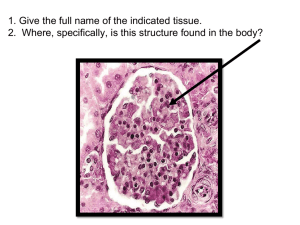
A case of J.M., 80/M J.A.M 80/M, Married Filipino Roman Catholic DOB: June 24, 1942 Buenavista, Bohol Chief Complaint: Hematuria History of Present Illness: ● 4 days PTC ○ Had onset of difficulty in voiding associated with urinary hesitancy and pain ○ Tried to remedy by increasing oral fluid intake but with no relief ○ In the interim, patient was not able to urinate for 2 days ○ Tolerated the condition, no consult done, no meds taken History of Present Illness: ● 1 day PTC ○ Patient decided to take 1 Sambong tablet ○ Patient was able to urinate hours after, characterized as dribbling and bloody amounting to approx. ½ cup, with 3 episodes ○ This was associated hypogastric pain with PS 3-4/10 ○ Tolerated the condition. No consult done History of Present Illness: ● Morning PTC ○ Still had one episode of hematuria, thus decided to seek consult at VSMMC-ER ○ No fever, cough, nausea and vomiting, edema, changes in bowel movements noted Past Medical History: ● Non hypertensive, non-diabetic, non-asthmatic ● No history of childhood illnesses:measles, mumps, german measles, and chickenpox. ● No past admissions ● No past surgeries ● No known food or drug allergies Family History: ● No known heredofamilial diseases in the maternal or paternal side ● One sibling has breast cancer Personal and Social history ● ● ● ● ● ● Occasional alcoholic beverage drinker Non-smoker Denies illicit drug use Eats 3x a day consisting of rice, fish, and vegetables Drinks 8-10 glasses of water a day Lives with one child and spouse and two grandchildren Physical Examination ● General survey: patient is awake, alert, not in respiratory distress ● Vital signs: Temp: 37.5 C BP: 130/80 mmHg RR: 20 cpm HR: 80 bpm O2: 99-100% Physical Examination Skin: senile turgor and mobility, warm to touch HEENT: anicteric sclerae, pink palpebral conjunctiva, moist lips and oral mucosa, no ear discharges, no alar flaring C/L: ECE, clear breath sounds, no retractions CVS: adynamic precordium, DHS, no murmurs Abdomen: (+) distended abdomen, (+) tenderness hypogastric area, NABS, soft, no organomegaly Physical Examination GUT: Grossly male genitalia, (-) KPS, (-) masses/lesions Ext: (+)5 cm lacerated wound on left lower leg, Strong peripheral pulses, CRT<2secs, (-) edema Neuro: Cranial nerves intact Sensory: 100% Motor: 5/5 on all extremities DRE: (+) ~2-3 cm movable mass with rubbery consistency at 11 o’clock Differentials Prostate Cancer Nephrolithiasis Urinary Tract Infection ● Rule in: ○ (+) advanced age ○ (+) difficulty voiding ○ (+) hematuria ○ (+) dysuria ○ (+) mass on DRE ● Rule in: ○ (+) abdominal pain ○ (+) hematuria ○ (+) dysuria ○ (+) difficulty voiding ● Rule in: ○ (+) difficulty voiding ○ (+) hematuria ○ (+) dysuria ○ (+) abdominal pain ● Rule out: ○ (-) nocturia ○ (-) frequent urination ○ (-) firm/hard mass ○ (-) no history of STI’s ○ (-) no family history of prostate cancer ● Rule out: ○ (-) nausea ○ (-) vomiting ○ (-) CVA tenderness ○ (+) mass on DRE ● Rule out: ○ (-) nocturia ○ (-) frequent urination ○ (+) mass on DRE Diagnosis Urinary Tract Obstruction Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Lacerated Wound, Left lower leg Basis: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Hematuria Anuria Abdominal pain Difficulty voiding Poor stream (+) mass in DRE Abdominal tenderness Bladder distention Advanced age (80yo) Labs: CBC Urinalysis Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) Creatinine BUN BUA SGPT SGOT HbA1C Serum electrolytes Gene Xpert Lipid profile Imaging Chest X-ray PAL Ultrasound KUB CBC WBC HGB HCT PLT N 7.92 115 L 31.70 L 193 82 H L 11.50 L M 5.90 E 0.50 L B 0.10 Creatinine 11.14 H BUN 74.80 H BUA 10.60 H Na 116.90 L SGPT/ALT 23.00 K 3.63 SGOT/AST 40.00 H Cl 83.00 L HbA1C 5.50 iCa 1.00 L T-PSA 20.57 H Electrolytes Plans: Therapeutic 1. 2. 3. 4. Tamsulosin 400 mcg/tab OD Finasteride 5mg/tab OD Cefixime 200mg/tab BID x 14 days Infected wound: Tetanus toxoid 0.5cc/vial injected via deep IM on left deltoid Tetanus Immunoglobulin 250 IU/ml injected via deep IM on right deltoid Plans: Attach FBC Advise for referral for evaluation to Urology department Case Discussion ● Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) refers to the nonmalignant growth or hyperplasia of prostate tissue and is a common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms in men ● Disease prevalence has been shown to increase with advancing age ● Histological prevalence of BPH at autopsy is as high as 50% to 60% for males in their 60's, increasing to 80% to 90% of those over 70 years of age Stromal and epithelial cell proliferation in the prostate transition zone (surrounding the urethra) leads to compression of the urethra and development of bladder outflow obstruction (BOO) which can result in clinical manifestations of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urinary retention or infections due to incomplete bladder emptying Observation ● Watchful waiting is a process to manage patients by giving lifestyle advice ● Examples include weight loss, reducing caffeine intake or reducing fluid intake in the evening, and avoiding constipation to try and reduce risk factors and improve LUTS Medical Therapy ● Alpha-blockers ➔ Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor blockage results in stromal smooth muscle relaxation thus improving flow ➔ Examples include selective Alpha-blockers such as Tamsulosin (400mcg once daily) and Alfuzosin (10mg once daily) ● 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors: ➔ Such as finasteride (5mg once daily) and dutasteride block conversion of testosterone to DHT ➔ Causing shrinkage of the prostate and takes several weeks to show noticeable improvement ● Antimuscarinics: Increased urgency (overactive bladder) and frequency blocking muscarinic receptors on detrusor muscle reduces smooth muscle tone and can improve symptoms in those with overactivity. Examples include solifenacin, tolterodine, and oxybutynin ● In practice, the combination of an alpha-blocker and alphareductase inhibitor is often used to achieve improvements in voiding symptoms. ● Surgery Refractory urinary retention Recurrent urinary infections Haematuria refractory to medical treatment (other causes excluded) Renal insufficiency Bladder stones Increased post-void residual High-pressure chronic retention (absolute indication THANK YOU!