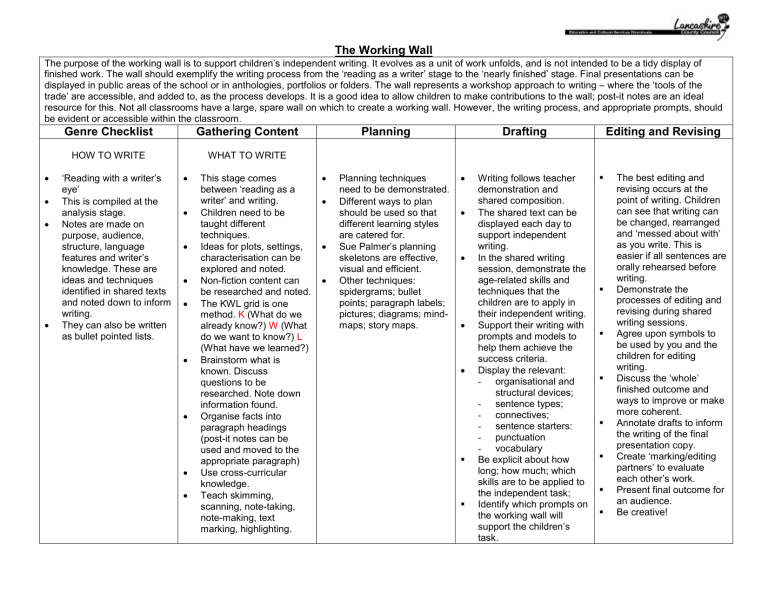
The Working Wall The purpose of the working wall is to support children’s independent writing. It evolves as a unit of work unfolds, and is not intended to be a tidy display of finished work. The wall should exemplify the writing process from the ‘reading as a writer’ stage to the ‘nearly finished’ stage. Final presentations can be displayed in public areas of the school or in anthologies, portfolios or folders. The wall represents a workshop approach to writing – where the ‘tools of the trade’ are accessible, and added to, as the process develops. It is a good idea to allow children to make contributions to the wall; post-it notes are an ideal resource for this. Not all classrooms have a large, spare wall on which to create a working wall. However, the writing process, and appropriate prompts, should be evident or accessible within the classroom. Genre Checklist Gathering Content HOW TO WRITE WHAT TO WRITE ‘Reading with a writer’s eye’ This is compiled at the analysis stage. Notes are made on purpose, audience, structure, language features and writer’s knowledge. These are ideas and techniques identified in shared texts and noted down to inform writing. They can also be written as bullet pointed lists. This stage comes between ‘reading as a writer’ and writing. Children need to be taught different techniques. Ideas for plots, settings, characterisation can be explored and noted. Non-fiction content can be researched and noted. The KWL grid is one method. K (What do we already know?) W (What do we want to know?) L (What have we learned?) Brainstorm what is known. Discuss questions to be researched. Note down information found. Organise facts into paragraph headings (post-it notes can be used and moved to the appropriate paragraph) Use cross-curricular knowledge. Teach skimming, scanning, note-taking, note-making, text marking, highlighting. Planning Planning techniques need to be demonstrated. Different ways to plan should be used so that different learning styles are catered for. Sue Palmer’s planning skeletons are effective, visual and efficient. Other techniques: spidergrams; bullet points; paragraph labels; pictures; diagrams; mindmaps; story maps. Drafting Writing follows teacher demonstration and shared composition. The shared text can be displayed each day to support independent writing. In the shared writing session, demonstrate the age-related skills and techniques that the children are to apply in their independent writing. Support their writing with prompts and models to help them achieve the success criteria. Display the relevant: - organisational and structural devices; - sentence types; - connectives; - sentence starters: - punctuation - vocabulary Be explicit about how long; how much; which skills are to be applied to the independent task; Identify which prompts on the working wall will support the children’s task. Editing and Revising The best editing and revising occurs at the point of writing. Children can see that writing can be changed, rearranged and ‘messed about with’ as you write. This is easier if all sentences are orally rehearsed before writing. Demonstrate the processes of editing and revising during shared writing sessions. Agree upon symbols to be used by you and the children for editing writing. Discuss the ‘whole’ finished outcome and ways to improve or make more coherent. Annotate drafts to inform the writing of the final presentation copy. Create ‘marking/editing partners’ to evaluate each other’s work. Present final outcome for an audience. Be creative! Main Objective: ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ Genre Checklist Purpose and Audience ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ Structure and organisation ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~ Gathering Content K W L Planning Introduction Diagram Genr e Language features ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~ Writer’s knowledge~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~ Key Features: ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~~ ~~~~~ The Daily Gossip Annotated Example ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~ Drafting Shared writing ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ Marking Ladder Success Criteria Objective ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~ ~~~~~~~~~~ Editing and Revising Symbols Connectives Planning Skeletons ~~~~~~~~~~ Editing and Revising Punctuation . , ? ! “” : ; -… ( ) Spelling Paragraph Re-order sentence Better vocab Missing word Add detail Punctuation ~~~~ // * ^ + p ~~~~ Bright Ideas and Brain Waves! Technical Vocabulary WAGOLL What a good one looks like