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact pattern None Replace intermediate gear if out of limits Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace intermediate gear Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace intermediate gear if out of limits Check for wear on inside diameter of gear Maximum diameter is 1.378 inch (Figure 5-14, dimension A) None Replace intermediate gear if out of limits No cracks permitted None Replace intermediate gear shaft Intermediate gear (Figure 3-12, 117) Intermediate gear shaft (Figure 3-12, 113) Check for cracks by magnetic particl inspection, Specification MIL-M-47230, grade A 5-32 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Intermediate gear shaft (Figure 3-12, 113) continued Check outside diameter of shaft Minimum shaft diameter is 0.5899 inch None Replace intermediate gear shaft if out of limits Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Replace oil pump housing if out of limits Oil pump housing (Figure 3-12, 26) Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials Change 22 5-33/(5-34 blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Oil pump housing (26, figure 3-12) - continued Check for nicks or dents No nicks or dents permitted None Replace oil pump housing Check for wear or elongated shaft holes Minor wear permitted. No elongated shaft holes permitted (figure, 5-15) Wear limits shall not exceed those specified in table 5-3 Replace oil pump housing if out of limits Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace pump drive gear Check for pitting on gear teeth Pitting on tooth contact area shall not exceed 0.010 in. deep and 4% of individual gear tooth contact pattern None Replace pump drive gear if out of limits Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace pump drive gear if out of limits Check for chipped teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace drive gear Check for wear on gear teeth Minimum diameter is 2.6078 in. (figure 5-16, dimension A) None Measure drive gear diameter over 0.0864 in. diameter pins. Ensure measurement pins reflect true diameter by being flush to surface of gear teeth. Replace pump drive gear if out of limits Pump drive gear (33, figure 3-12) 5-35 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Pump drive gear (33, figure 3-12) - continued Maximum diameter is 0.2505 in. (figure 5-16, dimension B) None Replace pump drive gear if out of limits Check for cracks in teeth by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M-47320, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace both pump element gears Check for scoring and chipped gear teeth No scoring permitted. No chipped teeth permitted None Replace both pump element gears Check for wear on gear teeth and/or housing Gear to housing clearance not to exceed 0.004 in. (see figure 5-15, table 5-3, ref. 15) None Replace both pump element gears or housing if necessary Check gear bore inside diameter Pump element gear (36, figure 3-12) Ring gear (69, figure 3-12) None Replace ring gear Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped gear teeth permitted None Replace ring gear Check for scoring Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace ring gear if out of limits 5-36 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Ring gear (69, figure 3-12) - continued Check for pitting Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 in. deep and 4% of tooth contact pattern None Replace ring gear if out of limits Check for wear on internal spur gear teeth Maximum diameter is 5.0503 in. None Measure diameter of ring gear between 0.06382 in. diameter pins. Ensure measurement pins are flush to surface. Replace ring gear if out of limits Check for wear on internal involute spline Maximum diameter is 1.6313-0.0864 in. diameter None Measure diameter of involute spline teeth between pins. Ensure measurement pins are flush to surface. Replace ring gear if out of limits Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace straight drive shaft Check for worn or damaged threads No worn or damaged threads permitted Damaged threads may be chased Chase threads per TO 1-1A-14 or replace straight drive shaft Check wear of internal splines Maximum shaft diameter is 0.6790 in. None Measure inside diameter of internal spline between 0.0864 in. diameter pins. Ensure pins are flush with splines. Replace straight drive shaft if out of limits Straight drive shaft (78, figure 3-12) 5-37 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Zerol bevel gear (45, figure 3-12) Check for cracks in teeth by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M-47320, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace Zerol bevel gear Check for pitting on gear teeth Minor pitting not to exceed 0.010 in. deep and 4% of tooth contact pattern None Replace Zerol bevel gear if out of limits Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped teeth permitted None Replace Zerol bevel gear Check for scoring on gear teeth Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace Zerol bevel gear if out of limits Check for wear on gear teeth No abnormal wear permitted None Replace Zerol bevel gear Check for wear on internal spline Maximum diameter of internal spline is 0.679 in. None Measure inside diameter of internal spline between 0.0864 in. diameter pins. Ensure pins are flush with splines. Replace Zerol bevel gear if out of limits Check for cracks by magnetic particle inspection, MIL-M47230, grade A No cracks permitted None Replace Zerol pinion Check for chipped gear teeth No chipped gear teeth permitted None Replace Zerol pinion Zerol pinion (91, figure 3-12) 5-38 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Zerol pinion (Figure 312, 91) - continued Check for pitting Minor pitting shall not exceed 0.010 inch deep and 4 percent of tooth contact patter None Replace Zerol pinion if out of limits Check for scoring Slight scoring is permitted 1/3 the way in from tip of teeth None Replace Zerol pinion if out of limits Check bore for wear Maximum diameter shall not exceed 1.0005 inch (Figure 5-17, dimension A) None Replace Zerol pinion if out of limits Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, Type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials (Figure 5-18) Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Braze cracks per Section 5-3n Check for warping of housing forward and aft flanges No warpage permitted Flanges may be straightened Straighten flanges per T.O. 11A-1 Check for burn deformation between manifold bosses or in tail cone No burn deformation permitted between manifold bosses or in tail cone None Replace combustor housing assembly Check for leakage using penetrant, Specification MILI-25135, type I, method A, level 2, to interior surfaces only No leakage permitted to exterior surface None Braze cracks per Section 5-3n COMBUSTOR ASSEMBLY (Figure 3-28) Combustor housing (Figure 3-28, 17) Change 22 5-39 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Combustor housing (17, figure 3-28) Continued Check combustor housing alignment, igniter plug alignment, and injector alignment No misalignment permitted None Check housing alignment, igniter plug alignment, ring alignment, and injector alignment using inspection f ixture, ST62880 (10, f igure 2-1). Replace combustor housing if out of limits Check that all ports are free of foreign objects No foreign objects permitted None Remove any foreign objects using low pressure air (30 psig) Check for wear on combustor housing diffuser Inside diameter of housing diffuser is 5.098 - 5.103 in. (f igure 5-18, dimension A) (average of four places) None Using inspection f ixture, ST62880 (10, f igure 2-1), measure diameter of combustor housing diffuser. Replace combustion housing if out of limits Check for wear on tail cone of combustor housing assembly Outside diameter of tail cone is 6.672 6.702 in. (f igure 5-18, dimension B) (average of four places) None Using inspection f ixture, ST62880 (10, f igure 2-1), measure tail cone diameter of combustor housing. Replace combustor housing if out of limits Check for damaged thermocouple boss No damage permitted None Repair thermocouple boss per paragraph 5-3n. (3) 5-40 Change 17 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspect/ Item No. Inspection Requirements (APU) - Continued Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Combustor liner (Figure 3-28, 15) Check atomizer fittings for clogs or restrictions No clogs or restrictions permitted None Flow check atomizer fitting per Section 5-3d(4). Repair atomizer fitting if clogged Check for carbon deposits No carbon deposit permitted None Remove carbon deposits by ultrasonic cleaning per Section IV - Cleaning Check for cracks by fluorescent penetrant inspection, ASTM E1417, Type I, Method B or D, Sensitivity Level 3 materials (Figure 5-19) Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C None Braze cracks per Section 5-3n Ensure freedom of movement of igniter plug grommet No damage permitted None Apply non-carbon penetrating oil, VV-P-216, to free igniter plug grommet or replace grommet per Section 5-3o Check for burn away of parent metal immediately behind indentations on cooling rings No burn away permitted None Replace combustor liner if out of limits Check inside diameter, in a restrained condition, for roundness Minimum/maximum wear limits are specified in Figure 5-19 (dimensions A and B). A tight fit through 360o between seal ring and combustor housing must be maintained None Measure both inner diameters using inspection fixture, ST61404 (Figure 2-1, 9). Replace combustor liner if out of limits Check for erosion or distortion of fuel nozzle No erosion or distortion permitted None Replace fuel manifold Check for looseness of tube assemblies in distribution boss No looseness permitted None Braze cracks per AWS C3.6 using brazing alloy per AWS A5.862T BAU 4 Check for cracks, kinks or distortion No cracks, kinks or distortion permitted None Replace fuel manifold Fuel manifold (Figure 3-28, 9) Change 22 5-41 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-2. Inspection Requirements (APU) -Continued Inspect/ Item No. Max Serviceable Limits Max Repairable Limits Corrective Action Fuel manifold (9, figure 3-28) - continued Check for looseness of tube assemblies in distribution boss No looseness permitted None Braze cracks per MIL-B-7883, Type II, grade B, using brazing alloy per AWS A5.8-62T BAU 4 Check for cracks, kinks or distortion No cracks, kinks or distortion permitted None Replace fuel manifold Check for bent or plugged fuel nozzles No bent or plugged fuel nozzles permitted None Flow check fuel manifold per Section 5-3d (2). Replace fuel manifold if out of limits Check filter fitting for clogs or restrictions No clogs or restrictions permitted None Flow check fuel manifold per Section 5-3d (2). Replace filter fitting if out of limits Check for cracks or dents No cracks or dents permitted None Replace fuel nozzle and fitting Check for damaged or stripped threads No damaged or stripped threads permitted None Replace fuel nozzle and fitting Check for clogs or restrictions No clogs or restrictions permitted None Flow check per Section 5-3d (2). Replace fuel nozzle if out of limits Fuel nozzle and fitting (3 and 2, figure 3-28) 5-42 Change 6 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-1. Inspection of Bearing Aft Carrier Change 22 5-43 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-2. 5-44 Change 16 Inspection of Bearing Front Carrier TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-3. Inspection of Diffuser Housing 5-45 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-4. Inspection of Load Compressor Diffuser 5-46 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-5. Inspection of Rotor Shaft Figure 5-6. Inspection of Seal Plate Change 9 5-47 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-7. Inspection of Turbine Nozzle 5-48 Change 3 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-8. Inspection of Accessory Drive Pinion Figure 5-9. Inspection of Accessory Gear 5-49 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-10. Inspection of Carrier Assembly Figure 5-11. 5-50 Inspection of Cover TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-12. Inspection of Gear Planet Set Figure 5-13. Inspection of Hub Ring Gear 5-51 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-14. Inspection of Intermediate Gear 5-52 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-15. Inspection of Oil Pump Housing Assembly 5-53 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-3. Oil Pump Housing Assembly, Dimensional Limits Ref. Fig. 5-15 Description 1 Pump drive gear to housing. Total clearance 0.0300L 2 Pump drive gear to driver shaft 0.0020L 3 Pump drive gear keyway width (two places) 0.1000 4 Pin outside diameter (OD) (3 each) 0.0900 5 Driver shaft OD 0.2485 6 Pin to driver shaft (two places) 0.0010L 7 Pump drive gear to driver shaft 0.0020 8 Pump drive gear keyway width (two places) 0.1000 9 Driven shaft OD 0.2485 10 Pump drive gear keyway width (two places) 0.1000 11 Pin to driven shaft 0.0010L 12 Driven shaft to pump element gear 0.0020L 13 Driver and driven shafts housing holes (four places) 0.0020L 14 Pump element gears end play (two places) 0.0030L 15 Pump element gear OD to housing bore 0.0040 NOTES: 1. Pump drive gear inside diameter (ID) - 0.2500-0.2505 in. 2. Pump element gear ID - 0.2500-0.2505 in. 3. Driver shaft and drive shaft OD - 0.2490-0.2492 in. 5-54 Replace if dimension exceeds TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-16. Inspection of Pump Drive Gear Figure 5-17. Inspection of Zerol Pinion 5-55 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-18. Inspection of Combustor Housing 5-56 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-19. Inspection of Combustor Liner 5-57 TO 2G-T62T-43 REPAIR AND REPLACEMENT. 5-3. a. of Nicks, Scratches, Burrs and Surface Blemishes. Repair nicks, scratches, burrs, and surface blemishes as follows: (1) (2) (3) Clean component using applicable cleaning instructions per Section IV Cleaning. (2) Place sheet of abrasive crocus cloth, P-C-458, on a true flat surface. (3) Place contact surface down on abraded or scored end of component (table 5-4). (4) Ensure even metal removal by applying light hand pressure while moving part in figure-8 pattern. (5) Remove minimum amount of metal necessary to eliminate scoring. (6) Polish surface with abrasive stone, SS-S-736. Remove minor nicks, scratches, burrs, rubs, or surface blemishes from components (table 5-4) with abrasive crocus cloth, P-C-458. Immediately after cleaning and repair, treat and paint the surface per subparagraph o. Immediately after cleaning and repair, treat and paint the surface per subparagraph o. b. Removal of Scoring. Remove scoring on flat surfaces as follows: (1) Clean component using applicable cleaning instructions per Section IV Cleaning. Table 5-4. Fig.1 Index No. Components C. Using Abrasive Remove and repair threaded inserts, threads, O-rings, studs, dowel pins, and pins per TO 1-1A-8. Crocus Cloth, P-C-458 Fig.1 Index No. Component Component 3-10/17 Adapter assembly 3-10/31 Inlet housing 3-10/53 Bearing aft carrier 3-10/39 Inlet guide vane 3-12/40 Bevel gear support 3-10/20 Load compressor 3-12/6 By-pass 3-3/18 Oil pressure 3-12/60 Carrier Assembly 3-10/59 Rotor shaft 3-12/63 3-10/45 Cover 3-3/16 Reduction drive cover 3-12/142 Reduction drive housing 3-10/60 Engine compressor 3-5/31 Turbine ignition exciter 3-2, detail B/25 Fuel purge valve 3-10/2 Turbine nozzle 3-12/77 Housing carrier 3-10/55 Turbine wheel 5-58 valve housing Diffuser Housing wheel wheel switch T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-19A Combustor Liner Assembly, Exploded View Change 9 5-58A T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-19B. Atomizer Fitting Repair 5-58B Change 9 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-19C. Flow Test of Atomizer Fittings Change 9 5-58C T.O. 2G-T62T-43 NOTES: UNEVEN WEAR PATTERNS ON THE EXTERNAL SPLINE OR EXTERNAL GEAR ARE NOT ACCEPTABLE. 2 3. 4. 5. 6. THE OIL RETAINER MUST BE LOCATED .13" TO .14" FROM THE EXTERNAL GEAR END AND MUST BE TIGHT. 8. 9. 10. PARTS WHICH DO NOT MEET THESE REQUIREMENTS DISPOSITION AT A LATER DATE. 5-58D) Change 9 SHOULD BE TAGGED UNSERVICEABLE AND HELD FOR T.O. 2G-T62T-43 d. Flow Testing. (1) Flow test fuel nozzle (3, figure 3-28) as follows: (a) Connect flow check fixture, ST92300 (75, figure 2-1) to a fuel manifold flow bench, 164101-100 (85, figure 2-1). (b) Install fuel nozzle (3) in flow check fixture, ST92300. warning Calibrating fluid, MIL-C-7024, type II, is toxic to eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Do not breathe vapors. Use in a wellventilated area. Wear eye and skin protection. Avoid use around sparks, open flame, and heated surfaces. (c) (d) (e) (2) Connect a source of calibrating fluid, MIL-C-7024, type II, at a pressure of 350 psig, 70-90°F, to fuel nozzle (3). Minimum fuel flow must be 14-16 pph. Observe fluid spray from nozzle. Spray must be conical, symmetrical, and free of voids and streaks. Verify that spray angle, when measured 1/2 in. downstream of nozzle, is greater than 70°. Replace fuel nozzle if it does not satisfactorily meet test parameters. Flow test fuel manifold (9, figure 3-28) as follows: (a) Install filter fitting (4, figure 3-28) in fuel manifold (9). (b) Install fuel manifold on fuel manifold flow bench, 164101-100 (85, figure 2-1) with fuel nozzles directed into the beakers provided with flow bench. Calibrating fluid, MIL-C-7024, type II, is toxic to eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Do not breathe vapors. Use in a well ventilated area. Wear eye and skin protection. Avoid use around sparks, open flame, and heated surfaces. (c) Use calibrating fluid, MIL-C-7024, type II, specific gravity of 0.815, at 80°F, as test fluid. Adjust inlet fluid pressure to 145 psig. Verify that flow rate is 288-312 pph. (d) The flow rate from each fuel nozzle shall not exceed ±4% from the average. (e) Test all fuel nozzles. Replace fuel manifold (9, figure 3-28) if it does not satisfactorily meet test parameters. (3) Flow test oil jet cartridge (75, figure 3-12) as follows: (a) Using oil, grade S 150, per ASTM 2422, flow test oil jet cartridge. NOTE All four jets of oil jet cartridge must flow freely. (b) Flow test at 0.3-0.5 gpm at 20 psi. (4) Flow test atomizer fitting (4, figure 5-19A) as follows: (See figure 5-19C. (a) Using a hydrometer, measure the specific gravity of test fluid. NOTE Atomizer fittings must be free of carbon deposits or other obstructions. Clean per paragraph 4.3.i. (b) Using a flow test bench, P/N 164101100, or equivalent, adjust test flow to 45.0 - 46.0 pounds per hour (pph). With a test fluid specific gravity of 0.78, pressure shall not exceed 2 psig. ( c To adjust variations in test fluid flow and specific gravity, verify pressure in accordance with the following formula: Pressure = Fluid Flow Specific Gravity x 1294 ( d ) Repeat step b. and c. for all atomizer fittings in each liner. ( e Repair atomizer fitting assemblies (4, figure 5-19A) if flow test indicates obstruction as follows: 1 Remove grommet (3). 2 Machine off clogged atomizer tube. Redrill fitting as shown in figure 5-19B. Clean, blast, and wrap fitting for 3 brazing. 4 Position tube and brazing onto atomizer fitting as shown in figure 5-19B. Change 9 5-59 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 5 e. Install new grommet per paragraph 5-30. Functional Test of Oil Pressure Switch. (e) Manufacture sleeve from 6A1-4V, AMS 4928, titanium bar material. (f) Inner Diameter (ID) of the sleeve, prior to installation on the compressor wheel, shall be 1.399-1.400 inches, with a (0.030-0.040 inch) x (44.5-45.5o) chamfer on the base of the sleeve ID. Verify ID (measure at top and bottom) and record in Table 5-6. WARNING Lubricating oil, Specification MIL-L7808, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. (1) Connect oil pressure switch (Figure 3-3, 18) to low pressure source of lubricating oil, Specification MIL-L-7808. (2) With no pressure applied, check that there is continuity through pins B and C. (3) f. NOTE Initial knurl depth may be increased as required to compensate for material removed during finish machining of OD. A 20 knurl/inch pitch is recommended for ease of fabrication. (g) Slowly apply pressure and observe when switch closes (continuity through pins B and C). Switch shall close at 6 (±1-1/2) psig on increasing pressure. Turbine Wheel, Engine Compressor Wheel, and Load Compressor Wheel Repair. (1) Repair diamond knurl (Figure 5-20) hub on engine compressor wheel (Figure 310, 60) as follows: (a) Measure runout on length ‘‘B’’ of the center bore diameter datum B per Dwg No. (55820) 161636. Maximum allowable runout is 0.0004 inch with respect to datum A . Replace wheels that fail inspection; do not proceed with sleeve repair. (b) Measure end (axial) runout on the backface of the wheel datum C per Dwg No. (55820) 161636. Maximum allowable runout is 0.0002 inch with respect to datum A . Replace wheels that fail inspection; do not proceed with sleeve repair. (c) Record engine compressor wheel S/N, located on the backface of wheel, in Table 5-6. (d) Machine compressor wheel hub, to remove damaged knurl, to an OD of 1.4015-1.4020 inches and a 0.030 inch max radius at the base, per Figure 5-20. Verify OD (measure at top and bottom) and record in Table 5-6. 5-60 Change 22 Cold-roll a pattern of 15-25 knurls/ inch into sleeve, per requirements of Figure 5-20. Cutting of the knurled pattern is not allowed. WARNING ASTM E1417 Fluorescent Penetrant materials may cause irritation to skin and eyes. Avoid inhaling powder or vapors, and use only in well-ventilated area. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. Wear nitrile gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and local Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations for additional information. (h) Fluorescent penetrant inspect compressor wheel hub OD and sleeve ID area per ASTM E1417, Type I, Method A, B or D, Sensitivity Level 3. No defects allowed. (i) As required, bag and tag (CAGE 96916) P/N 161636-3 in accordance with MIL-STD-130. Destructive etching/marking of the sleeve is not allowed. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 . . 1 Record APU S/N and engine compressor wheel S/N in Table 5-6. Include a completed copy of Table 56 with the permanent APU records for historical filing. 2 Record APU S/N and engine compressor wheel S/N in an electronic database (APU final assembly shop database may be utilized for this). Denote that the wheel has a sleeve repair. WARNING Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can injure human skin or tissue on contact. Liquid nitrogen will expand 696 times as it vaporizes, and if the liquid vaporizes in a sealed container, it can produce enormous pressures that could rupture the vessel. Nitrogen can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated or confined areas. Boiling and splashing occurs when filling a warm container with or when inserting objects into liquid nitrogen. Perform these tasks slowly to minimize boiling and splashing. Use tongs to withdraw objects immersed in a cryogenic liquid. Wear chemical splash goggles, face shield, and approved cryogenic gloves/ outer wear when handling liquid nitrogen. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (j) (k) (l) Oven-heat sleeve to 400 (±15)oF for approximately 30 minutes. Cool compressor wheel in liquid nitrogen for 20-30 minutes. Immediately install sleeve onto compressor wheel hub (chamfered ID facing down), ensuring sleeve bottoms out against wheel; there should be no gap between the sleeve and the compressor wheel. Machine sleeve OD to 1.5895-1.5990 inches. Apply the (0.18-0.22 inch) x (13-17o) chamfer and surface finish per requirements of Figure 5-20. Verify OD and record in Table 5-6. (3) Glass shotpeen aero surface of engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60), turbine wheel (55), and load compressor wheel (20) as follows: (a) Mask knurled area and bores. (b) Glass shotpeen per AMS 2430 to an intensity of ALMEN 0.010-0.012 N, using size AB shot and pressures not to exceed 70 psig. (c) Peenscan process inspect per Specification MIL-S-13165. Blade tune engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60), turbine wheel (55) or load compressor wheel (20) as follows: (a) Install engine compressor wheel, turbine wheel or load compressor wheel in vibration analysis tool, ST63939 (Figure 5-21). (b) Plug spectrum analyzer, SD340, of vibration analysis tool, ST63939 (figure 5-21), into power source. (c) Select voltage. (d) Turn on analyzer. No warmup time is necessary. (e) Secure accelerometer, M93, on vibration analysis tool, ST63939 (Figure 5-21), to steel base plate and plug cord into SIGNAL connector on analyzer panel. (f) Set steel base plate on dense neoprene pad. (g) Set analyzer controls as follows: Verify knurl depth and record in Table 5-6. NOTE A locally assigned S/N for denoting a repaired wheel is allowed, but not required. The only authorized inscription method is electro-chemical etch. Location to be on backface of wheel, but not on balancing ring. Do not tamper with existing information etched on back of wheel. (m) (2) The following documentation shall be provisioned for each knurl repair: 1 Cursor units - Hz 2 Cursor mode - Normal 3 Analysis mode - Peak 4 Start/Stop - Press if ready button light is steady 5 Display mode - Spect Change 22 5-60A T.O. 2G-T62T-43 6 Display Y-gain - LOG 0dB 7 Input frequency range (Hz) - 5K or 10K 8 Input level - 1 9 Sensitivity switch - MV/EU 10 Sensitivity dial - 0707 11 X-gain - X1 (h) To calibrate frequency pickup, install tuning fork (known frequency) into steel base plate (Figure 5-21). Pluck tuning fork and determine frequency 5-60B Change 22 with cursor. The frequency must be within ±25 Hz of the known frequency. (i) 1 Frequency check engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60), turbine wheel (55) or load compressor wheel (20) as follows: Install engine compressor wheel, turbine wheel or load compressor wheel on steel base plate, making sure the wheel is flat on and in direct contact with the steel base plate. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-20. Repair of Diamond Knurl 5-61 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-21. 5-62 Blade Tuning TO 2G-T62T-43 _ 2. If the analyzer was calibrated, return controls to positions listed in step (g). _3. Pluck blade of engine compressor wheel, turbine wheel, or load compressor wheel. _4. Determine blade frequencies by moving the cursor to the peak y-axis values on the CRT. The first significant peak left to right is the first mode, the second is the second mode, and the third peak is the third mode. _5. (j) Engine compressor wheel long blades shall have first mode natural frequencies between 19502500 Hz and second mode natural frequencies which must not fall between 5900 Hz and 6600 Hz. (k) Load compressor wheel blades must have a first mode frequency of 4350-4600 Hz. (1) Turbine wheel blades must have a first mode frequency of 34003650 Hz. (m) Provided all dimensional requirements are met, the required frequencies can be obtained as follows: NOTE Engine compressor wheel long blade second mode natural frequency is the primary concern. In case conflict arises in corrected first and second mode frequencies, a 0.12 cutback will increase first mode frequency approximately 150 Hz and second mode frequency approximately 480 Hz. To increase frequency, cut back leading edge of long blades (figure 5-21, view A-A). Reradius leading edge and blend with existing hub radius. 2. _ To decrease frequency, reduce blade thickness by burnishing, but maintain thickness tolerance. (n) Thin blades with second mode frequency of 5600-5800 Hz. (o) Thin or crop blades with second mode frequency of 5800-5900 Hz, depending upon first mode frequency. Clear the CRT prior to the next blade check by pressing START/STOP button so that red light blinks. _ Proceed with next blade 6. check. 1. _ (p) Crop blades with second mode frequency of 5900-6400 Hz. (4) Balance engine compressor wheel, turbine wheel, and load compressor wheel per Section VI - Assembly. g. Eddy Current Inspection. Eddy current inspection is used for detection of surface or subsurface discontinuities in holes and/or bores. An eddy current tester, FD-100 (1, figure 2-1), or equivalent should be used. The tester shall be calibrated using eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84, figure 2-1). (1) Set-Up Procedure. warning Properly ground equipment prior to use. Failure to do so may result in possible electrical shock. (a) Attach scanner head, power cord, and probe to eddy current tester, FD-100 (1, figure 2-1). Ensure probe is proper size and check for snug fit in bore. (b) Install chart paper for recording tests. 