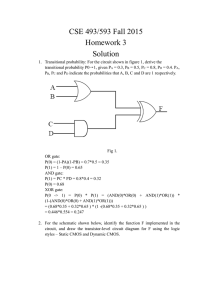
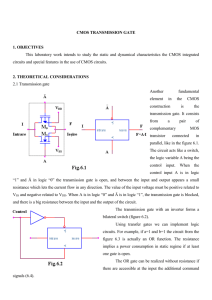
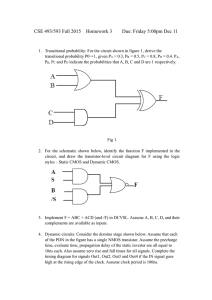
VLSI TECHNOLOGY Summer training repart Submitted in Partial Fulfiilrnent Of the Requirement af The Degree Of BACHELOR OF TECHNOLOGY In ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Completed at PIE INFOCOMM PVT.LTD.LUCKNOW Duration 11 june to 25 july,2018 Submitted By GIRJESH VERMA (1574831003) ahñansaL tosütute & Manage men I, Department of Electronics Engineering ACKNOWLEGEMENT I have taken efforts in this summer training report. However' it would not have been possible without the kind support and help of many individuals and organizations, I would like to extend my sincere thanks to all 1 am highly indebted to Mr.Nagendra Vadav Sir (HOD Electronics and Communicutiorý) for their guidance and constant supervision as well as for providing necessary information regarding the training. I would like tocxprcss my gratitude towards my parents & rncmbcr of PIE INFOCOMM for thcir kind co-operation and encouragement which help me in completion of this project1 would like to express my special gratitude and thanks to industry persons for giving me such attention and tinne. My thanks and appreciations also go to my Batehmates in making the report and people Who have willingly helped me out with their abilities. CONTENT INTRODUCTION TO VLSI 2. VLSI DESIGN METHODOLOGY System specification and arthiteeture destgn Functional design Logical design Fabrication Packaging 3. TOP DESIGN METHODOLOGY System level Algorithmic RTE Gate level TransistorOlso called switch) level 4. DESIGN TRENDS IN VLSI CHALLENGES IN VLSI TECHNOLOGY 6CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS Analog CMOS Resistance estimation Power consumption Dynamic dissipation Electronic data processing 9. CMOS logic gate design Combinational logic analysis Basic_Comhina1ional Logic Circuits AND-OR AND-OR Invert Logic: Exclusive-OR Logic: Exclusive-NOR Logic; Universal Gates 10_ DYNAMIC CMOS LOGIC 11. STATIC VERSUS DYNAMIC LOGIC 12. SEQUENTIAL LOGIC • • • SHIFT REGISTER. SERIAL DATA TO PARALLEL MEMORY MAPPING MEMORY ORGANISATION 14.TYPES OF TECHNOLOGIES SEMICONDUCVOR PROM EEPROM FLASH MEMORY NOR FLASH FLASH MEMORY 15.ANALOG DESIGN Analog ciruit P.N JUNCTION Reverse bias NPN Forward bias junction NPN reverse junction Relation between alpha and beta Small signal analysis VLSI DESIGN METHODOLOGY METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT THANSISTOR: layout LAYOUT RULES•, CONCLUSION 21. FUTURE SCOPE INTRODUCTION TO VLSI Integrated Circuits are tiny electronic circuit used to perform a specific electronic function, such as amplification. The first integrated Circuit (ICJ was invented by Jack Kilby in 1958. As suggested by Moore, the capacity doubled roughly every 18 month. Today, a large single VLSI chip contain over one billion transistors These days. VLSI chiefly contpnses Of Front End Design and Back End design, Front end design includes digital design using HDL and design verification through simulation and other techniques. The backend design comprises of CMOS library design and its characterization. It also covers the physical design and fault simulation„ VLSI DESIGN METHODOLOGIES The design methodology implies the complete process ofcreating a VLSI design. Following steps various steps involved in creating a VISI design from Concept t" the SYSTEM SPECIFICATION AND ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN VISI design cycle start with a formal specification of a VISI chip. At this stagey the system specifications are laid out. This involves a high level representation of the systern. FUNCTION DESIGN lil this Stage; main functional units of tbc system and the interconnect requirements between the units are identified The main purpose of this stage is to specify system behavior. in terms of Input, Output, and Timing of each unit. The outcome Of functional design is usually a diagram showing relationship of time and other aspects between units. LOGIC DESIGN In this stage. the logic for the VLSI system is designed, This includes. Boolean expressions. control now. word width, register allocation, etc. The outcome of this stage is Register Transtèr Level (RTM description. R TL is expressed in a Hardware Description Language (HDL) like VHDI. and Verilog. DESIGN Tbe purpose of the circuit design is to develop circuit representation based on the logic designThe outcome of this stage is a netlist, Netlist is an electronic circuit system consisting of all of the circuit element nameOrefercncc designators listed in a format with their input and output signal names. FABRICATION Fabrication process includes lithography. polishing, deposition, diffusion, etc. This process consists of several steps and requires various masks. Before the chip is mass produced, a prOlOtype is 'tunde and tested. Top-Down design Methodology In this methodology, a complete system is described at an abstruet level using hardware description language and use of EDA tools like partitioners and synthesizersr