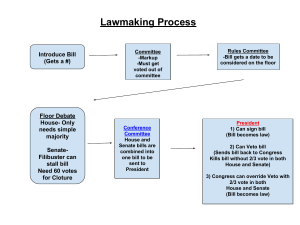
Unit 4 Gov’t ● The Executive Branch ● Carries out and enforces laws Made up of - President, Vice President, The Cabinet, The Executive Offices The President of The United States ● Leader of the Executive Branch ● Qualifications - 35 years old - Natural born citizen (in the U.S.) - Resident in U.S. for at least 14 years ● Informal Qualifications (needed but not mandatory) - Former government or political experience - Formal military experience - Skills in debating - Leadership skills ● Terms - 22nd Amendment passed in 1951: President is allowed to serve two 4 year terms - They can serve up to 10 years maximum (special circumstances) Presidential Succession (according to 25th amendment) ● Should the President die in office or not be able to fulfill his duty then he would be replaced in the following order 1- Vice President 2- Speaker of the House 3- President Pro Tempore (Senate) 4- Secretary of State 5- Secretary of Treasury ● This person would become President of the United States and serve out the term the President was elected for Roles and Powers of the President ● Chief Executive - The power to executes and carry out the law - Appoints top-ranking officers of Federal Government ● Commander in Chief - Leader of our nation’s military (armed forces) - Ask Congress to declare war ● Chief of State - Ceremonial head of government - Represents the U.S. in ceremonial gatherings ● Chief Legislator - Recommends Legislation; this is how the President exercises legislative power over Congress - Veto Power; Power to veto legislation from Congress (veto a bill from becoming a law) - Can call special sessions of Congress ● Chief Diplomat - Discuss foreign policy with other nations - negotiate/signs treaties with foreign nations - Appoints ambassadors ● Judicial Powers - Court, crime & punishment - Grants reprieves and pardons; the power to pardon criminals (let them out of jail) ● Chief of Party - Leads political party ● Economic Leader - Economic status of U.S. ($) The Vice President ● 2nd in command ● Presides over the Senate - Has power to break a tie (vote) in the Senate ● If the president dies in office the Vice President would become President and serve out the remainder of term the President was elected for ● Should the president be alive, but unable to fulfill his duties, the Vice President and the Cabinet would inform Congress in writing that the President was incapacitated before the Vice President could serve as President Balancing the Ticket ● A presidential candidate chooses a vice president that will help gain voter support in geographical areas that the president does not have support in. ● ● ● ● The Cabinet 15 Executive Departments Head of each department is the President’s main advisors - Titles are Secretary of State, Secretary of Treasury, etc Purpose of the executive departments is to oversee different areas of government responsibility Last department created was Homeland Security after 9/11 Impeachment ● To accuse a high ranking official of wrongdoing ● Only the House of Representatives has the power to accuse the President ● Only the Senate has the power to conduct the trial of an impeached official ● Only three in our history have went through the impeachment process: Andrew Johnson, Bill Clinton, Donald Trump The Electoral College ● Hold the actual power to elect the president ● Made up from members of the House of Representatives and Senate ● Each states has at least 3 presidential electors - 2 state senators + at least 1 house representative ● Equation used to determine electoral votes for each state: number of representatives plus senators ● Most states apportion their electoral votes among candidates using a “winner -take-all” system - Presidential candidate that receives the largest popular vote gets all the state’s electoral votes Concerns ● The winner of the popular vote is not guaranteed the presidency ● Most widely supported plan of reform for the Electoral College is the direct popular election plan Check and Balances- Balancing the Power Examples ● Congress proposes a bill to become a law,The President can veto the law if he does not approve it ● The President negotiates a treaty with another nation, The Senate must then vote on the treaty before it becomes effective ● The president nominates someone to a high ranking Federal position, The Senate (branch of Congress) must vote and approve the nomination before they can take office Why a President and not a King ? ● Our government is set up with check and balances to make sure the president never has too much power ● Our president has far more constraints (limits to his/her ability) than a king