5-63 TO 2G-T62T-43 (h) Insert probe into eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84), and rest scanner head on eddy current tester, FD-100 (1). Adjust meter needle to 50 using balance control. (c) Turn panel power and mode selector switches to “ON” position and allow equipment to warm up for 15 minutes. (2) Set eddy current tester, FD-100 (1, figure 2-1) function controls as follows: (a) Mode selector - Low (i) Scan bore of eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84), and observe stylus deflection on chart paper. (j) System is now ready for inspection. (b) Sensitivity - 12:00 position (c) Filter - 50 rpm (d) Scanner rpm - 50 (e) Chart: OFF - Calibration AUTO - Scanning ON - Paper feed (f) Chart speed - Slow (g) Zero - 5K or 10K (h) Heat - As required for legible trace NOTE Do not change controls after set-up is established, except for “zero” stylus adjustment. Zero stylus control is to be used to “mark” chart paper before and after each scanning sequence. The length of all scan charts must be within ±0.500 in. of eddy current inspection master, 163000, chart. ( i ) Balance - Zero (k) (j) Lift off/frequency - Zero (3) Calibrate eddy current tester, FD-100 (1, figure 2-1) as follows: (a) Position eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84, figure 2-1) in eddy current tester, FD-100 (1) with backface up. (b) Extend probe to maximum extended position. (c) Turn balance control to 0.50 (approximately). (d) Place probe coil on flat surface of eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84). (e) Turn lift off/frequency control until meter needle is at “NULL” position. ( f ) Remove probe from eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84), and readjust balance control to bring needle on scale. (g) Retract probe. 5-64 Scan eddy current inspection master, 163000 (84), before and after each test and periodically during inspection (not to exceed 8 hours). Record date and times on calibration run. NOTE If any periodic scan does not conform to requirements, recalibrate equipment. (4) Inspection procedure for turbine wheel (55, figure 3-10) (a) Visually examine turbine wheel and ensure bore is clean and free of foreign material. (b) Install turbine wheel in top ring of eddy current holder, ST64037 (15, figure 2-1), with backface up. (c) With probe in retracted position, place probe in bore of turbine wheel and check for proper alignment. Verify recorder stylus is centered. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (d) Eddy current inspection of center bore is to be performed for entire length of bore except for 0.250 (±0.125) inch from each end. (5) (e) Scan bore to extended probe position. (f) Remove probe and turn turbine wheel over. Be careful not to thin metal when dry blasting. (g) Place probe in turbine wheel bore and check for proper alignment. (h) Scan bore to retracted probe position. (i) Remove scanner head and turbine wheel from eddy current holder, ST64037 (Figure 2-1, 15). (j) (k) h. CAUTION (6) (2) Use protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. Review trace for any obvious indication of cracks. Typical indication of a crack would display a signal-to-noise ratio of 3:1. (3) WARNING Use protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (4) Put turbine nozzle into an oven maintained at 250oF for one hour. Remove turbine nozzle from oven and allow to cool. Preheat turbine nozzle in an oven maintained at 250oF. (8) Plasma spray as follows: Mask part for metal spraying. NOTE Ensure parent material thickness is 0.100 inch minimum. Machine to reduce diameter of turbine nozzle assembly (Figure 3-10, 2) by 0.020-0.024 inch at dimensions D and F, Figure 5-7. Remove nicks, scratches, erosion or rub marks per Section 5-3a with abrasive crocus cloth, A-A-1206. (7) (a) After completion of test, switch panel and mode selector switch to ‘‘OFF’’. Clean turbine nozzle assembly ultrasonically with aqueous cleaner, Specification MIL-C-87937, diluted to manufacturer specifications. Dry blast machined outside diameter with coarse-grit aluminum oxide. WARNING Turbine Nozzle Repair. (1) Mask part for dry blasting. i. (b) Plasma spray abraded coat using welding power, Metco 443 NS or equivalent per AMS 2437 to a coating thickness of 0.020-0.060 inch (c) Machine to dimensions D and F, Figure 5-7. Repair of Reduction Drive Housing Sleeves. (1) Check sleeves (Figure 3-12, 97 and 137) in reduction drive housing (142) to make sure it is within limits (Figure 522), in proper position, is not loose or damaged on inside diameter of surface. If necessary, remove sleeve (Figure 312, 137) and repair. If necessary, manufacture new sleeve (137) per Drawing (96916) 1B2270. Maximum dimension of bore for new sleeve (137) is 2.330 inch. Interference fit between sleeve and housing shall remain at 0.0035 to 0.0055 inch. Change 22 5-65 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 inch. Materials shall be AISI 4130 or 4340. Heat treat to 125-145 ksi, 26-32 HRC, per AMS 2759. Phosphate coat sleeves per Specification MIL-P-16232, Type M. WARNING Chemical conversion coating, Specification MIL-C-81706, type III, is toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. Avoid contact with skin. After preparation, wash hands and face thoroughly. (2) Apply chemical conversion coating, Specification MIL-C-81706, type III, per Specification MIL-C-5541 to opening in housing (142). (3) Apply sealant, Specification MIL-S22473, grade A, to new sleeve (Figure 312, 137) and install in housing (142). (4) Drill hole in sleeve (137) and reduction drive unit housing (142) (Figure 5-22) and install pin (Figure 3-12, 136). Machine pin (136) flush with inside diameter (ID) of sleeve (137). (5) j. . . WARNING Blacklights emit UV-A (ultraviolet) radiation. Overexposure to UV-A radiation can cause premature skin aging and may cause skin cancer and cataracts. The required intensity for this process is above the threshold limit value for UV-A radiation at 15 tested. Wear long sleeve clothing, ultraviolet protective safety glasses, and gloves. (2.1) Magnetic particle inspect per ASTM E1444. Reject for cracks or indications extending over an edge. (3) With carrier assembly (60) or cover (63) warm (up to 300oF), apply sealant, Specification MIL-S-22473, grade A, to new sleeve (73 or 74) and install in either carrier assembly or cover. Press sleeve in bore of component to a full depth until sleeve firmly seats. (4) Finish grind/machine bore depth and inside diameter of sleeve to dimensional requirements of Figure 5-23. Machine snap ring groove into sleeve (75) per Drawing (55820) 161779. Grind ID of sleeve (137) to dimensional and finish requirements (Figure 5-22). Replacement of Carrier Assembly Sleeves. WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (1) (2) Heat carrier assembly (60) or cover (63) to 300oF and place dry ice, CGA G6.2, in sleeves (73 or 74) to facilitate pressing sleeves from either carrier assembly or cover. If necessary, manufacture new standard or oversized sleeve (Figure 5-23) to provide an interference fit of 0.002-0.004 5-66 Change 22 WARNING Chemical conversion coating, Specification MIL-C-81706, type III, is toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. Avoid contact with skin. After preparation, wash hands and face thoroughly. (5) Touch up with chemical conversion coating, Specification MIL-C-81706, type III, per Specification MIL-C-5541, all machined surfaces. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 j1. . . Replacement of Carrier Assembly Oil Jet Ring. WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (1) Heat carrier assembly (Figure 3-12, 60) to 350oF and cool oil jet cartridge (75) with dry ice. WARNING ASTM D 5363 AN0151 sealant may cause eye and skin irritation. Wear gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (2) Apply sealant, ASTM D 5363 AN0151, Grade A, to the contact surfaces of the oil jet cartridge (75). Use sealant sparingly, ensuring that no excess sealant enters oil cavity. (3) Press oil jet cartridge (75) into carrier assembly (60), ensuring oil jet cartridge (75) is fully seated in housing. Ensure that each of the three prongs of the oil jet cartridge face into the metal webs of the housing and not towards the three bearing bore bushings, as per HamiltonSundstrand Drawing No. 161779-101. (4) With oil jet cartridge (75) installed, locate and machine drill a new 1/32 inch retaining pin hole 120 (±15) degrees right or left from previous hole. Do not drill into metal web with oil passage. If both metal webs have been previously used, replace housing. Previously used oil jet cartridges will have an existing hole, which can be used as a pilot hole for the drill. New oil jet cartridges will require a newly drilled hole. Housings with new oil jet cartridges shall be drilled as an assembly in one operation. k. (5) Install new spring pin (76) into drilled hole. (6) Flow test carrier assembly per Table 53d(3). Replacement of Housing Carrier Liners and Pipe Plugs. (1) Heat housing carrier (Figure 3-12, 77) up to 300oF and press housing liner (96) and pipe plugs (81) from housing carrier. Discard housing liner (96) and pipe plugs (81). WARNING Cleaning solvent, MIL-PRF-680, Type II or III, is toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear goggles and solventresistant gloves. (2) Clean bores of housing carrier (77) using a brush, Specification MIL-B15319, type I, class 2, or equivalent and cleaning solvent, MIL-PRF-680, Type II or III. (3) After cleaning, dichromate treat bores and oil passages of housing carrier (77) per subparagraph p. WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (4) Cool a new housing liner (96) in dry ice or liquid nitrogen for 1 hour minimum and heat housing carrier (77) in an oven maintained at 250-300oF for 1 hour minimum. (5) Apply a coat of structural adhesive, EC1386, or equivalent to lip of housing liner (96) and press into housing carrier (77) until lip of housing liner is seated. Cure 1 hour in an oven maintained at 340-360oF. Change 22 5-66A/(5-66B blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-22. Repair of Reduction Drive Unit Housing Sleeves Change 22 5-67 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-23. 5-68 Change 22 Manufacture of Carrier Assembly Sleeves T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (6) Install pipe plugs (81) in housing carrier (77). Ensure that oil inlet port is plugged and that oil ejector hole is capped. WARNING ASTM D 5363 AN0151 sealant may cause eye and skin irritation. Wear gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. WARNING When using compressed air for cleaning or drying, regulate pressure not to exceed 30 psi. Wear eye protection. (7) (8) l. . . Apply compressed air of 20 psi or more to oil inlet port and check for leakage at lip of housing liner (96). If leaking occurs, apply structural adhesive, EC1386, or equivalent around housing liner (96) and cure for 1 hour in an oven maintained at 340-360oF. Recheck for leakage. (4) With bevel gear support (40) warm (up to 300oF), apply either retaining compound 680 or sealant, ASTM D 5363 AN0151, to new liners (42 or 43) and install in bevel gear support. Press liners in bore of component to a full depth until liners firmly seat. (5) Install pin (41) and machine flush with inside diameter of liner (42). Machine housing liner (96) to 0.9070.912 depth (Figure 5-24, dimension A). WARNING Replacement of Bevel Gear Support Liners. Blacklights emit UV-A (ultraviolet) radiation. Overexposure to UV-A radiation can cause premature skin aging and may cause skin cancer and cataracts. The required intensity for this process is above the threshold limit value for UV-A radiation at 15 tested. Wear long sleeve clothing, ultraviolet protective safety glasses and gloves. WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (6) Magnetic particle inspect per ASTM E 1444. (7) Finish grind/machine bore depth and inside diameter of liners (42 and 43) to dimensional requirements of Figure 525. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (1) (2) (3) Heat bevel gear support (Figure 3-12, 40) to 300oF and place dry ice, CGA G6.2, or liquid nitrogen, A-A-59503, in liners (42 or 43) to facilitate pressing liners from bevel gear support. If necessary, manufacture new liners from AISI 4130 per Figure 5-25 or Drawing (96916) 1B2270. Dichromate treat bevel gear support (Figure 3-12, 40) per Specification MILM-3171, type III, before installing liners (42 or 43). m. Turbine Ignition Exciter Functional Test. (1) Equipment used to perform the functional test shall consist of the following: (a) DC power supply - variable voltage (b) Range of 0-30 Vdc (minimum) (c) Igniter plug (Figure 3-5, 39) (d) Ignition cable (Figure 3-5, 27) Change 22 5-69 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-24. 5-70 Change 18 Manufacture of Housing Liner T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-25. Manufacture of Bevel Gear Support Liners Change 22 5-70A/(5-70B blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-25.1. Repair of Bevel Gear Support Housing Change 22 5-71 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (2) (3) (e) DC ammeter - current range of 0-5A (f) Test leads Limits for the turbine ignition exciter are as follows: (a) Input voltage - 14-30 Vdc (b) Input current (maximum) - 1.0 A (c) Spark rate - 2.7/sec minimum at 14 Vdc (d) Duty cycle - 1 minute on, 5 minutes off (e) Polarity - Pin B (+), Pin A (-) (b) Connect circuit. (c) Apply voltage and observe operation. Acceptable operation consists of proper spark rate (2.7/sec) and input current below maximum allowable value (1.0 A). (d) (a) Clean combustor housing (Figure 328, 17) or combustor liner (15) per Section IV - Cleaning. (b) Remove any oxide layer or scale using a stainless steel wire brush to brush down to bare shiny metal the brazed areas to be repaired. Methyl-ethyl-ketone, TT-M-261 and acetone, O-A-51, are toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear face protection and rubber gloves. . . NOTE Braze repair areas must be free of oil, grease, dirt, scale, artificial oxide films or any other foreign substance. Do not use flux. Turn off power supply. (c) Clean local area of braze repair using acetone, O-A-51. (d) Braze repair cracked area using tungsten arc process, with inert welding gas, and filler material per AMS 4777. Use minimum heat to perform repair. (e) Inspect repaired braze area by fluorescent penetrant inspection, MILSTD-6866, type I, method A. Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C. (f) If any cracks or incomplete repair areas are detected, repeat previous steps and reinspect. (g) Check dimensions of combustor housing on inspection fixture, ST62880 (Figure 2-1, 10). (h) Check dimensions of combustor liner on inspection fixture, ST61404 (Figure 2-1, 9). Operation at maximum voltage (30 Vdc). (a) n. Set power supply to the minimum input voltage (14 Vdc) and current limiter to maximum input current valve (1.0 A). Tungsten Arc Braze Repairs. WARNING Operation at minimum voltage (14 Vdc). (a) (4) (1) Set power supply to the maximum input voltage (30 Vdc) and current limiter to the maximum input current value (1.0 A). (b) Connect circuit. (c) Apply voltage and observe operation. Acceptable operation consists of proper spark rate (2.7/sec) and input current below maximum allowable value (1.0 A). (d) Turn off power supply. (e) Disconnect test circuit. Repair of Combustor Housing and Combustor Liner. Cracks or holes in welded or brazed areas may be repaired using either tungsten arc braze or vacuum furnace braze. Cracks in brazed area can be repaired by brazing per AWS C3.6 using brazing alloy per AMS 4777. 5-72 Change 22 (2) Vacuum Furnace Braze Repairs. (a) Clean combustor housing or combustor liner per Section IV - Cleaning. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-26. Inspection of Air Inlet Housing Change 18 5-72A T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-27. 5-72B Change 18 Inspection of Load Compressor Wheel Seal T.O. 2G-T62T-43 WARNING Methyl-ethyl-ketone, TT-M-261 and acetone, O-A-51, are toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear face protection and rubber gloves. . . NOTE Braze repair areas must be free of oil, grease, dirt, scale, artificial oxide films or any other foreign substance. (a) Clean combustor housing per Section IV - Cleaning. (b) Remove damaged fitting from combustor housing. (c) Place Thermocouple fitting, P/N (55820) 24003-1, inside hole. Fitting may be removed from P/N 24003-0 or manufactured from stainless steel rod QQ-S-763, Type 347 per drawing, P/N (55820) 161637. (d) Weld fitting to plate using AWS A5.9 (ER 347) or AMS 5680 (347) with 1/ 16" fillet. Do not use flux. (3) (b) Clean local area of braze repair using acetone, O-A-51. (c) Using a circular or semi-circular pattern, apply Stop-Off within 1/2 inch of the area to be braze repaired to prevent excess flow of braze. (d) Load braze filler material, BNI-2 per AMS 4777, to cover braze cracks using an eye dropper or equivalent. (e) Vacuum furnace braze per AWS C3.6. Brazing temperature range shall be 1950 (±25)oF. (f) Braze repair areas shall conform to the requirements of AWS C3.6. (g) Visually inspect repaired areas using a 10x magnifier. (h) Inspect repaired braze area by fluorescent penetrant inspection, MILSTD-6866, type I, method A. Acceptance criteria per MIL-STD-1907, Table III, grade C. WARNING Fluorescent Penetrant, ASTM E1417, is toxic and can cause injury to skin and eyes. Avoid inhaling powder or vapors, and use only in well-ventilated area. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. PPE: gloves and goggles. (e) o. Fluorescent penetrant inspect per ASTM E1417, using Type I, Sensitivity Level 3 or 4 materials. No indications permitted. Igniter Plus Grommet Installation. Install new igniter plug grommet (Figure 3-28, 18), new washers (19), and new spring (20) in combustor liner as follows: (1) Install igniter plug grommet (18) with flange of grommet inside combustor liner (16). (2) Hold igniter plug grommet (18) in position and insert clevis of flaring fixture, ST91064 (Figure 2-1, 74), through the grommet. (3) Install washers (Figure 3-28, 19) and spring (20) over igniter plug grommet (18). (i) If any cracks or incomplete repair areas are detected, repeat previous steps and reinspect. (j) Clean combustor housing or combustor liner per Section IV - Cleaning, to remove penetrant and Stop-Off. (k) Check dimensions of combustor housing on inspection fixture, ST62880 (Figure 2-1, 10). WARNING (l) Check dimensions of combustor liner on inspection fixture, ST61404 (Figure 2-1, 9). Lubricating oil, Specification MIL-L7808, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. Weld repair to Thermocouple boss for combustor housing (Figure 3-28, 17). Change 22 5-73 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (4) Apply a light coat of lubricating oil, MIL-L-7808, to tapered end of f laring f ixture, ST91064 (74, f igure 2-1). (5) Place cone on clevis of f laring f ixture, ST91064 (74). III and V, class 1A, per MIL-C-5541 to carrier assembly, bevel gear support assembly, reduction drive housing, and housing carrier reworked or exposed surfaces. (c) Apply black oxide coating per MIL-C13924, class I, to straight drive shaf t reworked or exposed surfaces. (d) Apply anodize per MIL-A-8625, type II, class I, to diffuser housing assembly reworked or exposed surfaces. CAUTION To ensure correct insertion of igniter plug, the igniter plug grommet must move freely; therefore, do not overf lare grommet. (6) (7) Unscrew nut and remove f laring f ixture ST91064 (74, f igure 2-1), from combustor liner (16, f igure 3-28). (8) Check igniter plug grommet (18) to ensure it moves freely, and f lare is enough to retain it in the combustor liner (16). (9) p. Install nut on clevis of f laring f ixture, ST91064 (74). While holding handle of shank, use wrench and tighten nut until the cone f lares the igniter plug grommet (18, f igure 3-28) over the washers (19) and the spring (20). Check that diameter of igniter plug grommet (18) across top of f lare is 0.59-0.65 in. (2) Repair painted exterior surfaces as follows: WARNING Epoxy polyamide primer, MIL-P23377, type II, and epoxy polyamide paint, MIL-C-22750, class I, type I, are toxic and f lammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear face protection and rubber gloves. NOTE Do not paint holes, threads, internal surfaces, or machined surfaces. (a) Apply one coat of epoxy primer, MIL-P-23377, type I, class C or N, or water borne epoxy primer, MIL-P-85582, type I, class 2 to component. Allow primer to dry for 4 hours. (b) Apply two coats of epoxy polyamide paint, MIL-C-22750, class I, type I, to component. Allow 4 hour drying time between coats of paint and 24 hour curing time af ter painting. Treatment of Surfaces and Metals. (1) Treat reworked and exposed surfaces as follows: WARNING Chemical conversion coating, MIL-C-81706, type III, is toxic and f lammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection. Avoid contact with skin. (a) (b) 5-74 Apply chemical conversion coating, MIL-C-81706, type III, class 1A, per MIL-C-5541 to inlet housing assembly, hourmeter junction box, housing by-pass valve, adapter assembly, and diffuser housing assembly reworked or exposed surfaces. Dichromate treat per MIL-M-3171, type I or VI, or apply chemical conversion coating MIL-C-81706, type Change 17 WARNING Sealant, MIL-C-81733, type III, is toxic. Use rubber or polyethylene gloves. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before eating or smoking. (c) Apply sealant, MIL-C-81733, type III, to housing carrier (77, f igure 3-12). T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (d) (3) Paint and treat exterior surface corrosion on adapter assembly, reduction drive housing, and housing bypass valve with Specification MILC-83285. Table 5-5 lists cleaning, treatment, finish and preservation of metals used in the APU and their areas of application. applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (4) Mask and chemically strip any remaining anodize coating from 1.800 inch bore. (5) Thoroughly housing. (6) Machine inside bore on the first bearing landing to make concentric with lower bearing bore in accordance with Hamilton-Sundstrand Drawing (55820) 161327. Thoroughly clean area to be anodized and protect non-anodized surfaces. WARNING Lubricating oil, MIL-PRF-7808, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. q. r. Preserve the accessory gear and gear planet set with either preservation oil, MIL-PRF6081, grade 1010, or lubricating oil, MILPRF-7808. Repair of Air Inlet Housing Bore. (1) Remove locking pin and retain for reuse. WARNING ASTM E1417 Fluorescent Penetrant materials may cause irritation to skin and eyes. Avoid inhaling powder or vapors, and use only in well-ventilated area. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. Wear nitrile gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (2) Fluorescent penetrant inspect bore in the locking pin area per ASTM E1417 using Type I, Method C, Sensitivity Level 3 materials. No cracks allowed. (3) Aqueous clean air inlet housing using procedures outlined in Section IV. cold water rinse the WARNING Specification MIL-A-8625 Anodizing Solution may burn eyes or skin. Avoid contact. Highly reactive; avoid contact with any other chemicals. Use in a well-ventilated area. PPE: chemical resistant gloves, chemical splash goggles, and face shield. Consult to applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (7) Apply a Type III anodize per AMS-A8625 (formerly Specification MIL-A8625) to the first carrier bearing landing machined surface, using one of the following techniques: WARNING Specification MIL-A-8625 Anodizing Solution may burn eyes or skin. Avoid contact. Highly reactive; avoid contact with any other chemicals. Use in a well-ventilated area. PPE: chemical resistant gloves, chemical splash goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. WARNING (a) Isoprep 184 may burn eyes or skin on contact. Prolonged contact with eye can cause blindness. Inhalation can cause respiratory tract irritation. For protection, wear chemical goggles and chemical protective gloves. Consult the For housings that do not exceed 1.802 inch diameter, either brush or tank anodize per AMS-A-8625 to 1.7996 to 1.8003 inch. (b) For housings with diameter of 1.802 to 1.804 inches, tank anodize per AMS-A-8625 to bring diameter down to 1.7996 to 1.8003 inches. Change 22 5-75 TO 2G-T62T-43 (8) Thoroughly cold water rinse the anodized area. (9) Demask housing and thoroughly rinse to remove any remaining anodize residue. (10) Install locking pin. (11) Alternate air inlet housing bore repair process. (a) (b) Set up and indicate housing in accordance with the callout for datum feature D in accordance with Drawing (55820) 161327. s. Machine upper bore A, as required to remove existing hard anodize, to a maximum dimension of 1.806 inches. To the extent possible, maintain runout and perpendicularity in accordance with Drawing (55820) 161327. If bore does not clean up at 1.806 inches, place housing on MRB. NOTE If bore B falls within the required ID of 1.7997 to 1.8003 inches, no processing of bore B is required. (c) (d) Machine lower bore B, only as required, to a maximum dimension of 1.806 inches. To the extent possible, maintain runout and perpendicularity in accordance with Drawing (55820) 161327. If bore does not clean up at 1.806 inches, condemn housing. Measure ID of bores A and B. Record both dimensions for use during the brush nickel process. t. WARNING Nickel plating solution can cause irritation and burns to the skin and eyes. Skin contact can cause sensitivity and allergic reaction. Mist can cause respiratory irritation if inhaled. Repeated, long term overexposure may cause cancer. Wear nitrile gloves, chemical splash proof goggles, face shield and apron. Consult the applicable Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) and most recent industrial hygiene survey for additional information. 5-76 Change 25 (e) Apply brush nickel coat in accordance with MIL-STD-865 to bores A and B to achieve an ID slightly below the required 1.7997 to 1.8003 inches to allow for final machine cleanup. (f) Machine bores A and B to requirements of Drawing (55820) 161327. Final ID shall be 1.7997 to 1.8003 inches. (g) Re-install locking pin. Repair of Rotor Shaft (Figure 3-10, 59) Bearing Journals. (1) Grind bearing journals (Figure 5-5, A and D) as required to obtain a diameter of 0.6593 to 0.6651 inch. Grind radius shall be 0.062 to 0.125 inch. Concentricity shall be maintained within 0.0005 inch. (2) Magnetic particle inspect bearing journals per ASTM E1444. (3) Shotpeen ground bearing journals with 0.0138 to 0.0280 inch diameter (S-170) shot 0.007 to 0.014 A2 intensity. (4) Chrome plate ground bearing journals in accordance with Federal Specification QQ-C-320 to obtain a diameter of 0.6691 to 0.6693 inch after finish grinding. (5) Bake at a temperature of 260 to 290oF for 5 hours. (6) Finish grind bearing journals as required to meet dimensional, concentricity, and surface finish requirements of drawing (55820) 161504. (7) Magnetic particle inspect finished shaft per ASTM E1444. Repair of Rotor Shaft (Figure 3-10, 59) Load Compressor Journal. (1) Grind load compressor journal (B, Figure 5-5) as required to obtain a diameter of 0.6701 to 0.6759 inch. Grind radius shall be 0.062 to 0.125 inch. Concentricity shall be maintained within 0.0005 inch. (2) Magnetic particle inspect load compressor journal per ASTM E1444. (3) Shotpeen ground load compressor journal with 0.0138 to 0.0280 inch diameter (S-170) shot 0.007 to 0.014 A2 intensity. TO 2G-T62T-43 (4) (5) Bake at a temperature of 260 to 290oF for 5 hours. (6) Finish grind load compressor journal as required to meet dimensional, concentricity, and surface finish requirements of drawing (55820) 161504. (7) u. Magnetic particle inspect finished shaft per ASTM E1444. Repair of Rotor Shaft (Figure 3-10, 59) Labyrinth Seal Journal. (1) v. Chrome plate ground load compressor journal in accordance with Federal Specification QQ-C-320 to obtain a diameter of 0.6799 to 0.6801 inch after finish grinding. Grind labyrinth seal journal (Figure 55, C) as required to obtain a diameter of 1.1005 to 1.1055 inch. Grind radius shall be 0.062 to 0.125 inch. Concentricity shall be maintained within 0.0005 inch. dimension of 4.261-4.263 inches and a surface finish of AA125 to AA250. (2) Aqueous degrease housing for 20 to 30 minutes in accordance with NA 01-1A509. WARNING Fluorescent Penetrant, ASTME-1417, is toxic and can cause injury to skin and eyes. Avoid inhaling powder or vapors, and use only in well-ventilated area. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. PPE: gloves and goggles. (3) Fluorescent penetrant inspect per ASTM E1417, using Type I, Sensitivity Level 3 materials. No cracks allowed. (4) Oven bake housing at 250oF for 2 hours. (2) Magnetic particle inspect labyrinth seal journal per ASTM E1444. WARNING (3) Shotpeen ground labyrinth seal journal with 0.0138 to 0.0280 inch diameter (S170) shot 0.007 to 0.014 A2 intensity. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts. (4) Chrome plate ground labyrinth seal journal in accordance with Federal Specification QQ-C-320 to obtain a diameter of 1.1095 to 1.1105 inch after finish grinding. (5) Bake at a temperature of 260 to 290oF for 5 hours. (6) Finish grind labyrinth seal journal as required to meet dimensional, concentricity, and surface finish requirements of drawing (55820) 161504. (7) Magnetic particle inspect finished shaft per ASTM E1444. Repair of Reduction Drive Housing (Figure 3-10, 142). (1) Machine the ID (6.000 to 6.001 inches) by 0.900 to 0.920 inch deep to a dimension of 6.024 to 6.030 inches and surface finish of AA250 and the ID (4.250-4.249 inches) by 0.980-1.040 inches deep to a (5) With the exception of the machined surface, mask all areas for grit blast. Plug all oil passages. WARNING Aluminum Oxide Powder may release toxic materials during abrasive blasting. Avoid exposure to skin and breathing of dust. Ensure dust is contained in blasting cabinet. Allow ventilation to clear dust before opening cabinet door. Wear safety glasses and hearing protection during glove-box blasting. Consult local industrial hygiene survey for additional information. (6) Blast the machined surfaces using 20grit aluminum oxide (Metcolite C) or equivalent. Change 25 5-77 TO 2G-T62T-43 w. WARNING HFE does not have established occupational exposure limits. It is not expected to cause adverse health effects under normal conditions. However, as with any chemical, exposure should be avoided. This material is very volatile and should be used only with adequate ventilation. Inhalation of this material can cause absorption of fluoride. Safety glasses and gloves are recommended during use. Consult the applicable MSDS and more recent industrial hygiene survey for more information. (6.1) Vapor Degrease housing prior to metal spray. Do not handle or contaminate machined surfaces. (7) Mask the part for metal spraying. (8) Mount the part in a fixture for rotation. Replacement of Retaining Ring (Figure 3-5, 37) Silicone Pads. (1) Adhesive and/or silicone padding residue must be removed. Ensure that the surfaces of the containment rings are free of dirt and oil. Clean surface area with isopropyl (rubbing) alcohol. Apply alcohol with a clean, lint-free cloth. (2) Existing silicone pads may be reattached if they are not brittle or excessively cracked. If new pads are required, they are to be cut from Silicone Rubber Sheeting (0.3125-inch thickness), P/N M46089MSE3, NSN 9320-01-192-3040, or ASTM D1056, Grade 2D3, 0.3125 inch thick. Silicone Pads, P/N (96916) IC3556-1, IC3556-2, and IC3556-3, are to be cut in accordance with Drawing No. (96916) 1C3556. (3) Treat surface of silicone rubber with 180-grit sandpaper in order to create a rough surface to improve adhesion. Clean padding with ispropyl (rubbing) alcohol, TT-I-735. Apply alcohol with a clean, lint-free cloth. WARNING Aluminum/Nickel powder may cause skin dermatitis and eye irritation. Nickel is a suspected carcinogen, don’t permit spray dust to enter eyes, mouth or open wounds. PPE: NIOSH approved respirator, aluminized gloves and goggles. (9) Rotate the part and plasma spray the prepared surface with aluminum nickel powder (Metco 450, or equivalent). (10) Build the prepared surface to 0.030 inch oversize. (11) Clean all masking material from the part. NOTE For machining, use hard alloy tool (Kenametal No. 7 or harder) at surface speed to 10 to 20 feet per minute and a maximum feed of 0.002 inch per revolution. (12) Machine the part to applicalbe dimensional requirements of Drawing (55820) 161781-103. (13) Inspect to the requirements of drawing, (55820) 161781-103. 5-78 Change 25 WARNING RTV-3145 Electrical Insulating compound is an irritant to skin and eyes. PPE: safety glasses, butyl rubber gloves, and good ventilation. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for appropriate safety precautions. (4) Apply a thin coat of RTV-3145 High Temperature Adhesive or GE Silicone Adhesive to one surface of each silicone pad. (5) Attach silicone pads to inner surface of containment ring extension at 60degree intervals in accordance with Sundstrand Drawing No. (55820) 168347. (6) Hold silicone pads in place with either tape or clamps in order to prevent pads from detaching from the containment ring while drying. Allow 24 hours curing time. TO 2G-T62T-43 x. Repair of Accessory Gear (Figure 3-12, 120). NOTE Subject gears shall not be repaired if new gears are available. If gears become available, make buy vs. repair decision for all worn/damaged gears before performing repairs. (1) (3) WARNING Grind the internally splined end of Accessory Gear, P/N 163057-101, as required to remove scoring to a diameter of 0.440 (+0.0220/-0.0025) inch and grind length of 0.400 (±0.005) inch, measured from the internally splined end of the shaft. Grind radius shall be 0.062 to 0.125 inch. Concentricity shall be maintained within 0.0005 inch. Gear shall be scrapped if scoring still exists beyond 0.4375 inch diameter. Nickel plating solution can cause irritation and burns to the skin and eyes. Skin contact can cause sensitivity and allergic reaction. Mist can cause respiratory irritation if inhaled. Repeated, long-term overexposure may cause cancer. Wear nitrile gloves, chemical splash-proof goggles, face shield, and apron. Consult the applicable MSDS and most recent industrial hygiene survey for additional information. (4) Hard Nickel Sulfamate plate ground shaft surface in accordance with Local Processing Specification (LPS) CP01-2B-826, Revision C, to obtain diameter of 0.468 to 0.470 inch after finish grinding. (5) Finish grind plated gear shaft as required to meet dimensional, concentricity, and surface finish requirements of Hamilton-Sundstrand Drawing No. (55820) 163057. (6) Magnetic particle inspect finished accessory gear shaft per (96916) Inspection and Testing LPS CP09-2-J-4060 and ASTM E1444. No cracks allowed. WARNING ASTM E1444 Magnetic Particle materials may irritate skin and eyes. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact and avoid inhaling powder and vapors. Wear goggle, nitrate gloves, and apron. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for appropriate safety precautions. (2) Magnetic particle inspect machined shaft surface per (96916) Inspection and Testing LPS CP09-2-J-4060 and ASTM E1444. No cracks allowed. Table 5-5. MATERIAL CLEANING Aluminum Section IV Cres Magnesium Steel Section IV Section IV Section IV Titanium Section IV Shotpeen ground shaft surface with 0.0138 to 0.0280 inch diameter (S-170) shot, 0.007 to 0.014, A2 intensity. Materials Application Table TREATMENT FINISH PRESERVE Specification MIL-C-5541/ Anodize None Specification MIL-M-3171 Black oxide, chrome/ nickel plating Prime, paint None None Prime, paint Specification MIL-C-83285 None None None None Preservation oil, Specification MIL-L-6081, grade 1010 None Change 25 5-79 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 5-6. Engine Compressor Knurled Sleeve Data Inspection Required Dimension (inches) Actual Dimension (inches) Wheel S/N Pre-sleeve hub OD (top) 1.4015-1.4020 Pre-sleeve hub OD (bottom) 1.4015-1.4020 Sleeve ID (top) 1.399-1.400 Sleeve ID (bottom) 1.399-1.400 Finished sleeve OD (top) 1.5985-1.5990 Finished sleeve OD (bottom) 1.5985-1.5990 Knurl depth 0.010-0.015 APU S/N y. Repair of Reduction Drive Housing (Figure 3-12, 142). (2) NOTE If sealant has been previously applied and is still intact, the following procedures are not necessary. (1) Remove Air-Oil Separator Sleeve from reduction drive housing and inspect for corrosion on mating surfaces. Prepare surface for sealant by removing corrosion, and cleaning mating surfaces per Section IV or applicable local process specifications. WARNING PR1826 B-2 Sealing Compound may cause irritation of eyes, skin, nose, and throat. Prolonged or repeated exposure to skin may cause allergic reaction. Very large dose by inhalation may cause dizziness, drowsiness or liver damage. Wear butyl rubber gloves and safety glasses. Use with adequate ventilation. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. CAUTION Ensure holes in Air-Oil Separator Sleeve are not blocked. 5-80 Change 25 Sparingly apply PR1826 B-2 sealing compound in the location where the AirOil Separator Sleeve, P/N 163056-2, mates to the Reduction Drive Housing, P/N 161781-103. Allow 16 hours to cure. Use C-clamps to maintain pressure on sleeve while sealant is curing. WARNING AMS-S-8802 Sealant can irritate skin and eyes. Repeated or prolonged contact can cause an allergic skin reaction. Do not sand or grind on cured material. Use gloves, safety glasses, and adequate ventilation. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. CAUTION Ensure holes in Air-Oil Separator Sleeve are not blocked. (3) Alternate procedure: Sparingly apply AMS-2-8802 sealing compound in the location where the Air-Oil Separator Sleeve, P/N 163056-2, mated to the Reduction Drive Housing, P/N 161781103. Allow 72 hours to cure. Use Cclamps to maintain pressure on sleeve while sealant is curing. (4) Reattach Air-Oil Separator Sleeve by match drilling new pin holes and installing new pins in accordance with TO 2G-T62T-43 Hamilton-Sundstrand (55280) Drawing No. 161781. Do not install pins in same location as the old pin holes. (f) Face off any remaining material from the threaded plug flush to the face of generator pad bore. (5) Etch the letter R on the Air-Oil Separator Sleeve to denote that this repair has been performed. (g) (6) Reduction Drive Housing 10-32 Helicoil Insert repair for generator pad (6.000 to 6.001 inches) bore damaged/eroded/ worn beyond normal repairs. Any 10-32 helicoil/inserts that can simply be replaced with a 10-32 shall be replaced with a 10-32 helicoil or insert. Housings that are damaged beyond the following repair or cannot accept a 5/16-24 UNF3A machine bolt, shall be replaced. Adhering to the center datum locations, drill and tap plugs to accept a 10-32 UNF-3B helicoil. Lightly deburr the plugs. (a) Remove damaged 10-32 inserts. (b) Adhering to the center datum locations of the insert holes per drawing (55820) 161781, thread the 10-32 insert hole as necessary to accommodate a 5/16-24 UNF-3A machine bolt. (c) Ensure that all damage and debris has been removed from the three 1032 insert holes. Housings that exhibit oversized holes too large for the plug repair shall be replaced. (d) Manufacture Reduction Drive Housing Plugs. Make plug from bolt, part No. AN5CH6A. WARNING Epoxy Primer is flammable and toxic. Avoid inhaling. Use only with adequate ventilation, away from heat or open flame. Wear gloves and goggles. It can irritate skin and cause burns. In case of contact, immediately flush skin or eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Get medical attention for eyes. (h) Apply epoxy primer (Specification MIL-P-23377, type I, class C or N) to all tapped holes and sparingly to the OD of the 10-32 UNF-3B helicoils. (i) Sparingly apply sealant (Specification MIL-S-22473, grade A) to tapped holes to ensure full thread coverage and to ensure that sealant does not interfere with the ID of the inserts. (j) Install the 10-32 UNF-3B helicoils into each plug. (k) Allow sealant to cure 24 hours at room temperature or oven heat for 1 hour at 200 (±10)oF (93oC). Verify that sealant will not prevent installation of assembly bolts. (l) Machine housing to re-establish the O-ring groove. Maintain concentric and dimensional tolerances. WARNING Sealant can irritate skin and cause burns. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Wear gloves, goggles, and apron. In case of contact, immediately flush skin or eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Get medical attention for eyes. z. Repair of Diffuser Housing (Figure 3-10, 45). (1) NOTE Oversized holes may extend (break through) the thin-walled area of the (6.214 to 6.218 inches) O-ring groove. The plugs, once installed, will extend into the groove. The plugs will restore any broken out areas of the O-ring groove. (e) Install the threaded plugs, slotted side up, using sealant. Inspect throat area and diffuser mating surface for damage or other surface deviations. Housings which meet the following repair limitations shall be repaired per step (2) through (11). (a) Scoring on the throat area due to contact with the inducer which exceeds 0.005 inch in depth, but does not exceed 0.033 inch in depth. (b) Damage/out-of-roundness of the diffuser mating surface which is less Change 25 5-81 TO 2G-T62T-43 than 11.100 inches in diameter, but not more than 11.185 inches. (2) (3) (4) it is absolutely imperative that the air reaching the work surface be absolutely clean and free of oil and moisture. Machine the damaged throat area to a depth of 0.030-0.033 inch, and the damaged/out-of-round diffuser mating surface as necessary up to 11.181/11.185 inches, ensuring 0.010 inch minimum metal spray thickness. Fillet radius 0.030-0.050 inch. Refer to Figure 5-28 as necessary. The surface finish shall be no finer than 250 RMS. Vapor degrease housing per LPS CP 030-GG-9533 Hydrofluoroether Vapor Degreasing. All areas shall be masked as required to protect areas not designated for metal spray. Rubber plugs, masking tape, polished metal masks, masking compounds, etc., are acceptable. Plugs should extend 0.015-0.020 inch above finished coating. (5) Blast areas to be sprayed with Metcolite ‘C’ powder. Housings should be sprayed immediately after blasting operation. A maximum of 1 hour between blasting operation and application of metal spray coating is allowed. (6) Preheat housing to a temperature of 200-250oF. (10) WARNING Aluminum/nickel powder may cause skin dermatitis and eye irritation. Nickel is a suspected carcinogen; don’t permit spray dust to enter eyes, mouth or open wounds. PPE: NIOSH approved respirator, aluminized gloves, and goggles. (7) Apply Metco 450 ‘bondcoat’ until a thickness of approximately 0.006 inch is obtained. (8) Apply up to 0.045 inch thickness of Metco SF aluminum wire (I/S inch diameter). (9) The following should be observed during application of metal spray: (a) Clean cooling air shall be directed to the housing during each spraying operation, preferably to surfaces immediately adjacent to the surface to be sprayed. If this is not possible, 5-82 Change 25 (b) Surface temperature must be controlled by use of touch pyrometers while observing the preheat temperature of 200-250oF throughout the metal spray procedure. (c) Gun to workpiece distance shall be maintained at a distance of 4 to 6 inches. (d) Metal spray coating buildup shall be accomplished by two or more passes with gun. In no instance shall single pass coating thicknesses exceed 0.010 inch. (e) Metal spray coatings shall be applied with the gun angle to the substrate at no less than 45 degrees. (f) Unless otherwise directed, nitrogen shall be used in combination with hydrogen bottled gas to accomplish metal spray operations. In the event that Argon gas is employed, its purity shall be maintained. Machine the throat or diffuser mating surface to the dimensional finish requirements of the drawing P/N (55820) 161625. Ensure a smooth transition of all the metal sprayed areas into adjacent surfaces of the housing using appropriate machining practices. WARNING Specification MIL-C-81706 Chemical Conversion Coating contains carcinogenic chromates and contact may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Burns may not be immediately obvious. Avoid contact with eyes, skin or clothing. Keep away from oils, fuels, and other chemicals. Personnel shall wear butyl gloves, splash-proof goggles, and face shield. A respirator may be required when handling dry material. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for appropriate safety precautions. (11) Apply Specification MIL-C-81706 Class 1A Chemical Conversion Coating per Specification MIL-C-5541 to all machined surfaces. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-28. Metal Spray Repair; Diffuser Housing, Part No. 161625 Change 25 5-83 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 5-29. 5-84 Change 25 Oil Sump Leak Test Plate TO 2G-T62T-43 aa. Repair of inside diameter of bearing front carrier (Figure 3-10, 7). (1) Lightly machine the 2.01/1.98-inch diameter groove located behind diameter (A), per Figure 5-2, to remove any residual abradable coating in this area. (2) Drill all (12 each) diameter (F) holes, one at a time, before finish machining Diameter (A). (3) All final dimensions shall be in accordance with Hamilton-Sundstrand Drawing No. (55820) 161412. Change 25 5-85/(5-86 blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 SECTION VI ASSEMBLY 6-1. GENERAL. This section contains procedures for assembly of the APU, including combustor assembly, reduction drive unit, and turbine assembly. (17). Torque each pin to 40 to 60 inchpounds. f. Safety wire each pin (14) individually with lockwire, MS20995C32. 6-2. GENERAL ASSEMBLY PROCEDURES. Note the following before beginning assembly procedures: g. If removed, install loop clamp cushions (13) and loop clamps (12) on fuel manifold (9), approximately 45 degrees each way from 12o’clock position. There must be a minimum of 0.050 inch clearance. a. Perform assembly in a clean work area. b. Inspect all parts, not being replaced, per section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement, before reinstalling in APU. h. Assembly clearances are listed in procedural steps. Secure loop clamps (12) with bolts (10), washers (8), and nuts (11). i. Remove protective caps from tips of fuel manifold (9) and lubricate tips of fuel manifold with assembly f luid, RT-403A, No. 1. Be careful not to get assembly f luid in hole of nozzles. c. 6-3. ASSEMBLY OF COMBUSTOR ASSEMBLY. This section contains procedures for assembly of the combustor assembly. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers, refer to f igure 3-28. a. b. If previously removed, install spring (20), washers (19), and igniter plug grommet (18) per section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. CAUTION To prevent damage to fuel manifold tips and subsequent failure, do not bend tubes during installation of fuel manifold. Make sure tips do not damage O-rings in combustor liner. Lightly coat O-rings (16) with assembly f luid, RT-403A, No. 1. CAUTION j. Align fuel manifold (9) with mounting bracket on combustor housing (17). Carefully insert tips of fuel manifold (9) into six tube f ittings around combustor housing (17). k. Apply antiseize compound, Specif ication MIL-A-907, to threaded area of tube f ittings on combustor housing (17) and top of collar on fuel manifold (9). Torque to 55 to 65 inchpounds. l. Apply antiseize compound, Specif ication MIL-A-907, to threads and mating surfaces of bolts (6) and install bolts, washers (8), and nuts (7), securing fuel manifold (9) to combustor housing (17). Torque to 24 to 27 inchpounds. m. Apply a small amount of assembly f luid, RT403A, No. 1, to O-ring (5) and install O-ring and f ilter f itting (4) in fuel manifold (9). Torque to 135 to 150 inch-pounds. Do not use a sharp tool when inserting O-rings, as damage may occur. NOTE Exposure to heat causes O-rings to crystallize and deteriorate. Ensure all old O-ring material is removed, otherwise new O-rings may not f it properly. c. Using a 1/8-inch diameter pin punch, install O-rings (16) in atomizer f ittings of combustor liner (15). d. Insert pin punch, with rounded end into each atomizer f itting to make sure O-rings are seated in grooves. e. Lightly coat pins (14) with antiseize compound, Specif ication MIL-A-907, and install pins, securing combustor liner (15) to combustor housing (17). Align igniter grommet with igniter plug hole in combustor housing Change 19 6-1 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 inserts (128, 129, 130, 131 or 139) per section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. WARNING Primer and adhesive may cause eye and skin irritation. Wear protective goggles and gloves. Avoid prolonged breathing of vapors. e. CAUTION Determine shim (88) thickness as follows: (1) Add mounting distance stamped on Zerol pinion (91) to dimension A (bearing width) etched on outer race of bearing (92). This provides dimension B (Figure 6-1). (2) Subtract dimension E stamped on housing carrier (77) from dimension D stamped on housing (142) . This provides dimension C (Figure 6-1). (3) Subtract dimension B from dimension C (Figure 6-1). This provides thickness required for shim (88). Allowable tolerance on shim is ±0.001 inch. Do not allow primer or adhesive to get in orifice, as this will change/restrict flow pattern. n. If removed, install start fuel nozzle (3) in fitting (2) as follows: apply a thin film of primer, Specification MIL-S-22473, to three threads nearest top hex of fitting (2) and allow to dry. Apply adhesive, Specification MIL-R-46082, Type II, to the same area. Install start fuel nozzle (3) into fitting (2) and torque 35 to 40 inch-pounds. Stake in two places. o. Install fitting (2) into combustor housing (17). Torque to 95 to 105 inch-pounds. p. Install igniter plug (1) as follows: (1) Lightly coat first two threads of igniter plug (1) with antiseize compound, Specification MIL-A-907. (2) Install igniter plug (1) into mounting boss on combustor housing (17). Torque to 108 to 132 inch-pounds. f. 6-4. ASSEMBLY OF REDUCTION DRIVE UNIT. This section contains procedures for assembly of the reduction drive unit. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to Figure 3-12. a. Heat bearings (64), accessory pad cover (108), Zerol pinion (91), and housing (142) in an oven maintained at 250 to 300oF for a minimum of 30 minutes. b. Heat housing carrier (77) and hub ring gear (85) in an oven at 200oF for 10 minutes. c. If previously removed, install spring-slotted pins (141), oil/air separator sleeve (140), sleeve (137) or pin (136) per section V Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. d. If previously removed, install studs (133, 134 or 135), lockrings (132 and 138) or 6-2 Change 22 Determine shim (46) thickness as follows: (1) Establish dimension D, by placing ball bearing (55) in mounting block, ST90682 (Figure 2-1, 69), and measuring the movement between the inner race and the outer race of ball bearing (55) (Figure 6-2). Subtract the movement of inner race and the outer race of ball bearing (55) from the width of the outer race stamped on outer race of ball bearing (55). (2) Add mounting distance stamped on Zerol bevel gear (Figure 3-12, 45) to dimension D + A. This provides dimension B. (3) Subtract dimension B from C stamped on housing (142) . This provides thickness required for shim (46). Allowable tolerance on shim is ±0.0001 inch. g. Place accessory gear (120) and ball bearing (118) in a freezer for a minimum of 30 minutes. h. Install valve housing (103) as follows: (1) Install relief valve spring (105) into valve housing (103). (2) Install ball (104) into seat of housing (142). (3) Place relief valve spring (105) and valve housing (103) over ball (104) seat. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 housing (103) to housing (142). Torque to 20 to 25 inch-pounds. CAUTION Ensure that ball (104) and relief valve spring (105) are in proper position. Otherwise, valve housing (103) will be locked open and oil pressure will not develop. Severe damage to APU will result. (4) i. Install intermediate gear (117) as follows: (1) Install one retaining ring (127) in inside diameter of groove on intermediate gear (117) and heat in an oven not to exceed 250oF for a minimum of 30 minutes. (2) Install oil shield (119) in housing (142). Install vent plate (102), screws (99), and washers (100 and 101) securing valve Change 22 6-2A/(6-2B blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-1. Gear Shimming 6-3 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-2. Determination of Shim Thickness 6-4 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 . . WARNING WARNING Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. Wear protective gloves when handling chilled parts to avoid injury. Wear protective gloves when handling chilled parts to avoid injury. (1) Remove accessory gear (120) from freezer and install oil/air separators (121 and 122) on accessory gear (120). If previously removed, install plug (124) and dowel pin (125) per Section V Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (3) Remove intermediate gear (117) from oven and ball bearing (118) from freezer. (2) (4) Using arbor plate and driver, ST70286 (Figure 2-1, 37), and driver set, ST70414 (Figure 2-1, 38), press new ball bearing (Figure 3-12, 118) into inside diameter of intermediated gear (117). Ensure that outer race of bearing makes contact with retaining ring (127). NOTE If ball bearings (123) do not slide into place easily, it may be necessary to heat ball bearings. (5) Install another retaining ring (127) securing ball bearing (118) to intermediate gear (117). If necessary, heat ball bearings (123) in an oven maintained at 250-300oF for a minimum of 30 minutes. (4) Place accessory gear (120) on an arbor press. (6) Position bearing space (116) in housing (142). (7) Position intermediate gear (117) over bearing spacer (116). WARNING (8) Lubricate O-rings (114 and 115) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install O-rings on intermediate gear shaft (113). Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (9) Ensure that O-rings (114 and 115) are not cut and oil shield (119) does not slip when installing intermediate gear shaft (113). (10) (5) Remove ball bearings (123) from oven and press onto shaft of accessory gear (120) using bearing assembly tool, ST90671 (Figure 2-1, 68). Ensure that inner race of ball bearings contact shoulders of oil/air separators. (6) Remove accessory pad cover (Figure 317, 108) from oven and place in an arbor press. If previously removed, install inserts (111) or lockrings (110) per Section V. CAUTION j. (3) Using puller, ST70235 (Figure 2-1, 20), install intermediate gear shaft (Figure 3-12, 113) into housing (142), carefully slipping intermediate gear shaft (113) through ball bearing (118), bearing spacer (116), and oil shield (119). Secure with retaining ring (112). Install accessory gear (120) as follows: NOTE Index plugged end of accessory gear shaft away from accessory pad cover. (7) Install accessory gear (120) into accessory pad cover (108). A slight amount of pressure may be required to seat the bearing in accessory pad cover housing. NOTE If accessory gear (120) and accessory pad cover (108) won’t assembly easily, it may be necessary to place in freezer. (8) If necessary, place assembled accessory gear (120) and accessory pad cover (108) in a freezer for 30 minutes. Change 22 6-5 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (3) If previously removed, install key (95) using a soft mallet and tapping key into slot of straight drive shaft (78). (4) If previously removed, install housing liner (96) and pipe plugs (81) in housing carrier (77) per Section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. WARNING Wear protective gloves when handling heated or chilled parts to avoid injury. (9) If placed in freezer, remove assembled accessory gear (120) and accessory pad cover (108). (10) Lubricate O-ring (109) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install in groove provided on accessory pad cover (108). (11) Remove housing (142) from oven and install in assembly fixture, ST70370 (Figure 2-1, 37). (12) Install accessory gear (120) into housing (142). (13) Press accessory pad cover (108) into housing (142). Ensure bolt holes are aligned, and index pad on cover aligns with the housing pad. . Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (5) Place straight drive shaft (78) in dry ice, CGA G-6.2, for 20-30 minutes. (14) Temporarily install screws (106) and washers (107), securing accessory pad cover (108) to housing (142). (6) (15) Lubricate inner lip of shaft seal (126) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. Remove Zerol pinion (91) from oven and straight drive shaft (78) from dry ice, CGA G-6.2. (7) (16) Using guide tool set, ST90889-01 (Figure 6-3), install shaft seal (126) so that it bottoms against inner shoulder of housing (142) and accessory pad cover (108). Install Zerol pinion (91) over straight drive shaft (78). (8) Install retainer bearing ring (93) over straight drive shaft (78) with groove up. (17) k. . WARNING Install protective cover on accessory drive pad (108) and secure. Install straight drive shaft (78) and housing carrier (77) as follows: (1) If previously removed, install inserts (98) in housing carrier per Section V Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (2) Apply solid lubricant, MIL-PRF-46010, to threaded portions of straight drive shaft (78). 6-6 Change 22 NOTE Thrust race of bearings (90 and 92) must be away from Zerol pinion (91). Bearing inner race must contact Zerol pinion. Recessed face of retainer bearing ring (93) must face down (against bearings). (9) Using arbor press, arbor plate, ST70236, and driver, ST70282 (Figure 6-4), press bearings (90 and 92) onto straight drive shaft (78). TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-3. Installation of Shaft Seal 6-7 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-4. Installation of Bearings on Straight Drive Shaft 6-8 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (10) Place assembly into holding fixture, ST70266 (Figure 2-1, 28). Install locknut (Figure 3-12, 83). Using spanner wrench, ST70241 (Figure 2-1, 24), torque locknut (83) to 450-500 inchpounds. Stake locknut (83) in place. (11) Using a soft mallet, tap key (94) into slot on straight drive shaft (78). WARNING (12) Remove housing carrier (77) and hub ring gear (85) from oven. (13) Position shim (88) in housing carrier (77). (14) Position housing carrier straight drive shaft (78). (15) Secure retainer bearing ring (93) to housing carrier (77) with screws (86) and lockwashers (87). Torque screws (86) to 30-40 inch-pounds. Bend lockwashers (87) tabs to lock one end down in hole in housing carrier (77). (17) (77) over Using arbor press and driver, ST70283 (Figure 6-5), install hub ring gear (Figure 3-12, 85) and retainer (84) on straight drive shaft (78). Using holding fixture, ST70266 (Figure 2-1, 28) and spanner wrench, ST70243 (Figure 2-1, 26), install locknut (Figure 3-12, 89) on straight drive shaft (78) and torque locknut (89) to 450-500 inchpounds. Stake locknut (89) in place. (18) Heat housing (142) until it is warm to touch (100 (±10)oF). (19) Lubricate O-rings (79 and 80) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install O-rings in housing carrier (77). NOTE Make sure O-ring (80) is seated in groove of housing (142) and O-ring (79) does not move. (20) (21) NOTE Shaft seal (97) will be installed after all interior components of housing (142) are installed and after backlash check is completed. l. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (16) washers (59) to equal thickness of carrier assembly (60). Torque in three stages 10-12, 20-25. Torque sequence: 1, 4, 7, 2, 5, 8, 3, 6. Torque bolts (58) to 2025 inch-pounds. Install housing carrier (77) and assembled parts into housing (142), using aligning pin or equivalent. Temporarily secure housing carrier (77) in housing (142) with bolts (58), using Install Zerol level gear (45) and bevel gear support (40) as follows: (1) If previously removed, install inserts (44) in bevel gear support (40) per Section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (2) If previously removed, install liners (42 and 43) and pin (41). NOTE Side of retainer (49) with countersink holes must face Zerol bevel gear (45). (3) Position retainer (49) on Zerol bevel gear (45). (4) Using driver, ST70281 (Figure 2-1, 32), press ball bearing (Figure 3-12, 55) on Zerol bevel gear (45) with thrust side up. (5) Install spacer (56) on Zerol bevel gear (45). (6) Using driver, ST70282 (Figure 6-6), press ball bearing (54) onto Zerol bevel gear (45). Ensure inner races of bearing contact spacer (56). (7) Install locknut (51) finger tight. (8) Position balls (53) in groove in Zerol bevel gear (45), and using bearing installation tool, ST71240 (Figure 2-1, 56), install accessory drive pinion (52) on Zerol bevel gear (45). (9) Install locknut (50) finger tight. (10) Mount Zerol bevel gear (45) in holding fixture, ST70267 (Figure 6-6). (11) Using spanner wrench, ST70241 (Figure 2-1, 24), torque locknut (Figure 312, 51) to 450-500 inch-pounds. (12) Using spanner wrench, ST70243 (Figure 2-1, 26) torque locknut (Figure 3-12, 50) to 450-500 inch-pounds. Change 22 6-9 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-5. 6-10 Change 22 Installation of Hub Ring Gear and Retainer T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-6. Installation of Bearings on Zerol Bevel Gear Change 22 6-11 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (13) Stake locknuts (50 and 51) into grooves of Zerol bevel gear (45) shaft. (24) Remove holding bar, ST70254, and backlash gage, ST60811 (Figure 6-7). (14) Install Zerol bevel gear (45) and assembled parts into bevel gear support (40) housing and secure with screws (48). Torque to 24-27 inch-pounds. (25) Place housing (142) in holding fixture, ST70278 (Figure 6-9). (26) Using adapter, ST70242 (Figure 6-9), provide friction drag on Zerol bevel gear (45) until adapter, ST70242, just starts to move and check tooth pattern (Figure 6-9). (27) If required, remove bevel gear support (40) and shim (46) and adjust thickness of shim (46) to achieve desired pattern. Either add or remove 0.003 inch laminations. (Figure 6-8). (28) If shim (46) thickness is adjusted, repaint gear teeth with gear marking compound, Dykem blue, or equivalent. (29) Reinstall shim (46) and bevel gear support (40) and secure with screws (48). Torque to 24-27 inch-pounds. (30) Repeat steps (17), (21), and (22) to recheck backlash. (31) Lubricate inner lip of shaft seal (57) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (32) Using guide tool set, ST90889-04 (Figure 6-10), install shaft seal (57) in housing (142). Ensure that seal bottoms against flange end. (33) Remove housing (142) from holding fixture, ST70278 (Figure 6-9). (15) Lubricate O-ring (47) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install O-ring (47) on bevel gear support (40). (16) Install shim (46) on housing (142). (17) Lightly apply gear marking compound, Dykem blue, or equivalent, to teeth of Zerol bevel gear (45). WARNING Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (18) Oven heat housing (142) to approximately 100oF for installation of bevel gear support (40). (19) Install assembled bevel gear support (40) into housing (142). Engage gears, using nuts in three places to hold bevel gear support in place. (20) Secure bevel gear support (40) with cap screws (39). Torque to 20-25 inchpounds. (21) Insert holding bar, ST70254 (Figure 67), into spline of straight drive shaft (78) and lock in place. (22) Install backlash gage, ST60811 (Figure 6-7), and rotate straight drive shaft (78) in clockwise direction, to determine maximum backlash reading between accessory drive pinion (52) and Zerol bevel gear (45). m. Install ring gear (69) as follows: (1) Lubricate inner gear teeth on ring gear (69) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (2) Install ring gear (69) and retaining ring (68). (3) Using disassembling tool, ST70284 (Figure 2-1, 35), insert each leg of tool in equally spaced access slots inside ring gear (Figure 3-12, 69). Slots are recessed around perimeter of teeth that mate with splines of hub ring gear (85). Turn knurled knob of tool to compress retaining ring (68), then pull ring gear (69) into hub ring gear (85). Withdraw tool, allowing retaining ring (68) to seat in groove in hub ring gear (85). (4) Ensure that ring gear (69) is axially secure. NOTE Back lash tolerances must be between 0.002-0.010 inch. (23) If backlash is not within tolerance, correct as follows: (a) Over maximum tolerance, move gear toward cone center reduce shim (46) (Figure 6-8). (b) Under minimum tolerance, move gear away from cone center increase shim (46) . 6-12 Change 22 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-7. Installation of Backlash Gage 6-13 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-8. Backlash and Pattern Requirements 6-14 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-9. Installation of Adapter 6-15 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-10. Installation of Shaft Seal 6-16 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 n. Assemble and install carrier assembly (60) as follows: (1) (2) If previously removed, install dowels (67), inserts (72), spring-slotted pin (76), oil jet cartridge (75), and sleeves (73 and 74) per Section V. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (3) Install retaining ring (66) in carrier assembly (60). Freeze gear planet set (65) in dry ice, CGA G-6.2, for a minimum of 30 minutes. WARNING WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Figure 6-11. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (4) Remove bearings (64) from oven. (5) Using driver, ST90133 (Figure 6-11), press bearings (64) onto gear planet set (65). Ensure inner race of bearings contact shoulders of gear shafts. Installation of Bearings Change 22 6-17 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (6) Using arbor press and driver, ST90142 (figure 6-12) install bearings (64) gear planet set (65) in carrier assembly (60). Make sure etched side is up. (7) Install cover (63) on carrier assembly (60), and secure with bolts (61) and washers (62). Torque to 55-70 in. lb. (8) Install cover (82) in housing carrier (77). (9) Remove temporarily installed bolts (58) from housing carrier (77). (10) Install lube oil elbow (71) in carrier assembly (60). (11) Install gasket (70) on housing carrier (77). Figure 6-12. Installation of Gear Planet Set and Bearings NOTE (1) Make sure cover (82) is not loose and lube oil elbow (71) is installed correctly. If previously removed, install dowel pin (25) in housing (142) per Section V Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (2) Install one dowel pin (34) in driver shaft (37) and one dowel pin (34) in driven shaft (38). (12) Install carrier assembly (60) on housing carrier (77). (13) Install bolts (58) and washers (59). Torque in three stages 10-12, 22-25, and 30-37 in. lb. Torque sequence: 1, 4, 7, 2, 5, 8, 3, and 6. o. Assemble and install oil pump housing (26) as follows: 6-18 Change 13 (3) Install pump element gears (36) on driver shaft (37) and driven shaft (38). (4) Install assembled gears and shafts in oil pump housing (26). T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (5) Install cover (35) on oil pump housing (26) and ensure that dowel holes are aligned. (12) Replace pump drive gear (33) or oil pump housing (26) if required to meet requirements of test. (6) Install pump drive gear (33) and remaining dowel pin (34) on driver shaft (37). (13) Remove oil pump housing (26) from adapter, ST90030 (Figure 6-13). (7) Secure pump drive gear (33) with washer (32) and self-locking nut (31). Torque to 20-25 inch-pound. (14) Lubricate O-ring (Figure 3-12, 30) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install on oil suction tube (29). (8) Install assembled oil pump housing (26) on flow bench using adapter, ST90030 (Figure 6-13). (15) Install oil suction tube (29) in oil pump housing (26) and secure with cap screw (28). Torque to 20-25 inch-pound. (16) Lubricate gasket (27) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install on oil pump housing (26) mounting face. (17) Install oil pump housing (31) in housing (142). (18) Apply thread locking compound, Specification MIL-A-46146, type III, under head of screws (23 and 24) extend approximately 1 inch along shank. (19) Install screw (24) in hole next to oil port and shorter screw (23) in hole below screw (24). Torque to 20-25 inch-pound. WARNING Lubricating oil, Specification MIL-L7808, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. (9) Flow-check oil pump housing (Figure 312, 26) at 15 psig outlet pressure and zero inlet pressure, using lubricating oil, Specification MIL-L-7808, at 70oF. NOTE Flow rates are equivalent to 0.0364 cubic inch per revolution. (10) Run oil pump at 2400 rpm and measure flow. Minimum flow must be 144.0 pph (0.378 gallons per minute). (11) Increase pump speed to 4000 rpm and measure flow. Minimum flow must be 241.0 pph (0.630 gallons per minute). p. Using guide tool set, ST90889-01 (Figure 21, 71), install shaft seal (Figure 3-17, 97) in housing (142). q. Install oil filter element (11) as follows: (1) If removed, or new bypass valve housing (6) is required, install ball bearings (10) and valve spring (9). Make sure spring is against ball bearings (10). Change 22 6-19 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-13. Oil Pump Test Setup 6-20 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (2) Mount bypass valve housing (6) onto oil filter cap assembly fixture, ST70433 (Figure 2-1, 39). NOTE Spring pin (Figure 3-12, 8) should be flush with bypass valve housing (6). Do not push too hard or bypass valve housing will crush. (3) r. Tighten set screw and put bypass valve housing (6) under arbor press. Using a screw, press spring pin (8) into housing until flush with housing. (4) Lubricate O-ring (Figure 3-12, 7) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (5) Install O-ring (7) in groove around bypass valve housing (6). (6) Install oil filter element (11) on bypass valve housing (6). (7) Installed assembled oil filter element (11) and bypass valve housing (6) in housing (142) and sevure with retaining ring (5). Lubricate O-ring (21) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install on housing (142) flange groove of engine oil sump (22). (2) Install clamp (20) around engine oil sump (22) at attaching flange in 3 o’clock position away from carrier assembly (60). (3) Install engine oil sump (22) flange against housing (142) flange and secure with clamp (20). Orient the engine oil sump (22) drain with the turbine face. Torque nut on clamp to 20-25 inchpounds. (4) Install caplug (19) in engine oil sump (22). (5) Check that magnetic-drain plug (15) will hold its own weight when magnetically attached to a steel surface. Replace if weak. Lubricate O-rings (16 and 18) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (7) Install O-ring (18) self-closing valve (17) and install self-closing valve (17) in engine oil sump (22). Torque self-closing valve to 45-50 inch-pounds. (8) Install O-ring (16) on magnetic-drain plug (15) and install magnetic-drain plug (15) in self-closing valve (17). Torque magnetic-drain plug to 25-30 inch-pounds. (9) Safety wire magnetic-drain plug (15) with lockwire, MS20995C20. s. Install accessory drive gasket (14) and accessory pad cover (13) on housing (142) and secure with bolts (12). Torque to 20-25 inch-pounds. t. Install caplug (1) and plug (2) as follows: Install engine oil sump (22) as follows: (1) (6) u. (1) Lubricate O-ring (3) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (2) Install O-ring (3) on plug (2). (3) Install plug (2) in housing (142) and safety wire with lockwire, MS20955C20. (4) Install caplug (1) in housing (142) and safety wire with lockwire, MS20995C20. If removed, install nameplate (4) with adhesive, Specification MIL-A-46146, type III. 6-5. ASSEMBLY OF TURBINE ASSEMBLY This section contains procedures for balancing and assembly of the turbine assembly and rotor assembly. Unless otherwise indicated, index numbers refer to Figure 3-10. a. If removed, install load compressor seal (Figure 3-10, 21) on load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20) as follows: Change 25 6-21 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 . . load compressor. Hold pressure until both pieces stabilize at room temperature. WARNING Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can injure human skin or tissue on contact. Liquid nitrogen will expand 696 times as it vaporizes, and if the liquid vaporizes in a sealed container, it can produce enormous pressures that could rupture the vessel. Nitrogen can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated or confined areas. Boiling and splashing occurs when filling a warm container with or when inserting objects into liquid nitrogen. Perform these tasks slowly to minimize boiling and splashing. Use tongs to withdraw objects immersed in a cryogenic liquid. Wear chemical splash goggles, face shield, and approved cryogenic gloves/ outer wear when handling liquid nitrogen. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (5) b. Handle load compressor seal (21) carefully to avoid damage to knife-edges. (1) (2) Heat load compressor seal (21) to 600650oF and immerse load compressor wheel (20) in liquid nitrogen, A-A59503, for 10 minutes. Remove load compressor wheel (20) from liquid nitrogen and install on locally fabricated holder (Figure 2-1, 90), with hub shaft facing upward. Balance re-worked rotor shafts (59) as follows: NOTE New rotor shafts are pre-balanced from the factory, thus do not require re-balancing. (1) Set rotor shaft (59) on V-blocks of rotor assembly inspection fixture, ST64016 (Figure 2-1, 14). Set up on Datums -Aand -B- (Figure 6-18) and check runout. Runout at Datums -A- and -B- is 0.0002 inch. NOTE Forward bearing (Figure 3-10, 11) and aft bearing (Figure 3-10, 61) may be installed on shaft and used in lieu of the balancing supports (Figure 2-1, 80 and 81). Thermal burns can result from exposure to or contact with hot materials with a temperature above 115oF. Long, asbestos-free heat-resistant gloves, chemical goggles, and a full face shield must be worn when handling hot materials. CAUTION Machine grind OD of load compressor seal (21) to 1.3395 to 1.3405 inches as required. Replace load compressor seal (21) if dimensional requirement is not met. (2) . . . . Install balancing support, ST94276 (Figure 2-1, 80) and balancing support, ST94281 (81), in balancer, HBH-003 (2) or locally approved equivalent. NOTE Do not move balancing belt once in position or balancing may be thrown off. Rotor shaft must move freely in balancing supports or balancing may be thrown off. Balancing supports must be kept clean or balance may be thrown off. Nominal rotor shaft speed is 940 rpm. (3) Remove load compressor seal (21) from oven and position over hub shaft of load compressor wheel (20) with chamfered side facing down. (3) Install rotor shaft in balancer, HBH-003 (2) or locally approved equivalent and position balancer belt near plane B (Figure 6-18). (4) Using locally fabricated driver (Figure 2-1, 89) and hydraulic or arbor press, press load compressor seal (21) onto hub shaft of load compressor wheel (20). Be sure seal is flush against backface of (4) Dynamically balance rotor shaft not greater than 0.001 inch-ounce (1 moz) in planes A and B (Figure 6-18). Material may be removed from noted areas on rotor shaft diameter. 6-22 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 WARNING Compressed air used for cleaning can create airborne particles that may enter the eyes. Use approved goggles, face shield, and hearing protection when using compressed air for cleaning, cooling or drying. Air pressure shall not exceed 30 psig. Compressed air shall not be directed towards self or other personnel. c. (5) Remove any loose particles from balancing procedure with shop air. (6) Remove rotor shaft (59) from balancer (Figure 2-1, 2). Assemble load compressor wheel (Figure 310, 20), engine compressor wheel (60), and rotor shaft (59) as follows: (1) Using micrometers, measure and record dimensions J, H, and N on Table 6-1 (Figure 6-22, detail J, N, H). Replace parts that do not meet dimensional requirements. WARNING Thermal burns can result from exposure to or contact with hot materials with a temperature above 115oF. Long, asbestos-free, heat-resistant gloves, chemical goggles, and a full face shield must be worn when handling hot materials. (2) Place engine compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 60) and load compressor wheel (20) in an oven stabilized at 650 (±25)oF for a minimum of 2 hours. WARNING Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can injure human skin or tissue on contact. Liquid nitrogen will expand 696 times as it vaporizes, and if the liquid vaporizes in a sealed container, it can produce enormous pressures that could rupture the vessel. Nitrogen can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated or confined areas. Boiling and splashing occurs when filling a warm container with or when inserting objects into liquid nitrogen. Perform these tasks slowly to minimize boiling and splashing. Use tongs to withdraw objects immersed in a cryogenic liquid. Wear chemical splash goggles, face shield, and approved cryogenic gloves/ outer wear when handling liquid nitrogen. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (3) Install rotor shaft in rotor assembly tool, ST71234 (Figure 6-19), place in liquid nitrogen, A-A-59503, cool for 10 minutes prior to installation. (4) Remove rotor shaft from liquid nitrogen and place in base plate of load compressor rotor assembly tooling, ST71219 (Figure 6-19). (5) Install aft bearing (61) on rotor shaft (59), thrust side down (Figure 6-19). (6) Remove engine compressor wheel (60) from oven and install on rotor shaft (59). (7) Install shaft on rotor assembly (tool), ST71234, ener-pak of stretch tool, ST71078, and nut of rotor assembly tool, ST71234 (Figure 6-19), on engine compressor wheel (60). Set pump to 8,000 pounds and hold until parts equalize to room temperature. WARNING Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can injure human skin or tissue on contact. Liquid nitrogen will expand 696 times as it vaporizes, and if the liquid vaporizes in a sealed container, it can produce enormous pressures that could rupture the vessel. Nitrogen can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated or confined areas. Boiling and splashing occurs when filling a warm container with or when inserting objects into liquid nitrogen. Perform these tasks slowly to minimize boiling and splashing. Use tongs to withdraw objects immersed in a cryogenic liquid. Wear chemical splash goggles, face shield, and approved cryogenic gloves/ outer wear when handling liquid nitrogen. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Change 22 6-23 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (8) Remove assembly from base plate of ST71219 and place the load compressor end of rotor shaft (59) into liquid nitrogen, A-A-59503, for 10 minutes. Ensure aft bearing (61) does not contact the liquid nitrogen. (2) (9) Remove load compressor wheel (20) from oven and install on load compressor wheel assembly (tool), ST71236 or 18D8325-1 (Figure 2-1, 54). (10) Install stretch tool, ST71078 (40), and locally manufactured adapter, 18C87861, on rotor shaft (59) and press load compressor wheel (20) on rotor shaft (59). Set pump on stretch tool, ST71078 (Figure 2-1, 40) to 8,000 pounds and hold set until temperature of parts stabilize to room temperature, then remove pump and load compressor wheel assembly (tool), ST71236 or 18D8325-1 (54). NOTE Runout measurements may be taken on balancer in lieu of rotor assembly inspection fixture, ST64016. (3) Install rotor assembly on V-blocks of rotor assembly inspection fixture, ST64016 (Figure 2-1, 14). (4) Measure and record runout at engine compressor wheel face. Mating face runout is 0.0002 inch maximum (Figure 6-20, surface X) and inside diameter is 0.0008 inch maximum (Figure 6-20, diameter Y), full indicator movement. (5) Remove material as required from engine compressor wheel (60) in accordance with Figure 6-16 or load compressor wheel (20) in accordance with Figure 6-17. Do not undercut backface of wheels or remove material from areas not allowed by Figure 6-16 and Figure 6-17. NOTE Record part and serial numbers of aft and forward bearings. d. (11) Remove rotor assembly from stretch tool, ST71078 (Figure 2-1, 40), and install in rotor fixture, ST70137 (17). (12) Install forward bearing (Figure 3-10, 11) with thrust side toward load compressor wheel (20). (13) Using wrench, ST71191 (42), install forward bearing (11) on rotor shaft (59) with thrust side toward engine compressor wheel (60). Locate forward bearing (11) at edges of threads (Figure 6-20). Install nut (4) on rotor shaft and tighten with wrench, ST71191, until forward bearing (11) bottoms out on load compressor wheel (20). e. Check balance at nominal rotor speed of 940 rpm. Amount of unbalance shall not exceed 0.010 inch-ounce (10 moz) on left plane and 0.030 inch-ounce (30 moz) in right plane (Figure 6-21). Remove assembly from balancer. Assembly turbine wheel (Figure 3-10, 55) to the load compressor wheel (20), engine compressor wheel (60), and rotor shaft (59) assembly as follows: (1) Install rotor assemly in rotor fixture, ST70137 (Figure 2-1, 17). (2) Using turbine stud torque wrench, ST71238 (Figure 2-1, 55) or ST383169, install stud (58) into rotor shaft (59). Torque to 190-230 inch-pounds. Remove turbine stud torque wrench. CAUTION WARNING Protect bearings from contamination when removing material from engine compressor wheel during balancing. MIL-PRF-907 Antiseize Compound may irritate skin upon repeated contact or in sensitive individuals. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. Wear nitrile gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Balance load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20), engine compressor wheel (60), and rotor shaft (59) assembly as follows: (1) Install rotor assembly in balancer, HBH-003 (Figure 2-1, 2) or a locally approved equivalent balancer, and install balancer guide piece over rotor assembly. 6-24 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Do not install seal plate (57) at this time. (3) Ensure mating surfaces of engine compressor wheel (60) and turbine wheel (55) are clean. Apply thin coating of antiseize compound, MIL-PRF-907, to turbine wheel. (4) Install turbine wheel (Figure 3-10, 55) over stud (58) and mate with engine compressor wheel (60). (5) f. Check for unbalance of rotor assembly. Maximum unbalance allowance for left plane is 0.010 inch-ounce (10 moz) and 0.030 inch-ounce (30 moz) for right plane (Figure 6-21). Runout at turbine wheel hub shall not exceed 0.0015 inch for right plane (Figure 6-22, detail GG). NOTE A single digit number on the face of load compressor seal (Figure 3-10, 21) represents the runout of the seal OD in ten thousandths. For example, for a load compressor seal (21) with number ‘‘2’’ on the backface, add 0.0002 to 0.0012; runout shall not exceed 0.0014 inch. (2) (3) Turbine wheel shall be indexed (up to 3 times) first to obtain runout or minimum balance conditions prior to material removal from turbine wheel. Any material removed shall conform to the requirements of Figure 6-15. (4) Remove slave nut (54). (5) Install turbine wheel puller, ST71186 (Figure 2-1, 41) and remove turbine wheel (Figure 3-10, 55). (6) Install seal plate (57) with chamfered outside diameter adjacent to engine compressor wheel (60). (7) Install turbine wheel (55), aligning match-marks, and using stretch tool, ST71078 (Figure 2-1, 40), locally manufactured adapter, 18C8786-1, and enerpak of stretch tool, measure stud (Figure 3-10, 58) at 4,000 pounds. (8) Stretch stud (58) at 6,000 to 8,000 pounds and remeasure (Table 6-1, position 7, and Figure 6-22, detail 7). If stretch does not equal 0.017-0.019 inch, unstretch and discard stud. Repeat procedures from paragraph 8.5.2. Install slave nut (54). Balance the final rotor assembly as follows: (1) runout etched on load compressor seal (21) (Figure 6-22, detail AA). Install rotor assembly on V-blocks of rotor assembly inspection fixture, ST64016 (Figure 2-1, 14). Check runout on the forward-most ring of the load compressor seal (Figure 3-10, 21) outer diameter. Total indicated reading shall not exceed 0.0012 inch more than NOTE Ensure entire rotor assembly is matchmarked and aligned. (9) Match-mark load compressor wheel (20), turbine wheel (55), engine compressor wheel (60), rotor shaft (59), and stud (58). Change 22 6-25 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-14. 6-26 Change 22 Balancer Setup (Ref) for Legacy Component-Balance Process T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-15. Balancing Turbine Wheel Change 22 6-27 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-16. 6-28 Change 22 Balancing Engine Compressor Wheel T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-17. Balancing Load Compressor Wheel Change 22 6-29 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-18. 6-30 Change 22 Balancing Rotor Shaft T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-19. Installation of Engine Compressor Wheel Change 22 6-31 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 6-32 Change 22 Figure 6-20. Balancing Rotor Assembly Figure 6-21. Balancing Rotor Assembly T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 6-1. Clearance Chart Diametral Fits Fig. 6-22 Position Description J Aft bearing carrier inside diameter and bearing outside diameter H Labyrinth seal inner diameter and rotor shaft journal outer diameter N Aft bearing carrier inner diameter and engine compressor wheel (knurl outer diameter) Inside Diameter Outside Diameter Clearance 1.5751 1.5748 0.0005 1.5748 1.5746 0.0000 1.1135 1.1105 0.0040 1.1105 1.1095 0.0000 1.6038 1.6000 0.0053 1.6030 1.5985 0.0030 Maximum Minimum Record Radial Clearances Fig. 6-22 Position R Description Turbine wheel to turbine nozzle radial clearance 0.050 Record 0.025 Axial Dimensions Fig. 6-22 Position Description Manufacturing 1 Pinion assembly to adapter assembly clearance 1.120 - 1.204 2 Load compressor wheel to spacer clearance 0.015 - 0.020 3 Tolerance between rotor assembly and inlet housing 0.0175 - 0.0225 4 Turbine wheel tip to turbine nozzle clearance 0.010 - 0.031 5 Shim thickness 0.029 - 0.084 6 Shim thickness 0.037 - 0.082 7 Stud play 0.017 - 0.019 8 Shim tolerance 0.012 - 0.015 9 Turbine wheel tip to seal plate clearance 0.055 - 0.120 Record Actual Stretch Pages 6-35 and 6-36 have been deleted in their entirety. Change 22 6-33/(6-34 blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-22. Clearance Limits 6-37 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Any limits exceeded which require removal, rotation or replacement of parts will require complete rebalancing. g. Assemble turbine assembly as follows: (1) Remove rotor assembly (Figure 3-10, 22) from rotor assembly inspection fixture, ST64016 (Figure 2-1, 14), and set up in rotor fixture, ST70137 (17). NOTE Ensure alignment pins are engaged properly when support housing (30) and inlet housing (31) are mated. Local manufactured tool, PE0014DAC can be used to aid in alignment. (12) Secure support housing (30) to inlet housing (31) with bolts (25) and washers (14). Torque to 24-27 inch-pound. (13) Place assembly in a horizontal position. Using tension tester, ST64038 (Figure 2-1, 16), or LKG 05, measure the amount of pressure in grams, needed to move IGV drive gear (34). The pressure shall not exceed 226 grams to move IGV drive gear in either direction. If pressure exceeds tolerance, disassemble and locate cause before proceeding. NOTE When removing nut (4), use a 7/16inch diameter dowel pin to protect the splines on the rotor shaft before applying pressure. (2) Remove nut (Figure 3-10, 4), and load compressor wheel (20), using assembly aid (4 inch long x 0.437 inch diameter steel dowel), press off load compressor wheel (20) from rotor assembly (22). (3) If previously removed, install inserts (36) in IGV drive gear (34) per Section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (4) If previously removed, install inserts (27) and pins (28 and 29) in support housing (30) per Section V - Inspection, Repair, and Replacement. (5) Install IGV bushings (40) on inlet guide vanes (39). (6) Install IGV sector gears (38) on inlet guide vanes (39) and secure with locknuts (37). Torque to 1-5 inch-pound. Above run on torque. (7) Remove temporarily installed bolts (25) from inlet housing (30). Remove support housing (30) from inlet housing (31). (8) Install IGV drive gear bearing (35) and IGV drive gear (34) on support housing (30). Ensure IGV drive gear (34) is aligned with slot on support housing (30). (9) Install pin drive-flange (33) with bolts (32). Torque to 24-27 inch-pound. (10) Install inlet guide vanes (39) in support housing (30). (11) Align marks (dimples) between IGV sector gears (38) and IGV drive gear (34). 