SYSTEM All the inputs and outputs are described at this level. This level does touch the hardware Structure at all. simply treats the design like a black box. This is the highest level ofabstraction provided by most Ill)Ls. RTL (Register Transfer LeveL' Dataf10'Þ" At this level the module is designed by specifying the data now between the registers. GATE LEVEL The module is implemented in terms of logic gates and interconnections between these gates. Design at this level is similar to d"cribing a design in terms ofgate-level logic diagram. Leveg This is the lowest level of abstraction. A module can be implemented in terms of switches, storage nodes, and the interconnections between thent. CHALLENGES IN VLSI TECH. Shrinking geometries. lower power voltages. and higher frequencies Of integrated Circuits have a negative impact on reliability, All these tactors increase the number of occurrences of intermittent and transient fhults. The approach of fault avoidance and fåult tolerance is used to increase the reliability of VLSI circuits, As technology scales, new opportunities emerge for VLSI designers. Understanding technology trends and specific applications is the main criterion for designing emeicnt and cfik:ctive chips. There are several difficult and exciting challenges the design Of complex Integrated Circuits. TO continue its phenomenal historical growth and continue to follow Moore*s law, the semiconductor industry will requires advances on all fronts. CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductors (CMOS) have been one Of the main technologies for econornlc: growth during half-century, These circuits the Of many important products as personal computer, cellular phones, global positionlttg systems, medical instruments us well as other applications. MOS The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET or MOS, for short) is certainly the most dependable of the contemporary digital designs. Source surfåce level, the transistor can be considered to be a switch. The larger the voltages difference between gate and source the larger the current. INMOS TRANSISTOR NMOS Transistor consists of drain and source regwms, embedded in a p-type substrate. "MOS Transistor consists drain and source regions. embedded in a n-type substrate. In a complementary MOS teehnológy (CMOS), both deuces are present. The eireuit symbols for the various MOS transistors are shown In the a(tacent page. Fig; MOS TRANSISTORS OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF A MOSFET Fig: CHARACTERISTICS Fig. Operation or MOSFET THE CMOS TECHNOLOGY CMOS Stands for "Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor," This teehnólogy is used in making transistors. The CMOS-bnsed transistors either positive or ncgative charge, they run efficiently, using up very little power Due to this efficiency, processors that use CMOS-based transistors enn run at extremely high speeds Without getting too hot. DIFFUSION Diffusion is the movement Of impurity atoms at the surface or the silicon into the bulk Of the silicon. ION IMPLANTATION IOn implantation is the process by Which impurity ions are accelerated to a higlt velocity and physically lodged into the target material DEPOSITION Deposition i' the means by which various materials are deposited on the silicon wafer. The deposition is typically made through a chemical-vapour deposition (CVDIL Etching is the process of selectively removing a layer of materiál. When etching is performed. the etehani may remove portions or all ot- The desired material; The underlying layer; The masking Epitaxy growth consist of the formation of a layer of a single silicon on the surface of silicon Step 7 — Implantation of the NMOS and "MOS (not shown) source and drain diffusion. Step S — Deposit a thiCk ovide layer (BPSG —borophosphosilieate glass). Step 9 - Open contacts. Step 10 —Deposit first level metal. Step I l —Etching unwanted metal and passivation. CMOS INVERTER The circuit ADVANTAGES OF CMOS INVERTER • The voltage swing is the same the supply voltage • The size Of the transistors can be minimized. DIGITAL FUNDAMENTAL There are two types Of digital logic combinational logie and sequential logier In practice both types of logic are used. BOOLEAN ALGEBRA True is represented by the value False is represented by the value O. Variables are represented by letters and can have one ofthe two values. either 0 or Operations are functions Of one or more variables. AND is represented by OR is represented by X+Y NOT is represented by X' OPERATIONS AND EXPRESSIONS Addition and multiplication are the basic operation in Boolean algebra. ADDITION MULTIPLICATION o•o-o Djstribu(ive Law : BULES ОБ BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 2, з. 4. X-A.I А 5, 6. 