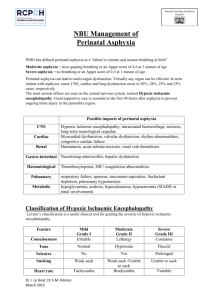
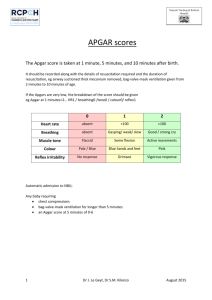
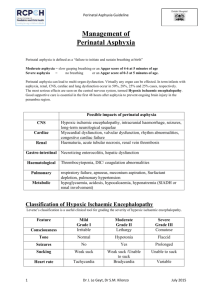
APGAR SCORE SILVERMAN SCALE RESUSCITATION AND INTENSIVE CARE OF NEWBORN ASPHYXIA APGAR SCORE • Apgar is a quick test performed on a baby at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. The 1-minute score determines how well the baby tolerated the birthing process. The 5-minute score tells the health care provider how well the baby is doing outside the mother's womb. In rare cases, the test will be done 10 minutes after birth. SILVERMAN SCALE • The Silverman Andersen Respiratory Severity Score (RSS) evaluates five parameters of work of breathing and assigns an overall score with a patient breathing comfortably a “0” and a patient in severe respiratory distress a “10”. NEWBORN ASPHYXIA • Asphyxia: means to be pulseless,but more useful is a definition of impaired or interrupted gas exchange. These situations can take place:a.Intrauterine: the gas exchange depends on the function of placenta,and the blood-flow in the umbilical vessels.b.Intrapartumc.Postnatal: after delivery the gas exchange take place in the pulmonary vesicles or alveoli and depends on the function of the heart, lungs and brain.The asphyxia can be acute or chronic. The chronic asphyxia can be complicated by an acute asphyxia. FREQUENCY • The frequency of asphyxia depends on which assessment you use to define asphyxia.The Apgar score define asphyxia as < 7 p at one minute/ The majority of these infants are mostly in very good condition some minutes later and few of them suffer a severe asphyxia.A National survey in Sweden gave an incidence of 1,7 % with a low Apgar score (3 or less at 1 minute or 6 or less at 5 minutes).The biochemical definition of asphyxia is pH< 7,10 in the umbilical artery.The electrophysiological definition of (intrauterine)asphyxia is prolonged bradycardia assessed by FHR.Recent studies have reported that 2 % of all newborns required assisted ventilation directly after the delivery. TREATMENT • 1.General principles. The primary objective in treating perinatal asphyxia is to restore an oxygen supply to the body tissues, especially the brain.This requires ventilation with oxygen and ensuring an adequate cardiac output. The secondary objective is evaluate the degree of hypoxic injury and to plan treatment. • 2. Specific therapy. Problems commonly associated with asphyxia are listed in Table 2. These conditions should be anticipated or considered and treated if present. When the heart rate is less than 100 beats/min ventilation is necessary. In 450 % ventilation with bag and mask is satisfactorily and the other 20 % had to be intubated. Management of the severely asphyxiated newborn • :Prevention of intrauterine asphyxia:-recognition of risk factors-fetal monitoring during labour-appropriate intervention Supportive care:adequate ventilation-prevention of hypoxemia, hyperoxaemia, hypercapnia-optimal perfusionMaintenance of adequate blood glucose levels Control ofseizures Avoidance of fluid overload Ethical aspects of resuscitation • Recommendation from the Swedish Pediatric Association.No further resuscitation:-Cardiac arrest in 20 minutesNormal' heart rate but no spontaneous breathing after 45 minutes of resuscitation. PROGNOSIS Prognosis is difficult because of the inability to establish the precise extent and duration of cerebral insult and injury. At the time of delivery low delayed Apgar scores between 0 and 3 at 10, 15 and 20 minutes of age are associated with significantly increased mortality and morbidity, e.g. cerebral palsy. The single most useful prognostic factor is the severity of the neonatal neurological syndrome.There are generally no long -term abnormalities reported following mild encephalopathy, whereas essentially all infants with severe encephalopathy have either died or developed multiple neurological sequel PROGNOSIS • Outcome is related to the severity and duration of the asphyxial insult and to the adequacy of compensatory mechanisms, resuscitation procedures, and specific treatment of multiorgan system involvement. • Neurologic outcome is the most difficult to predict but is best related to the degree of hypoxic encephalopathy and EEC activity in the neonatal period, and to findings on physical examination of the infant at 9 -12 months of age. THANK YOU