6-38 Change 22 WARNING Liquid nitrogen, Specification MIL-P27401, will freeze eyes and skin. Wear face protection, gloves, and apron during use. (14) Freeze labyrinth seal (52) and bearing aft carrier (53) in liquid nitrogen, Specification MIL-P-27401, (-250oF) for approximately 5 minutes. (15) Using manual press and arbor press guide, ST71207 (Figure 2-1, 45), install labyrinth seal (52) and bearing aft carrier (53) in inlet housing (31). Ensure keying dowel pin in inlet housing (31) matches cutaway in bearing aft carrier (53). Hold minimum pressure for seating until thermal fit is completed. (16) Deleted (17) Install O-rings (42) in inlet housing (31). (18) Set up rotor assembly (22) in rotor fixture, ST70137 (Figure 2-1, 17). (19) Determine follows: (a) shim (51) thickness as Using flat surface, press down on assembly function gage, ST63929 (Figure 2-1, 11), to preset dial indicator to zero. Preset length, dimension X (Figure 6-23), is 4.0080. Using an assembly aid (bullet shaped), to protect threads of rotor, install assembly function gage, ST63929 (Figure 2-1, 11), over engine compressor wheel T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (60) and press down. If dial reading is plus, subtract from 4.0080, if dial reading is minus, add to 4.0080. The result from this circulation is to be used as new dimension X in rest of equation. Remove assembly function gage, ST63929. (b) Install bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5), and assembly check gage plate, ST71217 (48). Measure dimensions A on inlet housing (31) and B on diffuser housing (45) (Figure 624). Subtract dimension of legs etched (7 inches if no etching) on bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5), from dimension A and B. NOTE 0.020 inch is desired clearance. (c) Determine shim (Figure 3-10, 51) thickness using the following formula: contain a neurotoxin that can be absorbed through the intact skin. Symptoms of overexposure include tingling or numbness in hands or feet. Wear nitrile gloves and chemical protective goggles. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. . . NOTE Proper indexing of housing assembly to inlet housing assembly is when, looking forward, the air inlet boss is at the 2:30 o’clock position. It may be necessary to secure diffuser housing (45) to inlet housing (31) with a shorter bolt (model 161327-104, use MS9914-12). (20) Apply assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, or lubricating oil, MIL-PRF-23699, on outside diameter and around top of diffuser housing (45). (21) Using shim thickness determined in step (17), install shim (51) on diffuser housing (45) with guide pins. (22) Using arbor press, install diffuser housing (45) on inlet housing (31) and secure with bolts (43) and washers (44). (23) Record selected shim (51) thickness as position 6 on Table 6-1, (Figure 6-22, detail 6). (24) Coat threads and shanks of bolts (1) with antiseize compound, Specification MIL-A-907. Dimension X - (Dimension A + Dimension B + 0.020) (d) Select appropriate shim size from following: P/N 161793-1 161973-2 161793-3 161973-4 161973-5 161973-6 161973-7 161973-8 161793-9 161793-10 161793-11 161793-12 161793-13 161793-14 161793-15 Dimension 0.010 0.015 0.020 0.040 0.050 0.052 0.054 0.056 0.058 0.060 0.062 0.064 0.066 0.068 0.070 WARNING . . Assembly fluid may cause irritation of the skin and eyes upon overexposure. PPE: chemical goggles and protective gloves. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. MIL-PRF-23699 Lubricating Oil can irritate skin or eyes upon contact. May WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (25) If necessary, put diffuser (Figure 3-10, 41) in dry ice and then install in diffuser housing (45) and secure with bolts (1). Torque to 24-27 inch-pounds. Change 22 6-39 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-23. 6-40 Change 22 Determination of Shim Thickness TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-24. Installation of Bridge Gage 6-41 TO 2G-T62T-43 (26) To ensure that correct shim (51) thickness has been determined, perform the following function as a double check: (a) Install rotor assembly (22) in rotor fixture, ST70137 (17, figure 2-1). (b) Install ring gage, ST61186-06 (8), on engine compressor wheel (60, figure 3-10). Ensure ring gage is properly seated and thickness of ring gage is 0.063 in. (c) Place inlet housing (31) over rotor assembly (22) with ring gage, ST61186-06 (8, figure 2-1), still in place. Do not damage labyrinth seal (52, figure 3-10). NOTE Be sure bolts (1) do not cause diffuser housing to bind on rotor fixture, ST70137. (d) Install bridge gage, ST60051 (figure 6-25), on inlet housing (31, figure 3-10). Measure depth and record measurement. (e) Remove inlet housing (31) and bridge gage, ST60051 (figure 6-24). and ring gage, ST6118606 (8, figure 2-1), from rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10). (f) Install inlet housing (31) over rotor assembly (22) without ring gage, ST61186-06 (8, figure 2-1). (g) Install bridge gage, ST60051 (figure 6-25), over inlet housing (31, figure 3-10). Measure depth and record measurement. (h) Subtract recorded depth obtained in step (g) from recorded depth obtained in step (d). Then subtract the answer from 0.063 in. Tolerance should be within 0.0175-0.0225 in. range, position 3, table 6-1 (figure 6-22, detail 3). NOTE If shim thickness obtained in step (23) is different from shim thickness obtained in step (17), use shim thickness obtained in step (23). 6-42 (27) If correct shim (51, figure 3-10) thickness has not been selected, disassemble turbine assembly, recalculate shim thickness, and install correct shim thickness. (28) Using flat surface and gage set block, preset functional gage assembly, ST63931 (figure 6-26), dial indicator to zero. Present length dimension X (figure 6-26) is 1.6950 in. gage block. (29) Install functional gage assembly, ST63931 (figure 6-26), over load compressor wheel (20, figure 3-10). Record reading on dial indicator. If dial reading is a minus, subtract from 1.6950. If the reading is a plus, add to 1.6950. The result from this calculation is to be used as new dimension X to determine shim thickness. (30) Determine and record thickness of shim (24) using the following formula: Dimension X - (Dimension A + Dimension B + 0.0175) (a) Install bridge gage, ST60051 (5, figure 2-1), across the front flange of the inlet housing (31, figure 3-10) and measure to load compressor wheel (20) seat to obtain dimension A. Subtract dimension of legs etched (7 in. if no etching) on bridge gage, ST60051 (5, figure 2-1), from measurement. (b) Dimension B is determined by installing load compressor scroll (23) on assembly check gage plate, ST71214 (47, figure 2-1). Position bridge gage, ST60051 (5, figure 2-1), across load compressor scroll (23, figure 3-10) and measure to base plate of assembly check gage plate, ST71214 (47, figure 2-1). Subtract dimension of legs etched (7 in. if no etching) on bridge gage, ST60051 (5), from measurement. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-25. Determination of Depth 6-43 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-26. Installation of Functional Gage Assembly (31) To ensure correct shim (24, figure 3-10) thickness has been determined, perform the following steps as a double check: (a) Remove load compressor scroll (23) from assembly check gage plate, ST71214 (47, figure 2-1) and turn load compressor scroll over. (b) Set load compressor wheel (20, figure 3-10) into load compressor scroll (23). (c) Set up load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (77, figure 2-1). over hub of load compressor wheel (20, figure 3-10) and set dial indicator to zero and lock. (d) Using a felt tip pen, mark position of load compressor scroll (23) 6-44 where load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (77, figure 2-1) is positioned, then remove load compressor clearance tool, ST93950, and load compressor wheel (20, figure 3-1) from load compressor scroll (23). (e) Use a depth micrometer to determine the exact height difference between load compressor wheel (20) and spacer of load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (77, figure 2-1). Record value. (f) Install shim (24) and secure load compressor scroll (23) to inlet housing (31) temporarily with setup bolts, washers, and nuts (three or more). T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (g) Install spacer on load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (Figure 2-1, 77), on rotor shaft (Figure 3-10, 59). (32) Clean bore of load compressor wheel (20) and apply a very thin coating of antiseize compound, MIL-PRF-907. WARNING WARNING MIL-PRF-23699 Lubricating Oil can irritate skin or eyes upon contact. May contain a neurotoxin that can be absorbed through the intact skin. Symptoms of overexposure include tingling or numbness in hands or feet. Wear nitrile gloves and chemical protective goggles. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. (h) Apply a light coat of lubricating oil, MIL-PRF-23699, to knurl of engine compressor wheel (60). (i) Install inlet housing (31) over rotor shaft (59). (j) Install load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (Figure 2-1, 77), over load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23) at the same position marked in step (d). Set pin of dial indicator on top of spacer of load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (Figure 2-1, 77). Dial indicator reading will reflect clearance of load compressor wheel (20), plus or minus height difference between spacer of load compressor clearance tool and load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20). Record valve obtained as position 2 (Table 6-1) (required clearance is 0.015-0.020 inch). (k) Remove load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (Figure 2-1, 77), from load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23) and spacer from rotor shaft (59). (l) Remove inlet housing (31) from rotor shaft (59). (m) Remove load compressor scroll (23) from inlet housing (31). NOTE Problems with axial fit of the load compressor wheel to the shoulder of the rotor shaft, may occur if too much antiseize compound is applied. (33) Reheat load compressor wheel (20) in an oven to 650oF for 1 hour. (34) Install predetermined shim (24) thickness and load compressor scroll (23) into inlet housing (31). Record shim thickness as position 5, Table 6-1 (Figure 622, detail 5). Appropriate shims are: P/N 161972-1 161972-2 161792-3 161972-4 161972-5 161972-6 161972-7 1619724 161792-9 161792-10 161792-11 161792-12 161792-13 161792-14 161792-15 Dimension 0.010 0.015 0.020 0.040 0.050 0.052 0.054 0.056 0.058 0.060 0.062 0.064 0.066 0.068 0.070 NOTE To check for proper indexing, the right IGV actuator pad should be 1/2 hole to the right of the 12 o’clock position, looking forward. (35) Secure load compressor scroll (Figure 310, 23) to inlet housing (31) temporarily with setup bolts, washers, and nuts (three or more). (36) Check for proper seating by ensuring that the shimmed space between the load compressor scroll (23) and the inlet housing (31) is closed. (37) Deleted (38) Deleted (39) Deleted (40) Deleted (41) Deleted Change 22 6-45 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (42) . . Set up load compressor restrainer, ST93951-04 (78). wheel WARNING Dry Ice, Carbon Dioxide (solid), CGA G-6.2, can cause severe skin burns and frostbite. Do not handle with bare hands. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear cryogenic gloves, chemical goggles, and face shield. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. Liquid nitrogen is extremely cold and can injure human skin or tissue on contact. Liquid nitrogen will expand 696 times as it vaporizes, and if the liquid vaporizes in a sealed container, it can produce enormous pressures that could rupture the vessel. Nitrogen can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated or confined areas. Boiling and splashing occurs when filling a warm container with or when inserting objects into liquid nitrogen. Perform these tasks slowly to minimize boiling and splashing. Use tongs to withdraw objects immersed in a cryogenic liquid. Wear chemical splash goggles, face shield, and approved cryogenic glove/ outer wear when handling liquid nitrogen. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (43) Chill rotor shaft (Figure 3-10, 59) with dry ice, CGA G-6.2, or liquid nitrogen, A-A-59503. (44) Remove load compressor wheel (20) from oven and install load compressor wheel onto rotor shaft (59). (45) Install load compressor wheel assembly (tool), ST71236 (Figure 2-1, 54), stretch tool, ST71078 (40), and load compressor wheel (Figure 3-10, 20). Set pump on tool to 8000 pounds. Maintain pressure for approximately 30 minutes until temperature of part stabilizes. CAUTION Due to the close tolerance runout of mating surfaces, any damage to mating surfaces will prevent obtaining a good rotor assembly/turbine assembly. (46) Remove load compressor wheel assembly (tool), ST71236 (Figure 2-1, 54), stretch tool, ST71078 (40), and install load compressor clearance tool, ST93950 (77), previously set to zero, on load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23). Indicator tip of tool is on hub of load compressor wheel (20). Check and record clearances at position 2, Table 61 (Figure 6-22, detail 2). (47) Remove temporarily installed bolts, washers, and nuts holding load compressor scroll (Figure 3-10, 23) to inlet housing (31). (48) Place adapter assembly (17) in freezer for 10 minutes. (49) Install load compressor diffuser (18) with aligning bolts, and O-ring (19). WARNING WARNING Wear protective gloves when handling heated parts to avoid injury. Wear protective gloves when handling chilled parts to avoid injury. (50) Use care when assembling thermal fit components to prevent damage to mating surfaces. Remove adapter assembly (17) from freezer and install. Secure with bolts (16), washers (14), and nuts (13). Align hole adjacent to strut of adapter assembly (17) at 12 o’clock position. Torque to 24-27 inch-pounds. (51) NOTE Note match marks on load compressor wheel (20). Install stud (15), adjacent to 6 o’clock position, facing aft, using nut (13) and washer (14). Torque to 24-27 inchpounds. (52) If previously removed, install pin (12) in bearing front carrier (7). CAUTION 6-46 Change 22 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (53) Install springs (8) in adapter assembly (17). (54) Using hand pressure, install forward bearing (11) in front bearing carrier (7). Ensure thrust side of forward bearing (11) is positioned down. (55) Determine and record spacer (9) thickness as follows: (a) (b) Using bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5), determine distance from top of adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17) to where forward bearing (11) seats on load compressor wheel (20) (Figure 6-27, dimension A). Subtract dimension of legs etched (7 inches if no etching) on bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5), from dimension A. Using bridge gage, ST60051 (5), determine distance from top of adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17) to where shim (24) seats (Figure 6-27, dimension B). Subtract dimension of legs etched (7 inches if no etching) on bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5), from dimension B. (c) Subtract measurement obtained in step (b) from step (a) and this will give dimension C. (d) Using bar stock and depth gage, determine distance from inner race to forward bearing (Figure 3-10, 11) face where spacer (9) sets on bearing front carrier (7) dimension D (Figure 6-27) . Forward bearing must be seated. (e) (57) Using hand pressure, install predetermined spacer (9) on bearing front carrier (7). Appropriate spacers (9) are: P/N 163223-11 163223-12 163223-13 163223-14 163223-15 163223-16 163223-17 163223-18 Dimension 0.209-0.211 0.212-0.214 0.215-0.217 0.218-0.220 0.221-0.223 0.224-0.226 0.227-0.229 0.230-0.232 0.233-0.235 0.236-0.238 0.239-0.241 0.242-0.244 0.245-0.247 0.248-0.250 0.251-0.253 0.254-0.256 Install bearing front carrier (7) in adapter assembly (17) and nut (4), aligning cutout in carrier with magnetic pickup hole and nut (4). CAUTION Be careful not to damage rotor blades when installing rotor assembly clearance gage. (58) Place turbine assembly in hydraulic press and install assembly clearance gage, ST71235 (Figure 2-1, 53), on top of adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17). Zero dial indicator. (59) Using hydraulic press, apply pressure to compress bearing front carrier (7) and springs (8). Measure and record as position 8, Table 6-1 (Figure 6-22, detail 8). Reshimming to achieve position 8 tolerance may be necessary. (60) Remove assembly clearance ST71235 (Figure 2-1, 53). (61) Install pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 (Figure 3-11), or locally manufactured tool, 18E2286-1 (96916) on to top of adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17). Tighten screws on tool and press down on toggle clamps until it is secure on bearing front carrier (7). (62) Using wrench, ST71191 (Figure 2-1, 42), remove nut (Figure 3-10, 4). (63) Deleted (64) Deleted (65) Lubricate O-rings (10) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install on bearing front carrier (7). (66) Deleted (67) Deleted (68) Deleted To obtain spacer (Figure 3-10, 9) thickness, use the formula: C - D - 0.013 (56) 163223-19 163223-20 163223-21 163223-22 163223-23 163223-24 163223-25 163223-26 Change 22 gage, 6-47 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-27. 6-48 Change 22 Determination of Spacer Thickness T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (69) Install pinion assembly (Figure 3-10, 5), using pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 (Figure 2-1, 46), to insert pinion into splined end of rotor shaft (Figure 3-10, 59). (70) Apply a small amount of assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, to steel balls (6) and install in groove provided at end of rotor shaft (59). (71) Reinstall nut (4) and tighten using wrench, ST71191 (Figure 2-1, 42). Torque to 1200-1350 inch-pounds. . Remove pinion installation and disassembly tool, ST71209 (Figure 2-1, 46), and stake nut (Figure 3-10, 4) in three equally spaced places. . (72) (73) (74) Install magnetic pickup (3) as follows: WARNING Loctite 272 sealing compound may cause dermatitis in sensitive individuals upon prolonged contact. Keep material away from skin. Wear butyl rubber gloves and safety glasses. Consult the applicable MSDS and local OSH regulations for additional information. (a) Apply a light coat of adhesive, Loctite 272, to threads of magnetic pickup (3). (b) Locate the highest position of any of the four lobes on the nut (4). If a lobe of the nut is not at a highest point when viewed through the magnetic pickup boss on the adapter assembly (17), rotate the turbine assembly. Rotate until highest point of nut is evidenced. (c) Install magnetic pickup (3) on loabe ouside diameter on nut (4). Back off magnetic pickup 1/4 turn and measure gap at four lobes (0.012-0.014 inch). If all gaps don’t meet clearance, take one with minimum clearance. Use key in electrical connector as index. (d) Tighten locknut of magnetic pickup (3) to 80-100 inch-pounds and safety wire with lockwire, MS20955C32. Install protective cap over connector end. Install bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 21, 5) on adapter assembly (Figure 3-10, 17). Measure and record distance from end of pinion assembly (5) to face of adapter assembly (17) (position 1, Table 6-1, Figure 6-22, detail 1). Subtract measurement from dimension of legs etched on bridge gage, ST60051 (Figure 2-1, 5). NOTE Compare all measurements to the minimum and maximum limits specified on clearance chart (Table 6-1). Rotor shaft should be in forward direction (clockwise looking forward). (75) Install protective cap on pinion assembly (Figure 3-10, 5) before turning turbine assembly over. (76) Using wire gage, ST60880 (Figure 2-1, 7), measure distance from underside of turbine wheel tips to top edge of seal plate (Figure 3-10, 57) and record as position 9, Table 6-1 (Figure 6-22, detail 9). (77) Install turbine nozzle (Figure 3-10, 2) and secure with bolts (1). Torque to 2527 inch-pounds. (78) Using wire gage, ST60880 (Figure 2-1, 7), measure turbine wheel (Figure 3-10, 55) to turbine nozzle (2) radial clearance and record as position R, Table 6-1 (Figure 6-22, detail R). (79) Using wire gage, ST60880 (Figure 2-1, 7), measure distance from turbine wheel tip to turbine nozzle (Figure 3-10, 2) and record as position 4, Table 6-1 (Figure 622, detail 4). Turbine nozzle can be repositioned to meet measurement requirements. 6-6. ASSEMBLY OF APU This section contains procedures for assembly of the APU after the subassemblies have been assembled. a. Install reduction drive unit (Figure 3-3, 33) in assembly build stand, ST71206 (Figure 21, 44). b. Install turbine assembly (Figure 3-3, 30) as follows: (1) Install adapter gasket (32) and O-ring (31) on reduction drive unit (33). (2) Install turbine assembly (30) on reduction drive unit (33) in a vertical position Change 22 6-49 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 and secure with bolts (29). Torque to 55-70 inchpounds over running torque. c. Install containment ring (Figure 3-5, 37) as follows: (1) (2) If previously removed, attach identification plate (36) with adhesive, Specification MIL-A-46146, type III, to containment ring (37) and apply UID labels in accordance with paragraph 6-8. Using spanner wrench, ST93975 (Figure 2-1, 79), install locking ring (Figure 3-5, 35) on right side only, looking from aft end, and engine mounting adapter (34) on turbine assembly (Figure 3-3, 30). Torque to 45-55 inch-pounds. Stake locking ring (Figure 3-5, 35) at three equally spaced places. 6-50 Change 23 (3) Lubricate O-ring (Figure 3-2, 51, detail G) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install O-ring (51). (4) Coat elbow (50) with antiseize compound, Specification MIL-A-907, and install in turbine assembly (68). (5) Position containment ring (Figure 3-5, 37) on turbine assembly (Figure 3-3, 30). (6) Using spanner wrench, ST93975 (Figure 2-1, 79), install locking ring (Figure 3-5, 35) on left side, looking from aft end, and engine mounting adapter (34) on turbine assembly (Figure 3-3, 30). Do not torque or stake locking ring at this time. TO 2G-T62T-43 Install duct support bracket (16) on containment ring (37) and secure with bolts (15), washers (14). and nuts (13). Do not torque at this time. (2) Install IGV drive link (8) to IGV actuator (6) and pin-drive flange (33, figure 3-10) and secure with bolt (7, figure 3-7) and nut (1). d. Install air flow sensor (25) and surge control valve (9) as follows: (3) Lubricate o-rings (7, 10, 18, 20, 23, and 26) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. Install insulation actuator bushings (5), bolts (3), and washers (4) on IGV actuator (6). (4) Install IGV actuator (6) on turbine assembly and secure with self-locking nuts (2). Torque to 100-130 in. lb. (5) Install nut (1) securing IGV drive link (8) to turbine assembly (30, figure 3-3). Torque to 22-27 in. lb. (6) Using wire gage, ST60880 (7, figure 2-1) adjust stroke of IGV actuator (6, figure 3-7) until gap between inlet guide vanes is 0.060-0.100 in. in fully closed position (17 places). Gap to be measured at root of IGV. (7) (1) (2) Install O-ring (23) with fitting (22) in air flow sensor (25). (3) Install bolt (21) securing fitting (22) to air flow sensor (25). (4) Install O-ring (20) with temperature sensor (19) in air flow sensor (25). (5) Install O-ring (26) with air flow sensor (25) to load compressor scroll (38). (6) Install V-band clamp (24) securing air flow sensor (25) to load compressor scroll (38). Torque to 30 in. lb. above prevailing torque. (7) Install O-ring (18) with duct assembly (17) on air flow sensor (25). Install eye bolt (20, figure 3-3) in reduction drive unit (33). g. Perform dimensional checks as follows: (1) Install lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, figure 2-1), in eye bolt (20, figure 3-3) and attachment point on containment ring (37, figure 3-5). (2) (10) Install duct assembly (6) to duct assembly (17) and secure with V-band clamp (5). Torque to 30 in. lb. above prevailing, torque. Using suitable hoist (minimum 2,000 lbs. lifting capacity) and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, figure 2-1), hoist APU over layout table. (3) Lower APU onto assembly build stand, ST71206 (44), attached to layout table, and secure APU. (11) Install O-ring (10) with surge control valve (9) on duct assembly (17). (4) Remove hoist and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82), from APU. (5) Remove bolts (32, figure 3-5) and bushing (33) from bottom of containment ring (37) and install assembly aid tool bolt. (6) Shim front engine trunion mounts and adjust rear support of assembly build stand, ST71206 (44, figure 2-1) to level APU within 0.001 in. (8) Install V-band clamp (12) securing duct assembly (17) to air flow sensor (25). Torque to 30 in. lb. above prevailing torque. (9) Install O-ring (7) on duct assembly (17). (12) Install V-band clamp (8) securing surge control valve (9) to duct assembly (17). Torque to 30 in. lb. above prevailing torque. e. f. Install IGV actuator (6, figure 3-7) as follows: (1) Install IGV actuator stop (9) to IGV actuator (6). 6-51 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-28. Tolerance Specifications (Sheet 1 of 2) 6-52 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-28. Tolerance Specifications (Sheet 2 of 2) 6-53 TO 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Refer to Figure 6-28 for location of all dimensions. (7) Align dimension measuring equipment to parallel with Z-axis of APU. (8) (9) Measure dimension between pilot of reduction drive unit output shaft inside diameter and centerline of front trunion mounts (left and right). Dimension should be 2.44 ±0.01 in., both sides. Measure dimension between Z-axis centerline of reduction drive unit accessory pad cover (13, figure 3-12) and Z-axis centerline of duct assembly (17, figure 3-5) extension flange. Dimension should be 10.10 ±0.07 in. (10) If necessary, loosen bolts (29, figure 3-3) securing turbine assembly (30) to reduction drive unit (33) and adjust to attain dimension in step (9). Retorque bolts (29) to 55-70 in. lb. Recheck steps (8) and (9). (16) Measure dimension between Z-axis centerline of turbine rotor shaft (59, figure 3-10) and Z-axis centerline of surge control valve (9, figure 3-5) aft flange. Dimension should be 6.78 ±0.03 in. (17) If necessary, adjust surge control valve (9) or duct assembly (17) to attain tolerance in step (16). If duct assembly (17) is adjusted, recheck step (9). (18) Measure dimension between Y-axis centerline of left rear trunion mount and Y-axis centerline of surge control valve (9, figure 3-5) aft flange. Dimension should be 6.79 ±0.03 in. (19) If necessary, adjust surge control valve (9) or duct assembly (17) to attain tolerance in step (18). If duct assembly (17) is adjusted, recheck steps (9) and (16). (11) If necessary, loosen bolts (58, figure 3-12) to obtain more rotation of reduction drive unit. Retorque bolts (58) to 33-37 in. lb. in three steps. Torque sequence shall be: 1, 4, 7, 2, 5, 8, 3, and 6. (20) Leave APU on layout table, and install air inlet duct (13, figure 3-6) as follows: (12) Measure height of both rear trunion mounts from surface of layout table. Both dimensions should be the same, ±0.015 in. (b) Install O-ring (15) and bottom half of air inlet duct (13). (13) If necessary, loosen bolts (1, figure 3-10) in diffuser housing (45) and rotate powerhead (aft half of APU) to align rear trunion mounts with Y-axis centerline of APU. Retorque bolts (1) to 24-27 in. lb. It adjustment is made, recheck steps (8) through (12). (14) Measure dimension between left, rear trunion mount and X-axis centerline of duct assembly (17, figure 3-5) extenDimension should be sion flange. 11.280 ±0.057 in. 6-54 (15) If dimension obtained in step (14) is not within tolerance, replace duct assembly (17, figure 3-5) and recheck steps (9) through 14). (a) Apply assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, to O-ring (15, figure 3-6). (c) Install upper half of air inlet duct (13) (d) If removed, install bands (8) on air inlet duct (13) and secure with bolts (11), bushings (12), washers (10), and nuts (9). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. (e) Connect bands (8) and torque nuts (16) to 20-22 in. lb. above running torque. (f) Install temperature sensor (14) to air inlet duct (13). Torque to 135-150 in. lb. