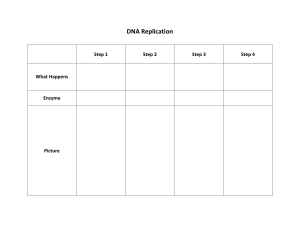
Discovering DNA structure Nitrogen bases Sugar Phosphate These 4 diagrams below are what we call “nucleotides”. Use these diagrams to answer the following questions 1. Look at the nucleotides in the previous slide. What are the three common parts of a nucleotide? A.they all have blue bases B.they have phosphate C.they different shades of blue 1. What is the ONE part of a nucleotide that differs among the four DIFFERENT nucleotides The purple c 3. List the 4 different kinds of nitrogen bases A.adenine B.thymine C.cytosine D.guanine 4. A real DNA molecule consists of THOUSANDS of nucleotides paired together. What is the pairing arrangement of the nitrogen bases? Look and see which bases fit together ___a___ pairs with _t______ and _g____ pairs with __c____ 5. Go back to the first slide and put your nucleotides together to form a double sided DNA strand. They fit together like a puzzle piece 6. WHERE does one nucleotide molecule connect to the next molecule? Hint: there are 2 sites of connection. To each other 7. Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of adenine and thymine nucleotides in a molecule? Why? Yes 8. Are there always going to be an EQUAL number of guanine and cytosine molecules in a molecule of DNA? Why? No because its guanine and cytosine 9. Scientist abbreviate the nitrogen bases by using the first letter of each base So… A always binds to __u_ G always binds to _c__ The structure of DNA is actually in a DOUBLE HELIX arrangement. DOUBLE HELIX means that the two long chains of nucleotides are arranged in a spiral like a twisted ladder 10. The sides (or ‘Uprights”) of the ladder are made up of alternating _____phosphate________ and _____deoxyribose_____ molecules 10. The steps (or rungs) of the ladder are made of __nitrogen bases__________ held together by HYDROGEN BONDS. Practice! If I were to give you 1 strand of DNA with the bases, could you make the 2nd strand of DNA using the complementary base pairs? GATCCCGTTATAG C cuagggcaauaucg