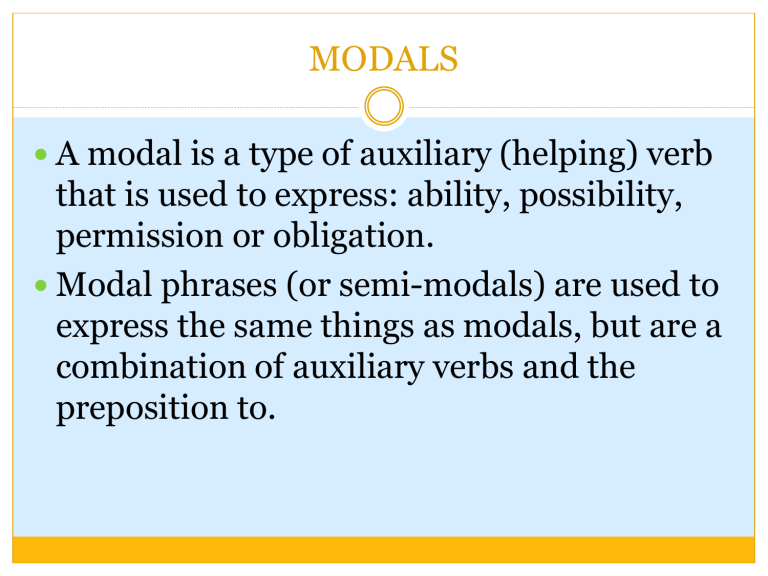
MODALS A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. Modal phrases (or semi-modals) are used to express the same things as modals, but are a combination of auxiliary verbs and the preposition to. MODALS Modal verbs are used to express certain hypothetical conditions, such as advice, capability, or requests. They’re used alongside a main verb to change its meaning slightly. Because they’re auxiliary verbs, they can’t necessarily be used on their own. MODALS Consider the difference between these two examples: I swim every Tuesday. I can swim every Tuesday. MODALS The first example is a simple factual statement. The speaker participates in a swimming activity every week on Tuesdays. The second example uses the modal verb can. Notice how the meaning changes slightly. The speaker does not swim every Tuesday; they’re saying they are capable of swimming every Tuesday if they need to. Examples 1. Can/could/be able to 2. May/might 3. Shall/should 4. Must/have to 5. Will/would 1. Can, Could, Be Able To Can, could and be able to are used to express a variety of ideas in English: A. Ability/Lack of Ability 1. Tom can write poetry very well. 2. I can help you with that next week. Lack of Ability 1. I can’t beat Zorro in a swordfight. 2. I can’t eat 4 cups of rice in one sitting. More examples of Modals Incorrect: I can to help you this afternoon. Correct: I can help you this afternoon. Correct: I will (I’ll) be able to help you this afternoon. Possibility / Impossibility B. can / can’t + base form of the verb 1. You can catch that train at 10:43. 2. He can’t see you right now. He’s in surgery. could + base form of the verb 1. I could fly via Amsterdam if I leave the day before. Possibility In situations when something is possible but not certain, use the modal verbs could, may, or might. 1. Judging by the clouds, it might rain today. 2. She may become the youngest pro soccer player ever. Impossibility 1. Sneeze with Your Eyes Open. 2. Strange Tongue Tricks. ... 3. Touch Your Nose or Chin With You Tongue. 4. Wiggle Your Ear. ... 5. Twitch Your Nose. ... 6. Lick Your Elbow. ... 7. Raise One Eyebrow. ... 8. Touch your index finger and pinky finger C. Ask Permission / Give Permission Can + Subject + base form of the verb (informal) 1. Can you lend me ten dollars? 2. Can you call me later? Can + base form of the verb (informal) 1. You can borrow my car. 2. You can have it if you want. Could + subject + base form of the verb (polite) 1. Could I have your number? 2. Could I talk to your supervisor please? Must, Have to, Need to, Don’t have to, A. Necessity or Requirement must / have to / need to + base form of the verb 1. You must have a passport to cross the border. 2. Elisabeth has to apply for her visa by March 10th. 3. I need to drop by his room to pick up a book. 2. I needed to drink a few cups of coffee in order to stay awake. Must, Have to, Need to, Don’t have to, B. Almost 100% Certain must + base form of the verb 1. Thomas has lived in Paris for years. His French must be very good. C. To Persuade must / have to + base form of the verb 1. You must try this wine. It’s excellent. 2. You have to visit us while you’re in town. D. Prohibited or Forbidden must not / mustn’t + base form of the verb 1. You must not drive over the speed limit. 2. 2. You mustn’t leave medicines where children can get to them.