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (21) Measure dimension between X-axis centerline of left, aft trunion mount, and Xaxis centerline of air inlet duct (13). Dimension should be 4,460 ±0.057 in. (22) If necessary, adjust or replace air inlet duct (13) to attain tolerance in step (21). (23) Measure dimension between Z-axis centerline of reduction drive unit (33, figure 3-3) accessory pad and Z-axis centerline of air inlet duct (13, figure 3-6). Dimension should be 1.25 ±0.03 in. (24) If necessary, adjust air inlet duct (13) and recheck step (21). (25) Install lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, figure 2-1) in eye bolt (20, figure 3-3) and in attachment point on containment ring (37, figure 3-5). (26) (27) (28) Using suitable hoist (minimum 2,000 lbs. lifting capacity) and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, figure 2-1), hoist APU from layout table. Lower APU onto assembly build stand, ST71206 (44) , on service cart, MIL-T16549G. Secure APU to stand. If removed, install band clamp (11, figure 35). Torque to 24-27in. lb. i. Torque duct support bracket (16) bolts (15) on containment ring (37) to 24-27 in. lb. j. Install connector mounting bracket (23, figure 3-3) on reduction drive unit (33) and secure with washers (22) and bolts (21). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. Install oil pressure switch (18) as follows: (1) Lubricate O-ring (19) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (2) Install O-ring (19) with oil pressure switch (18) in reduction drive unit (33). Hand tighten oil pressure switch (18). (3) l. m. Lubricate O-rings (5 and 6) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1. (2) Install O-rings (5 and 6) and spring pin (7) in inlet housing manifold (3) and manifold assembly (4). (3) Install inlet housing manifold (3) on manifold assembly (4), and loosely secure with bolts (1) and washers (2). (4) Lubricate O-rings (60, 62, and 64, figure 3-2, detail G) with assembly fluid, RT403A, No. 1. (5) Install O-ring (64) and straight adapter (63) in inlet housing manifold (72). (6) Install O-ring (62) and orifice fitting (61) in inlet housing manifold (72). (7) Install O-ring (60) and elbow (59) in inlet housing manifold (72). Ensure elbow (59) is facing forward. (8) Install inlet housing manifold (72) on turbine assembly (68) and tighten bolts (1, figure 3-6) and washers (2). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. (9) Install diffuser to tee PCD air tube assembly (65, figure 3-2, detail G) on orifice fitting (61). (10) After steps 2 through 9 have been completed, torque straight adapter (63) to 180-200 in. lb., orifice fitting (61) to 135150 in. lb., and elbow (59) to 135-150 in. lb. Remove hoist and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82), from APU. h. k. (1) n. Install combustor assembly as follows: (1) Remove temporarily installed assembly aid tool bolt from bottom of containment ring (37, figure 3-5). (2) Remove engine mounting adapter (34) and locking ring (35) on left side, looking from aft end. (3) Slide containment ring (37) to one side. (4) Install diffuser to tee PCD air tube assembly (65, figure 3-2, detail G) to turbine assembly (68). Torque both ends to 135-150 in. lb. (5) Reposition containment ring (37, figure 3-5) and install bushing (33) and bolts (32). Torque to 190-230 in. lb. (6) Install seal ring (28, figure 3-3) on turbine assembly (30). Safety wire oil pressure switch (18) with lockwire, MS2095C32. Install turbine ignition exciter (31, figure 3-5) on containment ring (37) with three-pin connector (P302) facing forward, when looking from side. Secure with bolts (29), washers (30), and nuts (28). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. Assemble and install inlet housing manifold (3, figure 3-6) as follows: Change 3 6-55 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (7) Apply anti-seize compound, MIL-A-907, to inside diameter of combustor liner and cone. (8) Using combustor puller, ST71201 (42, figure 2-1), install combustor assembly (27, figure 3-3) on turbine assembly (30). caution Do not tap clamp (24) when tightening nut. Do not use lubrication to assist with assembly of clamp. (9) (10) (11) (12) o. Install clamp (24). Locate with drain fitting at 6 o’clock, looking forward, and clamp (24) at 45°. Torque to 45-55 in. lb. above nut run on torque. Install combustor puller, ST71201 (43, figure 2-1), and tap three times on combustor puller. Retorque to 45-55 in. lb. Install temporary shipping plug in place of O-ring (26, figure 3-3) and check valve (25). If engine mounting adapter (34, figure 35) and locking ring (35) have not been installed or have been removed; install engine mounting adapter (34), using spanner wrench, ST93975 (79, figure 2-1) on left side of containment ring (37) looking forward. Torque to 45-55 in. lb. Stake locking ring (35) at one place. washers (9) and self-locking nuts (8). Torque to 190-230 in. lb. (3) p. Assemble and install fuel control enclosure base (44, figure 3-4) as follows: (1) If removed, install gasket (45) on fuel control enclosure base (44). (2) Remove temporarily installed bolts (42) and washers (43) from reduction drive unit (33, figure 3-3) accessory pad. (3) Install fuel control enclosure base (44, figure 3-4) to reduction drive unit (46) and secure with bolts (42) and washers (43). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. (4) Install engine accessory drive gasket (34) on fuel electronic control assembly (33). (5) Install fuel electronic control assembly (33) to fuel control enclosure base (44) and secure with bolts (31) and washers (32). Torque 55-70 in. lb. (6) Install elbow (41) on fuel control enclosure base (44), parallel to flange, and secure with locknut (38) and washers (39 and 40). Torque to 180-200 in. lb. (7) Lubricate O-ring (26) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with elbow (25) in fuel electronic control assembly (33). Torque elbow (25) to 5070 in. lb. (8) Install enclosure elbow to fuel pump tube assembly (24) on elbows (25 and 41). Torque to 270-300 in. lb. Install engine hydraulic starter (10, figure 33) as follows: (1) Install gasket (11) on reduction drive unit (33). (2) Install engine hydraulic starter (10) on reduction drive unit (33) and secure with 6-56 Change 3 Lubricate O-ring (13) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with nipple (12) on engine hydraulic starter (10). Torque to 135-150 in. lb. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (9) Install support clamp (23) and bracket (14) on enclosure elbow to fuel pump tube assembly (24) and secure with bolt (20), washer (22) and nut (21). (10) Lubricate O-ring (30) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with nipple (29) on fuel electronic control assembly (33). Torque to 135-150 in. lb. (21) Install enclosure spacer assembly (18) to fuel control enclosure base (44) and tighten studs. (22) Connect connectors of fuel electronic harness (16) to fuel electronic control assembly (33). (23) Install tiedown straps (15) on fuel electronic harness (16). (11) Install main fuel control to elbow tube assembly (28) on to nipple (29). (24) (12) Install tube elbow (27) on to main fuel control to elbow tube assembly (28). If previously removed, install gasket (6) on fuel control enclosure cover (5). (25) (13) Lubricate O-ring (37) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with elbow (36) on fuel electronic control assembly (33). Install fuel control enclosure cover (5) to enclosure spacer assembly (18) and secure with studs (1), springs (2) and washers (3 and 4). (14) (15) Lubricate O-ring (18, figure 3-2, detail B) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16), connecting elbow (36, figure 3-4) to fuel control enclosure base (44). Torque locknut (35) on elbow (36) to 40-50 in. lb. and start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) to 135-150 in. lb. Lubricate O-ring (17, figure 3-2, detail B) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19) to fuel control enclosure base (44, figure 3-4). Torque to 135-150 in. lb. (16) If removed, apply adhesive MIL-A46106, to gasket (19) and install on fuel control enclosure base (44). (17) Remove protective caps and plugs from all connectors of fuel electronic harness (16). (18) Install gasket (17) and fuel electronic harness (16) to enclosure spacer assembly (18) with large key at 12 o’clock position on fuel control enclosure base (44). (19) (20) Secure fuel electronic harness (16) and gasket (17) to enclosure spacer assembly (18) with screws (7), washers (9) and self-locking nuts (8). Install support clamp (13) on fuel electronic harness (16) and secure bracket (14) to support clamp (13) with bolts (10), washers (11) and nuts (12). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. q. Install gasket (17, figure 3-3) and reduction drive cover (16) on reduction drive unit (33) and secure with washers (15) and self-locking nuts (14). Torque to 190-230 in. lb. r. Assemble and install hourmeter junction box (18, figure 3-8), assembly as follows: (1) (2) Install terminal lugs (7) to studs on terminal boards (26) and secure with washers (30), lockwashers (29) and nuts (28). Remove tags and connect wiring to components (see figure 3-9 for wiring diagram). (3) Install terminal board strips (27, figure 3-8) and terminal boards (26) to hourmeter junction box (18) and secure with screws (23), lockwashers (25) and nuts (24). (4) Install connector (22) to hourmeter junction box (18) and secure with screws (19), washers (21) and nuts (20). (5) Install hourmeter junction box (18) to enclosure spacer assembly (31) and secure with screws (16) and washers (17). (6) Install event counter (15) to cover (4), and secure with screws (12), washers (14) and self-locking nuts (13). (7) If rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10) is removed, reset events counter (15, figure 3-8) as follows: (a) Install test leads from function generator/synthesizer to connections on events counter (15). Change 5 6-57 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (b) Apply 28 Vdc to events counter (15) and set frequency of function generator/synthesizer to zero. Run events counter until events counter reaches zero. Cycles per second should he 1-20. (2) Install start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) to bulkhead tee (35). (3) Install start fuel tee to start nozzle tube assembly (21) to bulkhead tee (35) and fuel nozzle (22). Torque to 75-80 in. lb. (4) Lubricate O-ring (32) with assembly fluid, RT-430A, No. 1 and install with orifice jet restrictor (31) to bulkhead tee (35). Torque bulkhead tee (35) to 75-85 in. lb., orifice jet restrictor (31) to 135150 in. lb. and start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) to 75-85 in. lb. (5) Install tee tube (30) to orifice jet restrictor (31). (6) Install purge valve to tee tube assembly (24) to tee tube (30). (7) Install fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20) to combustor assembly (74). warning Soldering fumes are toxic. Do not breath fumes. Solder in well-ventilated area. caution Use a minimum of heat when soldering components. Use a heat sink to prevent damage. Be careful not to break wires on event counter. (8) Using solder, QQ-S-571, Type Sn63, solder wires to event counter (15). NOTE When rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10) is overhauled, replace hour meters (11). (9) Install hour-meters (11) to cover (4) and secure with screws (8), lockwashers (10) and nuts (9). s. NOTE Fuel purge valve can be assembled on work bench prior to installation on APU. (8) Lubricate O-ring (29) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with tee (28) on fuel purge valve (25). (9) Lubricate O-ring (27) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1 and install with straight adapter (26) on fuel purge valve (25). Install fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20), connecting tee (28) and fuel purge valve (25) to fuel manifold on combustor assembly (74). (10) Connect terminal lugs (6 and 7) to hourmeters (11). (10) (11) Install gasket (5) and cover (4) to hourmeter junction box (18) and secure with screws (1), lockwashers (2) and washers (3). (11) Install fuel purge valve (25, figure 3-2, detail B) and tubing as follows: (1) Install bulkhead tee (35) and secure with washer (34) and locknut (33). 6-58 Change 5 Install fuel purge valve (25) and purge valve to tee tube assembly (24), connecting fuel purge valve (25) to tee tube (30). TO 2G-T62T-43 t. u. v. (12) Remove protective caps and install purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19), connecting tee (28) to fuel purge valve (25). ab. Lubricate O-ring (44, figure 3-2, detail F) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with reducer (43) on surge control valve (69). Torque to 180-200 in. lb. (13) After fuel purge valve (25) has been installed on APU, torque tube nuts on fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20), purge valve to tee tube assembly (24), tee tube (30), tee (28), and straight adapter (26) to 135-150 in. lb. ac. Lubricate O-ring (46) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with reducer (43) on IGV actuator (70). Install and connect ignition cable (27, figure 3-5) to turbine ignition exciter (31) and igniter plug (39). Torque both ends of turbine ignition exciter to 90-100 in. lb. Lubricate O-ring (49, figure 3-2, detail G) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with straight adapter (48) to engine oil sump assembly (71). Torque to 180-200 in. lb. Install oil hose assembly (47), connecting engine oil sump assembly (71) to straight adapter (63), on inlet housing manifold (72). Torque both ends to 270-300 in. lb. w. Lubricate O-ring (56) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with elbow (55) in reduction drive unit, (73). Torque to 135-150 in. lb. x. Install oil pressure-manifold housing to reduction drive tube assembly (54), connecting reduction drive unit (73) to elbow (59) on inlet housing manifold (72). Torque tube nuts to 135-150 in. lb. y. Lubricate O-ring (53) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with straight adapter (52) on turbine assembly (68). Torque to 180-200 in. lb. z. Install tee to gearbox adapter tube assembly (66) to turbine assembly (68) and orifice fitting (61). Torque both ends to 135-150 in. lb. aa. Lubricate O-ring (58) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. I, and install with high-oil temperature switch (57) in reduction drive unit (73). Torque to 45-50 in. lb. ad. Install tee (45) on IGV actuator (70). ae. Install tee to surge valve PCD air tube assembly (42), connecting PCD air to surge control valve (69) and tee (45) on IGV actuator (70). Torque tee to surge valve PCD air tube assembly (42) to 270-300 in. lb. and tee (45) to 180-200 in. lb. af. Lubricate O-ring (41) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install with straight adapter (40) through containment ring (33) to turbine assembly (68). Torque to 180-200 in. lb. ag. Install elbow (39) to straight adapter (40) on PCD air outlet on turbine assembly (68). NOTE Do not torque across body of air filter (37). ah. Install air filter (37) and filter to tee PCD air tube assembly (36) to tee (45) on IGV actuator (70). Torque 270-300 in. lb. ai. Install diffuser to filter PCD air tube assembly (38) to air filter (37) and elbow (39). Torque diffuser to filter PCD air tube assembly (38) and elbow (39) to 270-300 in. lb. aj. Remove all protective caps and plugs from connectors of engine control harness (13, figure 3-2, detail A). ak. Connect engine control harness (13) connector (J1) to connector mounting bracket (23, figure 3-3), and secure with bolts (5), washers (7), and nuts (6). Make sure key on engine control harness connector is at 12 o’clock position. Torque to 24-27 in. lb. al. Connect engine control harness connectors (13, figure 3-2, detail A) at: (1) Fuel control enclosure spacer, P2 (2) Hourmeter junction box, P3 (3) Purge fuel valve, P4 6-59 TO 2G-T62T-43 (4) Turbine Ignition exciter, P302 (5) Low oil pressure switch, P303 (6) Magnetic speed pickup, P304 (7) High oil temperature switch, P305 (8) Surge control valve, P306 (9) Ambient temperature, P307 (10) IGV actuator, P308 (11) Air flow sensor, P309 am. Apply anti-seize compound, MIL-A-907, to threads of combustor assembly prior to installing thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15). an. Install thermocouple harness (14) on left side of combustor housing, looking from aft of APU, and thermocouple harness (15) on right side, looking from aft of APU. Torque thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15) to 70-110 in. lb. ao. Connect thermocouple harness (14 and 15) connectors at: (1) Thermocouple harness, P8-J8 (2) Thermocouple harness, P9-J9 ap. Install support clamp (4, figure 3-3) on connector mounting bracket (23) and engine control harness (13, figure 3-2, detail A). Secure with bolt (1, figure 3-3). washer (3), and self-locking nut (2). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. aq. Install support clamps (6, figure 3-2, detail H) on filter to tee PCD air tube assembly (36, figure 3-2, detail F) and engine control harness (13). Secure with bolts (3, figure 3-2, detail H), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. ar. Install six sets of support clamps (6) on tee to gearbox adapter tube assembly (66, figure 3-2, detail G), oil pressure-manifold housing to reduction drive tube assembly (54), and engine control harness (13). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. as. Install support clamps (6 and 7, figure 3-2, detail C) on engine control harness (13). purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19), and APU. Secure support clamps with 6-60 bolts (10), spacers (11), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. at. Install support clamps (6 and 9) on start fuel control to tee tube assembly (16) and purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19), and to engine control (13). Secure with bolts (3), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. au. Install two sets of support clamps (6 and 8) on engine control (13), and thermocouple harness (14). Secure with bolts (3), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. av. Install support clamps (4, figure 3-5, detail A) on ignition cable (27) and thermocouple harness (40). Secure with bolts (1), washers (3), and nuts (2). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. aw. Install support clamps (7, figure 3-2, detail D) on engine control harness (13) at fuel control enclosure base assembly (75, figure 3-2, detail B) and secure with bolts (3, figure 3-2, detail D), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. ax. Install support clamps (6, figure 3-2, detail E) on fuel manifold to purge valve tube assembly (20), thermocouple harness (14), and ignition cable (67). Secure with bolts (3), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. ay. Install support clamps (6, figure 3-2, detail H) on purge valve to tee tube assembly (24, figure 3-2, detail B) and thermocouple harness (14). Secure with bolts (3, figure 3-2, detail H), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. az. Install support clamps (6, figure 3-2, detail H) on purge valve to fuel manifold tube assembly (19, figure 3-2, detail B) and engine control. harness (13). Secure with bolts (3, figure 3-2, detail H), washers (5), and nuts (4). Torque to 24-27 in. lb. ba. Install tiedown strap (12) on engine control harness (13, figure 3-2, detail A). bb. Install lockwire, MS20995C20. on engine control harness (13, figure 3-2, detail A) and thermocouple harness (14 and 15) connectors. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 NOTE If build-up is for APU part No. 161331135A, follow steps bc. through bj. If for part No. 161331-135 proceed to step bl. bc. Mount the oil cooler, (76, Figure 3-2, index I) to the top bracket, (84, Figure 3-2, index I) using seven bolts, (89, Figure 3-2, index I). Coat bolts with anti-seize compound, Specification MIL-A-907 and screw into seven self-locking nuts integral to the oil cooler. Torque bolts 24 - 27 inch-pounds using standard sequence in accordance with TO 1-1A8. bd. Screw Bulkhead Fitting Nut (79, Figure 3-2, index I) on to 45o Elbow Adapter Fitting (78, Figure 3-2, index I). Coat O-rings, (87, Figure 3-2, index I) with assembly fluid, RT403A, No. 1, and install onto fittings (77, Figure 3-2, index I) and (78, Figure 3-2, index I). Install fitting (77, Figure 3-2, index I) to the oil cooler inlet port and torque to 270 - 300 inch-pounds. Install assembled fitting (78, Figure 3-2 index I) to the oil cooler outlet port with end positioned towards the APU gearbox assembly and torque to 270 - 300 inch-pounds. Hold fitting (78, Figure 3-2, index I) while applying torque to nut (79, Figure 3-2, index I). be. bf. bg. bh. If applicable, remove the ‘‘oil in’’ port plug, part No. AN814-4DL, from the APU gearbox. Coat O-ring, (88, Figure 3-2, index I) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install onto fitting, (80, Figure 3-2, index I). Install the fitting into the gearbox at the ‘‘oil in’’ port, and torque to 135 - 150 inchpounds. If applicable, remove the ‘‘oil out’’ port plug, part No. AN814/4DL, from the APU gearbox. Coat O-ring, (88, Figure 3-2, index I) with assembly fluid, RT-403A, No. 1, and install onto fitting, (80, Figure 3-2, index I). Install the fitting into the gearbox at the ‘‘oil out’’ port, and torque to 135 - 150 inchpounds. Remove the plug between the ‘‘oil in’’ and ‘‘oil out’’ ports, part No. AN814-4DL, from the gearbox. Replace it with plug, (83, Figure 3-2, index I) using O-ring, (88, Figure 32, index I). Torque plug to 135 - 150 inchpounds. Safetywire in series with fittings (80, Figure 3-2, index I) in steps be. and bf. with MS20995C32 lockwire. Connect hose assembly, (81, Figure 3-2, index I), to the ‘‘oil in’’ fitting on the APU gearbox. Leave fittings finger tight to accommodate test cell maintenance. bi. Connect hose assembly, (82, Figure 3-2, index I) to the ‘‘oil out’’ fitting on the APU gearbox. Leave fittings finger tight to accommodate test cell maintenance. bj. Remove two forward bolts, part No. MS21280-11, from the oil breather pad. Apply anti-seize compound, Specification MIL-A-907, to two bolts, (90, Figure 3-2, index I), and use to mount the top bracket (84, Figure 3-2, index I) of the oil cooler to the breather pad. Torque bolts (90, Figure 32, index I) 55 - 70 inch-pounds. bk. If required, etch data plate with updated NSN: 2835-01-607-1588 and add an A to the existing part No. so that it reads 161331135A. bl. Remove APU from assembly build stand, ST71206 (44, Figure 2-1). 6-7. PRESERVATION FOR SHIPMENT AND STORAGE. Following completion of final performance runs and prior to removal of APU from test cell, perform preservation run per T.O. 00-85-3 and as follows: a. With APU operating in normal mode, simultaneously close the fuel supply valve to fuel pump inlet and open valve to supply of oil, MIL-L-6081, grade 1010. b. Continue to operate APU for a minimum of 1 minute on MIL-L-6081, grade 1010 oil. c. Shut down APU. WARNING Lubricating oil, MIL-L-7808 or MIL-L23699, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. d. Remove magnetic-drain plug (1, Figure 3-2, detail G) and self-closing valve (2). e. Place suitable container under engine oil sump (27, Figure 3-12) and drain oil, MIL-L7808 or MIL-L-23699, from engine oil sump. f. Reinstall magnetic-drain plug (1, Figure 3-2, detail G) and self-closing valve (2). g. Remove slave dipstick, if not previously removed. h. Inspect and replace oil filter element (11, Figure 3-12). i. Attach warning tag to APU stating ‘‘WARNING - No Oil in Gearbox.’’ Change 24 6-61 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 j. Remove APU from test cell per Section VII Testing and prepare for storage as follows: CAUTION (1) Ensure all test and slave equipment is removed from APU. (2) Install lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, figure 2-1), in forward and aft eye bolts (20, Figure 3-3) on APU. (13) Using an air evacuator, remove air from barrier bag until bag clings snugly to APU. (3) Using suitable hoist (minimum 2,000 lbs. lifting capacity) and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, Figure 2-1), hoist APU over skid (4, Figure 3-1) of shipping container, 166471-100 (86, Figure 2-1). (14) Remove air evacuator hose from barrier bag and immediately seal opening. (15) Leave APU undisturbed for 10 minutes. (16) Inspect barrier bag for leaks. Bag should remain taut and spring back when pulled on. (17) Install any applicable documents to outside of barrier material. (18) Install cover (3) over skid (4). (19) Secure cover (3) to skid (4) with lag screws (1) and washers (2). (20) Mark container per MIL-STD-129. (4) (5) Obtain bottom half of barrier material, MIL-B-131, class III, and put in position over skid (4, Figure 3-1). Lower APU on to skid (4) and secure APU to supports on skid with bolts (5), P/N MS9557-12, washers (7) and nuts (6). Torque to 30 - 35 in-lb. (6) Remove hoist and lifting fixture, ST94409 (82, Figure 2-1), from APU. (7) Install humidity indicator, MIL-I-8835A6, on the inside of barrier material bag. Humidity indicator must show through window in shipping container, 166471-100 (86, Figure 2-1). (8) Do not over evacuate air from bag. Wrap engine in cellulosic cushioning, PPP-C-843, and seal with pressure sensitive tape, MIL-T-22085, type II. Make sure there are no protruding corners and edges that will cut barrier material. (9) Place 88 units of desiccant, MIL-D3464, in bottom half of barrier material. (10) Position top half of barrier material, MIL-B-131, class III, over APU and place 104 units of desiccant, MIL-D3464, in top half of barrier material. (11) Align seam edges of the top and bottom pieces of barrier material. Staple near edge of seam around bag to keep even. (12) Heat seal seam, except for an opening large enough for insertion of air vac tube. Make sure there are no wrinkles in the seam that will cause fabric to pull and cause leaks. 6-62 Change 24 6-8. a. GENERAL PART MARKING. Label Part Marking (LPM). Where practical, the mark may appear on a data plate or label, providing it can withstand normal wear and tear, including the range of solvents or other chemicals that may come in contact with the label. b. Polyacrylic Labels. Polyacrylic labels are durable, flexible, and forgery resistant. These labels can be engraved using ND:YAG or CO2 lasers. Polyacrylic labels consist of a doublelayered, highly cross-linked film with modified acrylic adhesive and a dimensionally stable release paper. These labels are resistant to abrasion, grease, oils, and many other chemicals and are easily applied. No rivets or screws are needed as the label has an adhesive backing, which adheres to most plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics. The labels are temperature resistant. These labels can be formed into custom sizes and shapes, offer flexible handling, provide tamper evident properties, and are economical alternatives to rigid labels. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 NOTE Laser etched tapes should not be applied to surfaces that exceed temperature extremes, are exposed to heavy abrasive environments (without considerations for protective coatings), and are exposed to operational wear. Chemical compliance should be verified and referenced to the product-specific chemical testing list. c. Surface Preparation. NOTE Cleaning shall be performed in accordance with TO 1-1-169. Cleaning and Corrosion Prevention and Control, Aerospace and Non-Aerospace Equipment. For electrical equipment, cleaning and surface preparation shall be in accordance with TO 00-25-234. Observe all warnings and cautions contained in these documents. (1) Surface should be dry and free from any visible contaminants. If not, wipe with dry cheesecloth, CCC-C-440 or equivalent. (2) For metallic surfaces, apply Isopropyl Alcohol, TT-I-735 or MIL-PRF-87937, Type III or equivalent, liberally to the surface, wipe surface to be labeled until the surface is free from visible contaminants, dirt, hydraulic fluid, etc. and dry with cheesecloth. For electrical equipment, cleaning and surface preparation should be done in accordance with TO 00-25-234. (3) d. Allow area to dry. Inspection. NOTE All debris and corrosion must be removed from the UII mark prior to inspection. (1) Visually inspect for UII mark. If the item is not marked and markings are required, refer to Label Application for instructions. NOTE Damage may include scratches, wear and tear or environmental deterioration. (2) Visually inspect damage of UII mark. If the mark is damaged, read the mark and verify that it receives a PASS condition. (3) Result 1: Reader displays a PASS condition (an unused error correction of ≥25% or readability of ≤75%). Continue processing part. NOTE If the mark continues to receive a fail condition after numerous attempts and the item is a label or Identification (ID) plate, restoring is authorized. (See Restoring Section). If not a label or ID plate, contact Cognizant Engineer for directions. (4) Result 2: Reader displays a FAIL condition (an unused error of <25% or readability of >75%). Proceed to step d. (a) If the mark receives a PASS condition, item passes inspection. (b) If the mark receives a FAIL condition up to five times, see above note. Change 24 6-62A/(6-62B blank) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 e. 2-D Label Print. g. NOTE For Data Matrix Code symbols printed on labels, the minimum grade level of the mark (as defined in AIM DPM-12006 Direct Part Mark Quality Guideline) shall be as listed below. . . . . DPM 2.0/7.5-25/640/(45Q|30Q|90), where: Minimum print quality grade = 2.0 X dimension range of the application = 7.5-25 mils Inspection wavelength = 640 nanometers ±nanometers Lighting conditions = Medium Angle Four Direction (45Q) or Low Angle Four Direction (30Q) or Diffuse Perpendicular (90). f. 2-D Data Matrix Verification Process. . NOTE The software may not automatically confirm validation of the UII or verify the grade of the 2-D data matrix mark. The marking technician must select validation and verification from the menu. . . . When performing verification of mark, adjustments of the verifier may be required to obtain a proper pass condition. If the 2-D data matrix mark continues to receive a failure, contact the Cognizant Engineer for remarking authority and location. Ensure proper lighting is available. Dim ambient lighting as well as excessive ambient lighting will adversely affect verification results. 6-9. Label Application. (1) Perform the steps in the Surface Preparation paragraph, prior to label application. (2) Ensure area is dry prior to label application. (3) Clean hands to ensure they are free from any dirt, hydraulic fluids, grease, etc. (4) Peel label from backing by bending and lifting at the corners and/or edges. Affix label and apply pressure by rubbing the label surface to thoroughly activate the adhesive and to work out any air bubbles between the tape and surface. If possible, allow the label to set for a minimum of 6 hours prior to any use of the labeled item. Maximum adhesion occurs appoximately 24 to 48 hours after applying the label. UID SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION. a. Inspect UID label by using a 2D hand-help electronic reader. Reference TO 00-25-260. b. If UID label is not present or damaged, manufacture new label and install as shown in Table 6-2. c. Do not cover any existing markings. Reference TO 00-25-260. d. Cage code is that of the activity responsible for guaranteeing uniqueness of the sequencing code. e. For additional information, reference MILSTD-130( ) and TO 00-25-260. f. See applicable Illustrated Parts Breakdown (IPB), specific component sections and parts listing tables for additional part numbers that require unique identification (i.e. interchangeable, superseding, and/or replacement part numbers). Change 23 6-63 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 6-2. UID Label Requirements Noun Figure Showing UID Label Location 161331-135, *Figure 2-1 QSAS Engine 6-29 200733803-35 Reference TO 00-25-260 161347-1, *Figure 2-1, Index 76 Valve, Surge Control 6-30 200733803-17 200733803-35 (alt) Reference TO 00-25-260 161367-1, *Figure 2-1, Index 116 Actuator, IGV 6-31 200733803-17 200733803-35 (alt) Reference TO 00-25-260 161676-203, *Figure 21, Index 156 Control Assembly, Fuel, Electronic 6-32 200733803-17 200733803-35 (alt) Reference TO 00-25-260 161794-1, *Figure 2-1, Index 177 Starter, Hydraulic Engine 6-33 200733803-17 200733803-35 (alt) Reference TO 00-25-260 Marked Item Part Number(s), Figure, and Index Figure 6-29. 6-64 Change 26 UID Label Part Number UID Label Application/ Verification Information QSAS Engine UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161331-135) (Not to Scale) T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-30. Surge Control Valve UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161347-1) (Not to Scale) Figure 6-31. IGV Actuator UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161367-1) (Not to Scale) Change 26 6-65 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 6-32. Figure 6-33. 6-66 Change 26 Fuel Control Assembly UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161676-203) (Not to Scale) Hydraulic Start Motor UID Placement (Part Number(s): 161794-1) (Not to Scale) TO 2G-T62T-43 SECTION VII TESTING 7-1. GENERAL. This section contains information for testing the APU. Included are test setup requirements and instructions for performing operational checks. Tests are performed to make certain the APU has been overhauled/repaired properly and will fulfill the established operating requirements. Reference should be made to troubleshooting requirements (paragraph 7-4) for aid in determining a possible cause and remedy for malfunctions encountered during testing. 7-2. CALCULATIONS. Calculations that may be required to convert certain observed values to standard values are provided in the text, figures, or tables within this section. 7-3. TEST PROCEDURES. This section includes procedures for installation and use of the test cell Test cell adapter kit, 164650-100 (figure 7-2). adapter kit leading particulars are listed in Section I General Information. Maintenance, inspection, and repair technical data for the adapter kit can be found in the test cell adapter kit drawings. (3) Release ball lock pin (5) and install other side of lifting fixture, ST94409 (4), onto containment ring lifting bracket (6). Secure ball lock pin. (4) Connect lifting fixture, ST94409, (4) to a suitable hoist (minimum 2,000 lbs. lifting capacity) and carefully position APU over APU cart (7). (5) Lower and position APU between forward engine support (8) and aft engine support (9). (6) Align reduction drive unit mounting holes (10) on both sides of APU with pin assemblies (11) and place pin assemblies into mounting holes. Secure pin assemblies (11) with spring plungers (12) and jam nuts (13). (7) Loosen jam nut (14) on aft engine support (9) and adjust leveler (15) until aft end of APU is in a level position. Retighten jam nut when APU is in a visually level position. (8) Remove hoist from lifting fixture, ST94409 (4). (9) With APU being supported by forward engine support (8) and aft engine supp o r t ( 9 ) , remove lifting fixture, ST94409 (4), from eyebolt (1) and containment ring lifting bracket (6). NOTE Prior to testing, the APU shall be inspected for loose or improper assembly, dirt, or other contamination. An APU not meeting test parameters specified herein shall be rejected. An APU that has been reworked to correct faults found in testing shall be retested. a. APU Installation. Using engine support kit, 166819-100 (87, figure 2-1), install APU on APU cart, 167147-100 (7, figure 7-1), as follows: (1) Thread eye bolt (1) into reduction drive unit threaded attachment point (2). (2) Release ball lock pin (3) and install one side of lifting fixture, ST94409 (4), into eyebolt (1) located at reduction drive unit threaded attachment point (2). Secure ball lock pin. b. Test Setup. Interface the test cell adapter kit, 164650-100 (figure 7-2), with the APU and the facility test cell as follows: NOTE Installation of test cell adapter kit can be performed in order of convenience. (1) Connect exhaust duct pressure hose assembly from CAB AIR PRESS connector (6), on facility fluid panel (1), to EXHAUST DUCT PRESS connector (63) on APU cart (19). 7-1 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-1. 7-2 APU Installation T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (2) (3) Connect compressor inlet pressure hose assembly from EG PRESS/ACCESS flexible hose (2) on facility fluid panel (1), to COMP INLET PRESS connector (81) on APU cart (19). Connect oil cooling supply water hose assembly from WBB (WATER BRAKE B) SEAL COOL connector (7) on facility fluid panel (1), to OIL CLR WATER SUPPLY connector (90) on APU cart (19). (14) Connect oil cooler water discharge hose assembly (20), from OIL CLR DRAIN connector (110), to facility floor drain. (15) Connect load compressor discharge thermocouple connector (21) to mating facility connectors (for load compressor discharge temperature measurement) BAIRT1. (16) Connect compressor inlet thermocouple probes (22) to mating facility connectors (for compressor inlet temperature measurements) COMPIT, FANDT1, and FANDT2 (compressor inlet temperature to compressor inlet temperature thermocouples). (17) Connect lower exhaust adapter (28), from APU exhaust flange, to facility lower exhaust duct (30). (18) Connect five exhaust gas temperature thermocouple connectors (24) to mating facility connectors (for exhaust gas temperature measurements). Connect facility AIRHIT/ENGINE T/C 1 to ENGINE T/C 2. (19) Connect bypass duct flexible hose assembly (25), from upper exhaust duct adapter (27), to load compressor bypass duct (119). (20) Connect elbow adapter (26), on pneumatic accumulator tank (33), to facility hot bleed air duct (34). (21) Connect exhaust pressure flexible hose assembly (29), from facility lower exhaust duct (30), to EXHAUST DUCT PRESS connector (63) on APU cart (19). (4) Connect fuel inlet hose assembly from FUEL IN connector (8) on facility fluid panel (1), to FUEL INLET connector (82) on APU cart (19). (5) Install dynamometer assembly (108) on reduction drive unit (38) with interface gasket, MS9136-01, and secure with bolts, nuts, and washers. (6) Connect dynamometer water inlet hose assembly from WBA (WATER BRAKE A) CONTR connector (9) on facility fluid panel (1), to dynamometer water in (41). (7) Connect dynamometer seal water hose assembly to WBA (WATER BRAKE A) SEAL COOL connector (10), on facility fluid panel (1), and to dynamometer seal water connector (107), on seal water control valve (42). (8) Connect LUBE OIL PRESS connector (11), on facility fluid panel (1), to OIL PRESS connector (84) on APU cart (19). (9) Connect facility compressor discharge line to PCD connector (64) on APU cart (19). (10) Connect hydraulic supply hose assembly (15), from panel HYD RTN A connector (12) on facility fluid panel (1), to HYDRAULIC SUPPLY connector (103) on APU cart (19). (22) Connect elbow adapter assembly (31), to flange (32) on pneumatic accumulator tank (33) then, connect flexible hose assembly (23), to load compressor discharge duct hose assembly (35). (11) Connect preservation oil supply hose assembly (16), from facility preservation oil tank (14), to PRESERVATION OIL INLET connector (83) on APU cart (19). (23) (12) Connect hydraulic return hose assembly (17), from HYD RET A connector (12) on facility fluid panel (1), to HYD RTN connector (89) on APU cart (19). Connect engine (interconnect) control harness (39), from electrical junction box assembly, A4J3 (75), on APU cart (19), to main harness electrical connector (37). (24) Connect oil sump thermocouple connector (36) to mating facility connector (for oil temperature measurement). (13) Connect dynamometer water discharge hose assembly (18), from dynamometer water out (46), to facility floor drain. (25) Connect electrical cable connector from load cell (43), on dynamometer assembly (108), to facility test cell electrical interface WATER BRAKE A connector. Change 24 7-3 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 . . . NOTE If APU has been fitted with Air/Oil cooler (-135A) long plug is already installed. DRAIN connector (52) on APU cart (19), to fuel nozzle tee bracket connector (62). (33) Install O-ring, MS9387-06, and slave combustor drain valve, 163309-100 (58), located at 6 o’clock position on combustor housing. Torque fitting to 180-200 inch-pounds. (34) Connect combustor drain flexible hose assembly (57) from COMBUSTOR DRAIN connector (53) on APU cart (19), to combustor drain valve (58) on combustor assembly. (35) Remove combustor liner retaining pin 3 o’clock position, facing aft, and install PCD connector (60). (36) Connect PCD flexible hose assembly (59), from PCD connector (51) on APU cart (19), to PCD connector (60) on combustor assembly. (37) Connect facility test cell electrical interface cables to READY TO LOAD, A4J5 (65); FIRE STOP, A4J8 (66); STOP, A4J6 (67); ESCU PWR/PWR LATCH, A4J9 (68); START FUEL/EXC, A4J12 (69); MAG PICKUP, A4J15 (70); INST GND, A4J18 (71); 2-1/2 INCH (bypass) VALVE, A4J14 (72); T/C 2, A4J17, (73); T/C 1, A4J16 (74); MAIN FUEL, A4J13 (76); POWER GND, A4J11 (77); AND GEN MODE ONLY, A4J10 (78); (EWO) HI/LOW, A4J7 (79); and HYD ST VALVE, A4J4 (80) connectors on electrical junction box assembly, A4J3 (75), on APU cart (19). (38) Connect P exit facility cable (A5J1) to P EXIT pressure transducer electrical connector (85) on APU cart (19). Long plug is used only with oil cooler. Long plug is stored in APU cart receptacle when not in use. (26) If applicable (-135 APUs only), remove short plug between oil out and oil in ports, on reduction drive unit (38), and install slave long plug, 162199-1, with O-ring, MS9387-06. (27) For APU part No. 161331-135, remove oil in and oil out short plugs and install union fittings with O-ring MS9387-06. For APU part No. 161331-135A disconnect oil cooler, oil in and oil out lines from reduction drive unit. (28) Connect oil out flexible hose assembly (44), from OIL OUT connector (48) on APU cart (19), to cooler port on reduction drive unit (38). (29) Connect oil in flexible hose assembly (45), from OIL IN connector (47) on APU (19), to cooler port on reduction drive unit (38). (30) Connect fuel drain flexible hose assembly (49), from FUEL DRAIN connector (54) on APU cart (19), to fuel control containment box fuel drain connector (98). (31) Connect hydraulic start drain flexible hose assembly (50), from HYD START DRAIN connector (55) on APU cart (19), to hydraulic starter fluid drain connector (100) on engine hydraulic starter (97). (32) Connect start fuel drain flexible hose assembly (56), from START FUEL 7-4 Change 24 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 1 of 9) 7-5 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 2 of 9) 7-6 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 3 of 9) 7-7 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 4 of 9) 7-8 Change 8 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 5 of 9) 7-9 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 6 of 9) 7-10 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 7 of 9) 7-11 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 7-2: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Facility fluid panel EG PRESS/ACCESS flexible hose Compressor discharge pressure flexible hose Reduction drive unit vibration connector and cable Powerhead vibration connector and cable CAB AIR PRESS connector WATER BRAKE B SEAL COOL connector FUEL IN connector WATER BRAKE A CONTR connector WATER BRAKE A SEAL COOL connector LUBE OIL PRESS connector HYD RET A connector HYD SUP A connector Preservation oil tank Hydraulic supply hose assembly Preservation oil supply hose assembly Hydraulic return hose assembly Dynamometer water discharge hose assembly APU cart Oil cooler water discharge hose assembly Load compressor discharge thermocouple connector Compressor inlet thermocouple probe (3) Flexible hose assembly Exhaust gas temperature thermocouple connector (6) Bypass duct flexible hose assembly Elbow adapter Upper exhaust duct adapter Lower exhaust adapter Exhaust pressure flexible hose assembly Facility lower exhaust duct Elbow adapter assembly Flange Pneumatic accumulator tank Facility hot bleed air duct Load compressor discharge duct hose assembly Oil sump thermocouple connector Main harness electrical connector Reduction drive unit Engine control harness Reduction drive vibration sensor connector Figure 7-12 7-2. Test Cell Adapter 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. Dynamometer water in Seal water control valve Load cell Oil out flexible hose assembly Oil in flexible hose assembly Dynamometer water out OIL IN connector OIL OUT connector Fuel drain flexible hose assembly Hydraulic start drain flexible hose hose assembly PCD connector START FUEL DRAIN connector COMBUSTOR DRAIN connector FUEL DRAIN connector HYD START DRAIN connector Start fuel drain flexible hose assembly Combustor drain flexible hose assembly Combustor drain valve PCD flexible hose assembly PCD connector Powerhead vibration sensor connector Fuel nozzle tee bracket connector EXHAUST DUCT PRESS connector PCD connector READY TO LOAD (A4J5) FIRE STOP (A4J8) STOP (A4J6) ESCU PWR/PWR LATCH (A4J9) START FUEL/EXC (A4J12) MAG PICKUP (A4J15) INST GND (A4J18) 2-1/2 IN (bypass) VALVE (A4J14) T/C 2 (A4J17) T/C 1 (A4J16) Electrical junction box assembly (A4J3) MAIN FUEL (A4J13) POWER GND (A4J11) GEN MODE ONLY (A4J10) (EWO) HI/LOW (A4J7) HYD ST VALVE (A4J4) COMP INLET PRESS connector FUEL INLET connector PRESERVATION OIL INLET connector OIL PRESS connector Kit Test Setup (Sheet 8 of 9) Legend for figure 7-2 - Continued: 85. P EXIT AFS pressure transducer electrical connector 102. FUEL TO ENGINE connector 88. AP AFS pressure transducer electrical 104. Reduction drive unit vent drain connector connector 87. N2 Precharge pressure transducer electrical connector 88. Accumulator charge pressure 103. HYDRAULIC SUPPLY connector 105. Dynamometer water out thermocouple connector 106. Reduction drive unit drain flexible hose assembly transducer electrical connector 89. HYD RTN connector 107. Dynamometer seal water connector 90. OIL CLR WATR SUPPLY 108. Dynamometer assembly 91. Hydraulic flexible hose assembly drain cap 109. Reduction drive unit vent connector 110. OIL CLR DRAIN connector 92. Hydraulic start return flexible hose assembly 93. Hydraluic flexible hose assembly drain cap 94. Hydraulic starter supply flexible hose assembly 95. Hydraulic starter fluid supply connector 96. Hydraulic starter fluid return connector 111. HYD START/DUMP (A2J2) (+28 VDC) connector 112. FUEL VALVE electrical connector (A2J1) (+28 VDC) 113. P EXIT pressure connector 114. P NOZ pressure connector 115. P nozzle flexible hose assembly 97. Engine hydraulic starter 98. Fuel control containment box fuel drain connector 116. P exit flexible hose assembly 117. P nozzle connector 99. Fuel in connector 118. P exit connector 100. Hydraulic starter fluid drain connector 119. Load compressor bypass duct 101. Fuel in flexible hose assembly 129. ESCU Figure 7-2. Test Cell Adapter Kit Test Setup (Sheet 9 of 9) Change 8 7-13 TO 2G-T62T-43 (39) Connect P AFS facility cable (A5J2) to P AFS pressure transducer electrical connector (86) on APU cart (19). (A2J2) (+28 Vdc) connector (111) and FUEL valve electrical connector [(A2J1) (+28 Vdc)] (112), on APU cart (19). (40) Connect N2 precharge facility cable (A5J3) to N2 precharge pressure transducer electrical connector (87) on APU cart (19). (48) Connect P exit flexible hose assembly (116), from P EXIT pressure connector (113) on APU cart (19), to P exit connector (118) on load compressor discharge assembly. (41) Connect hydraulic accumulator charge facility cable (A5J4) to accumulator charge pressure transducer electrical connector (88) on APU cart (19). (49) Connect P nozzle flexible hose assembly (115), from P NOZ pressure connector (114) on APU cart (19), to P nozzle connector (117) on load compressor discharge assembly. NOTE Hydraulic flexible hose assembly drain caps (91 and 93) are provided to facilitate draining hydraulic fluid from the hoses. (42) Connect hydraulic start return flexible hose assembly (92), from hydraulic starter fluid return connector (96) on engine hydraulic starter (97), to APU cart (19). (43) Connect hydraulic starter supply flexible hose assembly (94), from hydraulic starter fluid supply connector (95) on engine hydraulic starter (97), to APU cart (19). (44) Connect fuel in flexible hose assembly (101), from FUEL TO ENGINE connector (102) on APU cart (19), to fuel in connector (99) on fuel control containment box fuel drain connector (98). (45) Connect dynamometer water out thermocouple connector (105) to mating facility FANCIT connector (for dynamometer water out temperature measurement) at the thermocouple. (46) Connect reduction drive unit vent drain flexible hose assembly (106), from reduction drive unit vent drain connector (104) on APU cart (19), to reduction drive unit vent connector (109) on reduction drive unit (38). (47) Connect test cell facility electrical cable to HYD START/DUMP VALVE 7-14 c. Pretest Procedures. The following procedures are to be performed prior to testing the APU. Controls and indicators for the adapter kit are illustrated in figure 7-3 and listed in table 7-1. Decoded BITE information is listed in figure 7-8. Refer to vendor manuals and technical data for additional operational data. Also refer to the test cell adapter kit drawings for additional technical data which includes detail component dimensions, functional schematics, and assembly descriptions. NOTE Facility calibration weights and dynamometer calibration support bracket assembly are used only during calibration of load cell. Load cell facility calibration weights and dynamometer calibration support bracket assembly should be removed from the dynamometer torque arm prior to running APU. d. Tare weight adjustment. Add tare weights (11, figure 7-3) to dynamometer torque arm (12), on dynamometer bracket assembly (13) of dynamometer assembly (14), and secure with through bolt, washers, and nut. Adjust tare weights until load cell indicated force, with dynamometer not turning, is zero. This procedure compensates for the dynamometer torque arm weight. TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-3. Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators (Sheet 1 of 3) 7-15 TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-3. Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators (Sheet 2 of 3) 7-16 TO 2G-T62T-43 Legend for figure 7-3: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Seal water control valve HYDRAULIC MANUAL DUMP valve HYDRAULIC DUMP SHUTOFF (manual) valve OIL COOLER DRAIN valve N2 BLEED valve N2 CALIBRATION ISOLATION valve Accumulator N2 PRECHARGE gauge HYDRAULIC SUPPLY SHUTOFF (manual) valve ACCUMULATION HYDRAULIC PRESS gauge Water outlet valve Tare weights Dynamometer torque arm Dynamometer bracket assembly Dynamometer assembly Hydraulic accumulator N2 service connector Bladder accumulator Accumulator Figure 7-3. Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators (Sheet 3 of 3) 7-17 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-1. Test Cell Adapter Kit Controls and Indicators Figure/ Index No. 7-3-1 Control/Indicator Seal water control valve Regulate dynamometer seal cooling water flow rate -2 HYDRAULIC MANUAL DUMP valve Manually bleed hydraulic fluid pressure from the accumulator -3 HYDRAULIC DUMP shutoff (manual) valve Block hydraulic fluid flow from APU cart, except for starter discharge -4 OIL COOLER DRAIN valve Control oil cooler supply cool-in water outlet flow rate -5 N2 BLEED valve Bleed nitrogen gas (N2) pressure prior to N2 precharge pressure gauge and N2 precharge transducer for calibration or removal. Used in conjunction with the N2 CALIBRATION ISOLATION VALVE (6) -6 N2 CALIBRATION ISOLATION valve Isolate ACCUMULATOR N2 PRECHARGE gauge and N2 precharge transducer during calibration. Used in conjunction with the N2 BLEED valve (5) -7 ACCUMULATOR N2 PRECHARGE Reference nitrogen pressure gauge. Use PRECHARGE gauge pressure transducer readout from computer during accumulator charging gauge 7-18 Function -8 HYDRAULIC SUPPLY SHUTOFF (manual) valve Block hydraulic fluid flow to APU CART -9 ACCUMULATION HYDRAULIC PRESS gauge Reference hydraulic fluid pressure gauge. Use pressure transducer readout from computer during accumulator charging -10 Water outlet valve Regulate water outlet flow rate from dynamometer assembly -15 Hydraulic accumulator N2 service connector Charge nitrogen side of the hydraulic accumulator. Remove protective cover for access T.O. 2G-T62T-43 e. Seal water flow rate adjustment. (1) Disconnect dynamometer water discharge hose assembly (18, figure 7-2) from dynamometer water out (46). (2) Open facility dynamometer water valve and adjust seal water control valve (42) for a flow of 12-14 fl. oz. (358-414 ml) per minute at dynamometer water out (46). (3) Reconnect dynamometer water discharge hose assembly (18) from dynamometer water out (46) to facility drain. f. Accumulator charging (nitrogen). warning Never operate the or system without ing and adjusted Serious injury and could result. N2 charging bottles a properly functionpressure regulator. component explosion Insure that test cell and computer have secured water, fuel, electrical signals and power, or hydraulic power prior to performing adapter kit maintenance. Failure to do so could result in serious injury or component failure. (1) Valve control settings on the adapter kit are to be positioned as follows prior to accumulator charging: (a) HYDRAULIC SUPPLY SHUT-OFF (manual) valve (8, figure 7-3) - Closed (b) Hydraulic accumulator N2 service connector (15) - Closed (2) (c) N 2 CALIBRATION ISOLATION valve (6) - Open (d) N2 BLEED valve (5) - Closed warning Do not charge accumulator with hydraulic fluid until immediately prior to starting APU. If a start attempt is aborted, discharge hydraulic fluid back to hydraulic fluid reserve. Personnel should not enter test cell with accumulator hydraulic fluid side in a pressurized condition. When any maintenance is performed, discharge nitrogen and hydraulic fluid pressure to avoid personnel injury. Hydraulic fluids often contain additives which may affect skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. These additives can be readily absorbed through the skin. Ensure fluid does not remain on skin. Use in well-ventilated area and do not breathe vapors. Wear faceshield and gloves. Keep away from sparks and flames. caution Due to the inherent internal leakage of the test cell adapter kit hydraulic start system, there will be a gradual decrease in hydraulic pressure. In the event that the start cycle is not initiated immediately and hydraulic pressure has dropped below 2850 psi, the hydraulic system must be recharged to 3000, +350, -150 psi prior to initiating another start cycle of the APU. (3) Valve control settings on the adapter kit are to be positioned as follows after accumulator charging: (e) HYDRAULIC MANUAL DUMP valve (2) - Open (a) HYDRAULIC SUPPLY SHUTOFF (manual) valve (8) - Open (f) HYDRAULIC DUMP SHUTOFF (manual) valve (3) - Open (b) Hydraulic accumulator N2 service connector (15) - Closed (c) N2 CALIBRATION ISOLATION valve (6) - Open (d) N2 BLEED valve (5) - Closed (e) HYDRAULIC MANUAL DUMP valve (2) - Closed (f) HYDRAULIC DUMP SHUTOFF (manual) valve (3) - Open Precharge accumulator with technical nitrogen, BB-N-411, type I, class 1, grade B, to 1500 ±50 psig at hydraulic accumulator N2service connector (15). Change 3 7-19 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (4) Fill accumulator with hydraulic fluid, MIL-H-5606, to 3000 + 150, -300 psig. j. Inlet Air System. The APU will be tested with an inlet muff installed. Ambient temperature resistance thermal device (RTD) will be installed and functional for all tests. Inlet air is drawn from the prevailing test cell environment. k. Water Dynamometer System. The APU will be tested using a water dynamometer system to simulate shaft loading of the reduction drive unit. l. Instrumentation. Prior to the initiation of the test, the instrumentation inspection, verification, and calibration will be performed per MIL-P-8686, MIL-STD-45662 (section 5.4), and TO 00-20-14. m. Safety Precautions. The following warnings shall be observed during APU testing: (5) Valve control settings on the adapter kit are to be positioned as follows: (6) g. h. (a) HYDRAULIC SUPPLY SHUTOFF (manual) valve (8) - Open (b) Water outlet valve (10) - Partially open (refer to dynamometer manual for further instructions) (c) Seal water control valve (1) - Partially open (refer to dynamometer manual for further instructions) (d) HYDRAULIC MANUAL DUMP valve (2) - Closed (e) HYDRAULIC DUMP SHUTOFF (manual) valve (3) - Open (f) OIL COOLER DRAIN valve (4) - Partially open (set to control oil temperature between 185-215°F and never exceed 275°F). (g) N2 BLEED valve (5) - Closed (h) N CALIBRATION ISOLATION valve (6) - Open (i) Hydraulic accumulator N2 service connector (15) - Closed . When accumulator (17) hydraulic fluid is at 0 psi, pressurize bladder accumulator (16) to 500 ±50 psi. . Fuel, Preservation Oil, and Lubrication Oil Requirements. (1) Fuel used during test shall be fuel, MILT-5642, JP-4, at 5-40 psig. (2) Preservation oil used during the preservation run shall be MIL-L-6081, grade 1010. (3) Lubrication oil used shall be MIL-L-7808. Add enough oil to bring oil sump to “full” mark on the slave dipstick. Exhaust System. APU exhaust will be ________________ ducted from the test cell through the facility system. i. Load Compressor Air System. Load compressor air will be discharged through the APU air flow sensor (AFS) measuring device and on to the adjustable facility flow throttling valve. The facility flow throttling valve is used to set the delivery back pressure during performance tests. 7-20 Change 3 warning . Fuel vapors are toxic and flammable. Do not breathe vapors. Use in wellventilated area. Wear eye protection. A suitable fire extinguisher should be available. All personnel within 25 feet of the area shall wear ear protection when APU is running. Lubrication oils may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in wellventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. . Personnel contaminated with fuel should immediately leave the area. Remove clothing as soon as possible and shower thoroughly. Do not remove clothes near any possible source of ignition. . when Do not stand next to turbine section APU is operating. Turbine blade failure could result in possible ejection of fragmented pieces. n. Shutdown Conditions. (1) The mandatory limits are those which would normally cause the APU to shutdown on its own protective circuits. Operation in excess of these limits shall be cause for immediate shutdown of the test unit and determination of the cause for failure of the automatic shutdown. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 (2) (3) The discretionary limits are those limits which rely on the observation of the test operator to initiate an APU shutdown, should APU operation exceed any of the specified limits. The test operator shall shut down the unit unless the test engineer is available for immediate consultation. These limits may be exceeded at the instruction of the test engineer within the limits of reasonable engineering practice. The following are the limits of operation to be observed during all phases of testing: as measured at the reduction drive unit oil vent. o. CAUTION Should any of the following conditions occur during testing, immediately shut down APU and take corrective action prior to continued testing. (a) Evidence of fuel or air leak. (b) Abnormal noise, smoking or exhaust flame. (c) Vibration in excess of 10 Gs at rotor frequency when operating under pneumatic and/or shaft load, or vibration in excess of 20 Gs at rotor frequency when operating under no pneumatic load (IGVs closed) nor shaft load. (d) Oil pressure falls below 18 psig at 100 percent speed (mandatory shutdown). Maximum oil pressure shall not exceed 60 psig for more than 30 seconds. (i) Speed variation at constant load exceeds 0.5 percent. Speed variation during on/off load transient exceeds 2 percent. (j) AFS corrected bleed flow less than 30 ppm (mandatory shutdown). (k) Oil consumption greater than that equivalent to 0.25 inch per 30 minutes, as measured on the engine oil sump dipstick. Preliminary Check. (1) Check APU mounting for security. (2) Check security of test equipment and fuel, oil, hydraulic, instrumentation, and electrical connections. WARNING Lubricating oil Specification MIL-L7808, may cause skin rash. Do not breathe vapors. Use in well-ventilated area. Wear eye protection and gloves. p. (3) Check lubricating oil supply. Lubricating oil used shall be Specification MILL-7808. Add or remove enough oil to bring engine oil sump level to ″full″ mark on the slave dipstick. (4) Ensure that all test cell switches, valve, and computer commands are in the correct pre-test positions. Recording Test Data. (e) Engine oil sump exceeds 275oF shutdown). temperature (mandatory (1) Record applicable APU test data and instrument readings (Figure 7-4 and Figure 7-5) during each test. (f) Surge at any time during operation or acceleration. (2) (g) Exhaust gas average temperature exceeds 1320oF for more than 10 seconds. Take a complete set of zero readings before starting APU and after shutdown. (3) Wait 2-5 minutes for APU temperature to stabilize before recording operating values. (4) Record time at each scheduled reading. NOTE CC/HR is the same as ML/HR. (h) Measurable oil consumption exceeds 20 cubic centimeters per hour (cc/hr) q. Deleted Figure 7-4. Deleted Change 22 7-21/(7-22 Blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-5. Acceptance Run Test Data Sheet (Sheet 1 of 2) 7-25 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-5. Acceptance Run Test Data (Sheet 2 of 2) 7-26 Change 8 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 WB. AFS = 29.92 * AFS COEF P. Bar0 AFS. AFS. PEX PIN Bleed Flow Calculation WHERE: (l- COEF COEF p’E;.‘:::F PB. COEF 1 PSI = = STANDARD PAFSDIF ’ PEX. COEF) l = = 0.54 0.65 ) - (P. INLET Pressure PIN. COEF) l t WB. AFS Calculation [P. EXIT + (P. BAR012.036)] ’ l 29.92 p, BARO 407 2.036 IN. HG BAR0 = 14.696 PSI 2.036 l Data Point PAFSDIF DATAPTl=lOOO ’ (P, EXIT + ( P. BARO/2.036)1 T. AFS + 459.67 CONSTANT CONSTANT Bleed PB. CORR = Calculations = 43.10 CONSTANT 1 .OO CONSTANT = COEF COR WB. AFS. C = (P. EXDUCT WHERE: 7-2. AFS COR l WHERE: Table / y = 29.92 IN. HG Conversion 27.74 l [ P. EXIT + (P. BAR0 /2.0360)] > 1 PSI = 27.74 IN. H,O Fuel Flow Calculation -W FUEL CW. FUEL = sJ 4) 6= P.BARO 29.92 (IN. HG) Horsepower CHP = $I = T INlAVG t 59.67 516.674(“R) IoF?1 Calculation HP s Change 3 7-27 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-2 Calculations -Continued Legend for Table 7-2: Symbol AFS AFS. COEF AFS. COR CHP CW. FUEL OF HP IN. Hz0 IN. HG P. BAR0 P. EXDUCT P. EXIT P. INLET PAFSDIF PB. CORR PEX. COEF PIN. COEF PPH PPM PSI PSIA PSIG “R T. AFS T IN/AVG W FUEL WB. AFS 6 @ a Air flow sensor Air flow sensor coefficient Air flow sensor correction coefficient Corrected horsepower Fuel flow corrected Degrees fahrenheit Horsepower uncorrected Inches of water Inches of mercury Barometric pressure Exhaust duct pressure AFS total pressure Inlet pressure Bleed air differential pressure at AFS Bleed pressure corrected Pressure exhaust coefficient Inlet pressure coefficient Pounds per hour Pounds per minute Pounds per square inch Pounds per square inch absolute Pounds per square inch gage Degrees ranking AFS bleed temperature Compressor inlet temperature (average) Fuel flow uncorrected AFS bleed flow uncorrected Barometer pressure correction factor Inlet temperature correction factor r. Deleted s. Oil consumption Measurement Procedure. The rate of oil consumption shall be measured using the following procedures: (1) (2) 7-28 During acceptance test run, step t, the APU shall be operated in the normal mode at a set point of 100 ±4 until engine oil sump temperature reaches 200 ±15°F. Shut APU down by initiating the cool down stop command. Record rundown time. Measure oil level on slave dipstick. Add or remove enough oil to bring oil level to “full” mark on slave dipstick. Change 3 Units Name t. HP PPH OF HP IN. Hz0 IN. HG IN. HG. IN. Hz0 PSIG IN. Hz0 IN. Hz0 PSIA .PPH PPM PSI PSIA PSIG “R OF OF PPH PPM (3) Upon completion of acceptance test run, engine oil sump oil level shall be measured on the sump dipstick when the APU oil sump temperature reaches 200 ±15°F. (4) Oil consumption greater than that equivalent to 0.25 in. per 30 minutes, as measured on the engine oil sump dipstick, is cause for rejection. Acceptance Run. If not previously removed, remove reduction drive unit mounted dynamometer and perform acceptance run as follows: (1) With the fuel and ignition system deenergized, initiate a cold crank and motor T.O. 2G-T62T-43 APU for 10 seconds. Verify positive oil pressure during APU cold crank. Observe rundown and listen for any abnormal noises. Check for fuel and oil leaks in test cell. (2) Reconnect fuel and ignition system. (3) Initiate a start. Shut APU down by initiating a stop command immediately upon accelerating above 50 percent speed. Observe rundown and listen for any abnormal noises. (4) Close test cell facility flow throttling valve and initiate a normal mode start. Allow APU to accelerate to 100 percent speed and run at full bypass for 10 minutes. Record data in test 1 (figure 7-5). (5) Adjust dynamometer/water control unit until shaft load indicator (CHP.AX) reads 40 ±3 HP. Run at this load for 15 minutes minimum and record data in test 2 (figure 7-5). Reduce shaft load to zero by adjusting dynamometer/water control unit. (6) Shut APU down and record rundown time in test 3 (figure 7-5). (7) With test cell facility flow throttling valve fully closed, initiate a start in the “normal” mode and allow APU to accelerate to 100 percent speed. Record data in test 1 (figure 7-5). Start time shall be 11.0 seconds or less, with test cell ambient temperatures above +40°F at prevailing ambient barometric pressure. Start time shall be 19.0 seconds (to 100 percent speed) or less, with test cell ambient temperatures below 40°F to -40°F. Initiate oil consumption measurement proceedings by performing step (8) and (9). NOTE Oil cooler water flow on test cell adapter kit should be adjusted to obtain 200 ±15°F oil temperature in the following step. (8) Operate APU in normal mode at a set point of 100 ±4 until engine oil sump temperature reaches 200 ±15°F. Shut APU down by initiating a stop command and record rundown time in test 2 (figure 7-5). (9) Measure oil level on slave dipstick. Add/remove enough oil to bring oil level to “full” mark on slave dipstick (figure 7-5). (10) Initiate a start. Run at no load for 10 minutes minimum. Initiate operation in EWO mode after no load run. NOTE While conducting acceptance test, the test facility must have its own capability to measure bleed air flow (within ±0.5%) and to quickly reduce the observed test data to standard conditions. (11) Open the test cell facility flow throttling valve until the APU by-pass valve is fully closed by monitoring the bypass valve angle (BYP.ANGLE). Close the facility bleed valve until the APU bypass valve just begins to open. Continue closing the facility bleed valve until corrected bleed flow reaches a point just above the minimum flow requirement (figure 7-6) at the corresponding inlet temperature. (12) Operate APU in EWO mode for 5 minutes and record corrected bleed pressure (PB.CORR) and other data in Test 5 (figure 7-5). (See Table 7-2 for bleed flow calculations.) (13) Shut APU down by initiating stop command and record rundown time in test 6. Measure oil consumption on slave sump dipstick when engine oil sump temperature reaches 200 +15°F. Oil consumption greater than 0.25 in. per 30 minutes of APU running time as measured on slave sump dipstick is cause for rejection. (14) The fuel flow shall not exceed 254 lb./hr corrected to sea level, 59°F standard day conditions (see Table 7-2 for fuel flow calculations). If the corrected bleed flow, pressure and EGT maximum that have just been determined, meet the minimum requirements shown in figure 7-6, the APU is acceptable. u. Heat Exchanger Removal. In the event an oil to water heat exchanger system is used, perform the following test. (1) Upon completion of acceptance run, steps (1) through (14) and confirmation of acceptable performance, disconnect the oil out flexible hose assembly (44, figure 7-2) and oil in flexible hose Change 14 7-29 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 assembly (45) from reduction drive unit (38). (2) If applicable (-135 APU only), remove Oring and slave long plug between oil out an oil in ports on the reduction drive unit (38) and install short plug. (3) If applicable (-135 APU only), remove Oring and union fittings and install oil in and oil out short plugs. For -135A engines, connect oil in and oil out lines from APU installed oil cooler to the reduction drive unit in accordance with paragraph 6-6, steps bh. and bi. Torque fittings 135 - 150 inch-pounds. (4) With facility flow throttling valve fully closed, initiate a normal mode start and allow APU to accelerate to 100 percent speed. Record maximum EGT observed and start time from 0-100 percent speed in test 7 (Figure 7-5). (5) Operate at full bypass for 2 minutes minimum. Leak check oil lines connected in step (3), and record oil pressure in test 8 (Figure 7-5). (6) Shut down and record rundown time in test 9 (Figure 7-5). If any leaks are 7-30 Change 24 observed, repair and repeat steps (4) and (5) above. v. Preservation. Prior to removal of APU from test cell, preserve APU per procedures listed in Section VI - Assembly. 7-4. TROUBLESHOOTING PROCEDURES. Troubleshooting procedures are keyed to the decoded Builtin-Test Equipment (BITE) indicators on the test cell information plate, mounted adapter kit electrical junction box. During APU start, BITE indicators identify APU warning and shutdown data after the event has occurred. The events that occur during APU startup are shown in Figure 7-7 and decoded BITE information is shown in Figure 7-8. Troubleshooting procedures for the APU are listed in Table 7-3. NOTE Upon initiation of a start, if APU does not start and if there are no obvious mechanical malfunctions at time of shutdown (i.e. loud noises at rundown, noises at rundown, continuous fuel flow from fuel drains or other detectable discrepancies), attempt a restart. T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-6. APU Acceptance Test Performance Change 1 7-31 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-7. APU Sequence Diagram 7-32 Change 8 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Figure 7-8. Decoded BITE Information Change 8 7-33 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Troubleshooting BITE Code/Trouble 1. Probable Cause Correction a. No electrical power to electrical system or ESCU Check circuit breakers and electrical circuit to ensure that electrical power is available at the start switch. If ok, replace slave ESCU a. Excess fuel from fuel control assembly (33, Figure 3-4) Perform start and monitor fuel control servo voltage acress TB-4-pins 10(+) and 9(-). If ok, replace fuel control. Otherwise, excessive + volts is probably shorted to fuel control servo circuit. Isolate wiring fault and repair per TO 1-1A-14 b. Invalid (multiple) signal from magnetic pickup (3, figure 3-10) 1. Check magnetic pickup J304 for resistance (1190-1450 ohms) pin A to pin B. Check magnetic pickup clearance to gear No BITE activity when initiating electrical power 2. Overspeed 2. Check harness wiring from magnetic pickup to APU pin A to pin T and pin B to pin U. Check interface wiring a. Internal failure Check rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10) by hand for freedom of rotation. If not free to rotate, disconnect hydraulic starter and turn rotor again. If rotor turns freely, replace hydraulic starter. If rotor does not turn freely, return APU to shop for inspection and repair as required b. Combustor assembly air leaks (figure 3-28) Check for leaks around combustor assembly. If leaks are found, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair of combustor assembly c. Faulty combustor section (figure 3-28) Borescope inspect hot section. Check for hot spots, erosion on rotor tips or turbine nozzle, burn spots in combustor, evidence of FOD, and carbon build-up at fuel atomizers. If faulty, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required d. Low fuel boost pressure Check fuel pressure to APU e. Contaminated fuel Check fuel for contaminants 3. Underspeed 7-34 Change 8 TO Table 7-3. Probable BITE Code/Trouble 3. ooome~ Underspeed continued f. - Troubleshooting - 2G-T62T-43 Continued Correction Cause Fuel purge valve (25, figure 3-2, detail B) malfunction 1. Check to see if fuel purge valve is mechanically stuck open. If open, replace fuel purge valve 2. Check continuity at fuel purge valve (L8) pin A to pin B. If open, replace fuel purge valve 4. 5. 0.00.. No oil pressure oa*oo* High oil temp Fuel control assembly 3-4) malfunctioning a. Low oil level Check oil level. b. Low oil pressure Verify oil pressure with direct reading gauge at reduction drive unit during motoring. If oil pressure falls below 18 psig at 100 percent speed, return APU to shop for inspection and repair as required c. Test cell oil cooler by-pass not removed d. Faulty oil pressure (18, figure 3-3) e. Faulty wiring or ESCU Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and oil pressure switch (18, If faulty, repair per figure 3-3). TO 1-1A-14. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU a. Improper Check oil level for proper servicing. Service as required b. Test cell oil cooler servicing (33, figure If failure occurs after load applied, replace fuel control assembly g. switch plug Service if low Remove oil cooler by-pass plug Oil pressure switch is normally open, closes at 5-6 psig oil pressure (incr), and opens at 5-7 Disconnect P303 psig (decr). from oil pressure switch and monitor continuity across J303 pins C and B. While motoring APU, monitor oil pressure with direct reading gauge. If switch does not close (continuity) at 5-7 psig, replace switch 1. Ensure oil cooler water is flowing and functioning properly 2. Remove oil cooler by-pass plug if still in place 7-35 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. BITE Code/Trouble 5. Probable - Correction Cause High-oil temperature switch (57, figure 3-2, detail G) Check for continuity between pin A to pin B on J305 of the hot switch. If open (at temperatures less than 275°F), replace high-oil temperature switch d. High-oil temperature switch (57, figure 3-2, detail G) faulty Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and hot high-oil temperature switch. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14 e. ESCU faulty Check for 28 Vdc at TB4 pin 5 to ground. If no 28 Vdc, replace slave ESCU a. Thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) wiring open Verify wiring between thermocouple and ESCU is not open. If ok, replace both thermocouples. Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per TO 1-1A-14 a. Thermocouple harness (14, figure 3-2, detail A) or wiring shorted Verify wiring between thermocouple and ESCU is not shorted. If ok, replace thermocouple (TC1). Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per TO 1-1A-14. Thermocouple probes (TC1 and TC2) open. Thermocouple harness (TC1) shorted 8. 0000e* Start fuel valve fail a. Faulty start fuel valve, wiring, ESCU 9. 0000.0 No temperature data, both probes a. Thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) or wiring faulty 7-36 Continued c. High oil temp continued 6. Troubleshooting or Verify wiring between start fuel valve on fuel control assembly (33, figure 3-4) and ESCU. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. Otherwise, check continuity (resistance, 28-30 ohms) of start fuel valve. If open or shorted, replace start fuel valve per TO 6J3-4-112-3. Otherwise, replace ESCU Check continuity of wiring between ESCU and thermocouples (TC1 and TC2). If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. Otherwise, replace thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Troubleshooting - Continued BITE Code/Trouble 10. Probable Cause Correction a. Excessive drag on APU Check rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10) by hand for freedom of rotation. If not free to rotate, disconnect engine hydraulic starter and turn rotor again. If rotor turns freely, replace engine hydraulic starter. If rotor does not turn freely, return APU to shop for inspection and repair as required b. Faulty main fuel valve on fuel electronic control assembly (33, figure 3-4) Check main fuel valve output for fuel. If no fuel or limited flow, replace main fuel valve per TO 6J3-4-112-3 c. Fuel nozzle (3, figure 3-28) clogged Return APU to shop for inspection and/or replacement of fuel nozzle d. Fuel control assembly (33, figure 3-4) malfunctioning Check fuel control outlet pressure by attaching pressure gauge to port on fuel pump. If faulty, replace fuel control assembly e. Low test cell fuel pressure Check test cell fuel pressure (minimum 6 psig) f. Contaminated fuel Check fuel for contamination g. Fuel purge valve (25, figure 3-2, detail B) malfunction 1. Check if fuel purge valve mechanically stuck open. If open, replace fuel purge valve Fail to accelerate (30 seconds) 2. Check fuel purge valve for continuity, pin A to pin B. If open, replace fuel purge valve 11. Temperature exit overtemp a. Temperature exit probe, wiring, or ESCU If test stand probe indicates no overtemp, verify continuity of wiring and temperature exit probe. If wiring or probe is faulty, repair per TO 1-1A-14 or replace as required. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU If both BITE and test stand probe indicate overtemp, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required 7-37 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Troubleshooting - Continued BITE Code/Trouble 12. Fail to accelerate (5 seconds) Probable Cause a. Engine hydraulic starter (10, figure 3-3) or APU seized or binding Check rotor assembly (22, figure 3-10) by hand for freedom of rotation. If not free to rotate, disconnect engine hydraulic starter and turn rotor again. If rotor turns freely, replace engine hydraulic starter. If rotor does not turn freely, return APU to shop for inspection and repair as required b. Ignition system faulty Check 28 Vdc power to engine hydraulic starter valve. If no 28 Vdc, verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and valve. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. If ok, replace ESCU C. 13. Thermocouple probe (TC1) open 14. Thermocouple probe (TC2) shorted 15. Speed data done flag 16. Overtemperature average 7-38 Correction No signal from magnetic pickup (3, figure 3-10) Check magnetic pickup for resistance (1190-1450 ohms) pin A to pin B a. Thermocouple harness (14, figure 3-2, detail A) or wiring open Verify wiring between thermocouple and ESCU is not open. If ok, replace thermocouple (TC1). Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per TO 1-1A-14 a. Thermocouple harness (15, figure 3-2, detail A) or wiring shorted Verify wiring between thermocouple and ESCU is not shorted. If ok, replace thermocouple (TC2). Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per TO 1-1A-14 a. Magnetic pickup (3, figure 3-10), wiring, or ESCU faulty Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and magnetic pickup. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. If wiring ok, check continuity (resistance, 1190-1450 ohms) across magnetic pickup. If open or shorted, replace magnetic pickup. If magnetic pickup is ok, check magnetic pickup clearance to gear a. Duct assemblies (6 and 17, figure 3-5) or APU exhaust restricted or obstructed Check for obstructions in duct assemblies and APU exhaust b. Residual fuel in combustor assembly (figure 3-28) Inspect slave check valve for obstructions. Clean or replace slave check valve if sticking T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Troubleshooting - Continued Probable Cause BITE Code/Trouble 16 000.0. Over-temperature average continued 17 0.000. Shorted oil pressure switch 18 0.000. Decelerate to 50% 19 ooeooe Main fuel valve fail Correction c. APU overload Remove overload and restart. faulty, check for mechanical restrictions. Remove any restrictions found d. Faulty thermocouple harnesses (TC1 and TC2) (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) or ESCU Compare thermocouple readings against test stand readings. If APU thermocouple readings ok, replace slave ESCU. Otherwise, replace thermocouples e. Faulty combustor assembly (figure 3-28) section Borescope inspect hot section. Check for hot spots, erosion on rotor tips or turbine nozzle, burn spots in combustor liner, evidence of FOD, and carbon buildup at fuel atomizers. If faulty, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required f. Check rotor for freedom of rotation. If binding, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required Rotor binding If still a. Oil pressure switch (18, figure 3-3) or wiring shorted Verify wiring between oil pressure switch and ESCU is not shorted. If ok, replace oil pressure switch. Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per T.O. 1-1A-14 a. Rotor (22, figure 3-10) binding Remove load and check rotation of rotor. Turn rotor by hand. If rotor drags, then return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair b. Fuel manifold (9, figure 3-28) clogged Return APU to shop for inspection and/or replacement of fuel manifold c. Engine loaded prior to ready-to-load or ESCU faulty If load applied too soon, remove load and restart. If still faulty, replace slave ESCU d. Fuel supply low Check fuel control outlet pressure by attaching gauge to port on fuel pump (minimum 200 psig). If faulty, check boost pressure. If ok, replace fuel control assembly a. Main fuel valve on fuel electronic control assembly (33, figure 3-4), wiring, or ESCU faulty Verify continuity of wiring between main fuel valve and ESCU. If faulty, repair per T.O. 1-1A-14. If ok, verify continuity (resistance, 2830 ohms) of main fuel valve solenoid. If open or shorted, replace main fuel valve per T.O. 6J3-4-112-3 Change 13 7-39 T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Troubleshooting - Continued BITE Code/Trouble 20. Thermocouple probe (TC2) open 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Both thermocouple probes (TC1 and TC2) shorted Fuel wrap test fail IGV wrap test fail By-pass wrap test fail Nozzle pressure greater than exit pressure 7-40 Change 13 Probable Cause Correction a. Thermocouple harness (15, figure 3-2, detail A) wiring open Verify wiring between thermocouple and ESCU is not open. If ok, replace thermocouple (TC2). Otherwise, repair faulty wiring per T.O. 1-1A-14 a. Thermocouple harnesses (14 and 15, figure 3-2, detail A) or wiring shorted Check continuity of wiring between ESCU and thermocouples (TC1 and TC2). If faulty, repair wiring per T.O. 1-1A-14. Otherwise, replace thermocouple harness assemblies a. Fuel control servovalve on fuel electronic control assembly (33, figure 3-4), wiring, or ESCU faulty Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and fuel control. If faulty, repair wiring per T.O. 1-1A-14. If the wiring is ok, check the ohms resistance (75-100 ohms) across the servovalve. If faulty, replace fuel control. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU a. Inlet guide vane (IGV) actuator (6, figure 3-7) or ESCU faulty Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and IGV actuator. If faulty, repair wiring per T.O. 1-1A-14. If wiring ok, check continuity (resistance, 28-30 ohms) across IGV actuator. If faulty, replace IGV actuator. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU a. Surge control valve (9, figure 3-5), wiring, or ESCU faulty Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and surge control valve. If faulty, repair wiring per T.O. 1-1A14. If wiring ok, check continuity (resistance, 28-30 ohms) across surge control valve. If faulty, replace surge control valve. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU a. Air flow sensor (25, figure 3-5) leak Check for leaks at air flow sensor. If leaks are found, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required T.O. 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Probable BITE Code/Trouble 25. 0.0000 Nozzle pressure Troubleshooting - Correction Cause b. Powerhead assembly Check P exit probe for clogged orifice. If clogged, replace air flow sensor (25, figure 3-5) c. Surge control valve (9, figure 3-5) shut with test cell outlet duct valve closed Check surge control valve for proper operation d. Inlet guide vanes (39, figure 3-10) won’t open on demand Check IGV actuator for proper operation e. Leak in line from air flow sensor (25, figure 3-5) to ESCU Check for leaks in line, at connections in P nozzle line, and in P exit line. If leaking, replace line a. Ambient temperature wiring shorted a. Duct assemblies (6 and 17, figure 3-5) leaking Check for ducting leaks. If leaking, repair. Otherwise, replace slave ESCU b. Leak in P nozzle line Check for leaks at P nozzle line and connections to ESCU a. Exit temperature probe or wiring shorted Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and exit temperature probe. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. Otherwise, replace exit temperature probe a. Improper load application Remove load and reapply properly b. Surge control valve (9, figure 3-5) faulty Check surge control valve for binding or erratic operation. If faulty, replace surge control valve C. PCD air supply to IGV actuator (6, figure 3-7) Check PCD air lines for contamination, restrictions, or leaks. Remove any contamination or restrictions. If ok, replace IGV actuator d. Internal failure Return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required e. Air flow sensor (25, figure 3-5) leaking Replace air flow sensor or V-band clamps if air flow sensor leaking f. Air flow sensor (25, figure 3-5) P exit or P nozzle orifice clogged Replace air flow sensor if orifice clogged greater than exit pressure continued 26. oe*o*o Ambient temperature probe shorted 27. l ooooo Nozzle pressure less than 5 psi (3.5 psi for ESCU 163250-300 and I probe or above) 28. oeooeo Exit temperature probe shorted 29. APU surges Continued Verify continuity of wiring between ESCU and ambient temperature probe. If faulty, repair wiring per TO 1-1A-14. Otherwise, replace temperature ambient probe Change 8 7-41 TO 2G-T62T-43 Table 7-3. Probable BlTE Code/Trouble Troubleshooting - Continued Cause Correction a. Test stand sensor system or APU internal failure Verify calibration and continuity of test stand vibration sensor system. If no defects exist, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required 31. Vibration from reduction drive unit exceeds limits a. Test stand sensor system or APU internal failure Verify calibration and continuity of test stand vibration sensor system. If no defects exist, return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required 32. Excessive oil consumption a. Oil has lost its anti-foaming qualities Replace oil in sump b. Buffer air lines loose Check all 1/4-inch nut torque c. Orifice missing from fitting Check fitting orifice Failure of labyrinth Return APU to shop for inspection and/or repair as required 30. Vibration from powerhead exceeds limits d. seal 7-42 seal or windback air lines for B- (61, figure 3-2) for TO 2G-T62T-43 FO-1. Electrical Subsystem (Sheet 1 of 2) FP-1/(FP-2 blank) TO 2G-T62T-43 FO-1. Electrical Subsystem (Sheet 2 of 2) FP-3/(FP-4 blank)