7, 8, 9, 1. А+А'В=А+В A Karnaugh map provides pictorial method Of grouping together expressions with common tictors and therefore eliminating unwanted variables. The K-map can also be described as a special arrangement Of truth table. CMOS CIRCUIT CHARACTERIZATION CMOS is a technology for constructing integrating circuits (ICs).CMOS technology is put to use in micmcontrollers, microprocessors, static RAM, and some other digital logic circuits. CMOS is both type Of CMOS PMOS circuis. For the reason that only one of the circuit types is on at any given time, CMOS chips need less power than chips which use only one type or transistork This makes them especially attractive for use in devices that are battery-powered, such as portable computers. There are two characterizations of CMOS: • • Low power consumption High noise immunity CMOS devices do not exhibit as waste heat as other variants Of logiev CMOS also grants a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was essentially for this reason that CMOS became popularly used technology to be in VLSI chips. The principal difficulty in using digital CMOS technology for analog de:stgn is that the method is optimized and distinguished for primarily onc trade-off i.e. between speed and the power dissipation. Technology characterization for analog design involves a number of issues. • • The large number of test structures requires substantial characterization time and effort. It is therefore desirable to automate the measurements to the extent possible. The test structures together with circuits must be composed such that they can he ported into the following generation of the process with minimal modifications. araeteriaation for Anal D The device circuit properties Of interest in analog design can be grouped into six categories: • Dc behavior • A c behavior • Linearity • Matching • Temperature dependence • Noise Power consu motion Static CMOS gates are very energy efficient beeause they diffuse nearly zero power when in idle. As the CMOS technology shifted below submicron levels the energy consumption per unit urea ofthe chip increased tremendously. Power dissolution in CMOS circuits takes place because Of two components: • Static dissipation dissipation Dynamic CMOS The resistance ofa uniform conducting slab is Where P" resistivity. 1• conductor length, conductor width Capacitance Estimation The total load capacitance on the output ofa CMOS gate is the sum of • • • Gate capacitance (of other inputs connected to the output Diffusion eapacitance logic gate) the drain regions eonneeted to the output) Routing capacitance (Of connections between the output and Other inputs) Power Consumpii01' The two components of CMOS power consunuption are Static dissipation Dynamic dissipation Static dissipation If the input is either at one of its steady state logic values (O or I), there is no direct path from supply ground, no static power dissipates, Howeverï some small static dissipation actually exists due to • • • • Reverse biased leakage between diffusion regions and the substrate Sub threshold conduction EDP indicates the use of mechanical methods to treat commercial data. Typically. this uses ntoderately simple. repetitious activities to process massive volumes of similar information updates, an inventory, booking and ticketing transactions to an airline's reservulion system. banking transactions applied to account as well as customer master files, billing for utility services. Data processing amenities became ready for use to snualler organization in name Of the Computer Services Bureaus, Organinltions used these for testing programs while awaiting arrival Of Combinational Logic In digital circuit theory, combinational logiC is a kind of digital logic which is performed by Boolean circuits, in which the output is pure function of the current input only' This is contradiction to sequential logic, where the output does not depend solely on the current input but also on the history the input. In other terrnst sequential logie has gnemory where as combinational logic docs noti Combinational logic is put to use in computer circuits to carry out Boolean algebra on input signals and also on stored data, Effective computer circuits normally consists of a rni'•aare of combinational as well as sequential logic. For instance, the part of an arithmetic logic unit (ALC), that does math calculations is assembled using combinational logic. Other eireuits which are used in Computers. such as full adders, half adders. full subtractors. half subtractorS. encoders. and built by Fig: AND-OR logic diagram 2. AND-OR Invert When the output of a SOP form is inverted. the eireuit is called an AND-OR-INVERT eireuit. The AOI configuration lends itself to POS implementation. The output expression can be changed to a POS expression by applying Demorgan's theorem twice shown below: .1 Fig: AND-OR-Jnvert logie diagram output of un Exclusive-OR gate is HIGH whenever its inputs and B are different, its logic The output of an Exclusive-NOR gate is HIGH whenever its inputs A and Bare thc same, its logic diagram is illustrated below: Fig: Exclusive-NOR logic diagraiïi NANO gates are sometimes called universal gates because they can be used to produce the other basic Boolean tuncti011SL _cDO_ (a) Ong NANO gate as an inverter (C) Three NAND gates used as an OR gate (d) Four NAND gates used as NOR gate NOR gates arc also universal gates and can form all of the basic gates. (O Three NOR gates LLsed as AND gate (d) Four NOR gates used as a NAM) gate DYNAMIC CMOS LOGIC the context of logic design. the phrase dynamic logic is used as compared to clocked logic as it makes clear the difference between this type of design and static logic. STATIC VERSUS DYNAMIC LOGIC • • the dynamic logic. clock signal ig put to use to evaluate combinational logic but in the static logic, this is not the ease. Dynamic logiC is twice us fist as static logic. Static Logic Example out—A Fig. CMOS NANO Fig. CMOS SAND SEOUENTIAL LOGIC Sequential logic is timed by clock pulses, e.g. type (lip -flop Here. in D flip-flop. on the rising edge of the clock pulse. the input D is copied 10 the output input at D is ignored at all times except during the rising edge of the clock pulse. The REGISTER- PARALLEL DATA TO SERIAL The input data shifis one place to the right on each clock pulse and serial data emerges from the output. cut DataInput DATA LATCH BINARY COUNTER CK MEMORIES Memory Can hc defined as a physical device Which is used to store data or programs. TYPES OF MEMORY Read Onlv (ROM) ROM is a non-volatile memory. is a collection Of stontge mechanism used in computers as well as in other electronic devices. MEMORY' CEIL A memory cell is the tiniest unit of information storage which holds a single or memory cells are classified together to form words. the position Of each cell in lhe memory is called physical address. Sume important terms defining a memory cell urc given below : number of bytes or bits that memory can take hold : capacity/size : the amount of time taken to access data depends on the physical position ofvhc datu within the memory. Aggess_tjme ; the time taken to read the data from a given memory location. bandwidth the speed at which the data can be transferred front the memory to the host computer. Latencv Latency alludes to the delay between starting memory access and the start of the transfer. Static memory onee we write the data into a. statie memory cell. data remains at that point until it is either modified by over-writing it with new data, or by removing the energy source if it is a volatile memory. 'inter-electrode eapaeitanee• of a FET. Ideal memory has the following characteristicsResct vector : The reset forces the program counter to address Oh on any given device yCC!Ot : the program counter is forced 10 address 0004b When an interrupt is a cknowledgcd. cžllibratiory informatwn : it is stored in the program ntemory in some devices. the pc address Of to for it permits a combination of upto S interrupts. procram memorv paging : CALL and GOTO instruetions have implementations. MEMORY ORGANISATION Data memory eon'prises Of l . General Purpose Register (GPR) - GPR area is regulated to make an allowance for addressing the general purpose RAM greater than 96 bytes Special Function Registers (SFR) -SFRs are for the registers that keep the authority of peripheral and core fimctions. BANKING The data mentory is divided into four different banks. INDIRECT ADDRESSING FSR REGISTERS : Indirect addressing be defined as a mode Of addressing data memory in Which the address Of the data memory in the instruction is not settled. Any instruction using the INOF register actually gains access to register that is pointed out by FSR (File Select Register) TX?.ESOESEMlCONDUCT0R PROM EEPROM An analog circuit is onc that uses consecutive time voltages and currents. A p-n junction is the interaction of the two semiconductor materials (p-type and nutype). P-N junctions are the primary building-blocks Of ntOst Of the semiconductot electronic devices such us diodes, solar cells, tntnsistors, LEDs and ICs. In NPN. conduction through the forward biased junction iS mainly by majority carrier electrons from the Il-material (emitter). While, in the reverse biased junetion, eleetrons are the minority carriers in the p•nuterial and the holes in the a-material. SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER DESIGN cornmon-gate(CG). and commonSingle stage amplifiers such as Case Of MOSFETs emittertCEJ amplifiers in ease Of BJTs are the basic building blocks of complex analog Systems. VLSI DESIGN METHODOLOGY INTRODUCTION: VISI is an acronym which stands for •Very Large Scale IntegratiOn'. This is field that involves packing more Land more logic devices into smaller areas. The number of applications of integrated circuits in high performance computing, consumer eleclronics. telecommunication and in field Of mechanical engineering(MEMS) has been rising steadily% and at a fast pacer 3. Geometrical layout domain The design Of VLSI processor may be divided in five major sections: I. High level design 2. Operative pan design 3. Control pan design 4. Memory design 5. Design of miscellaneous parts. The subsequent step is the logic design or networks which constitutes of subunits and registers. When logic networks or system architecture are designed, performance as well as errors are checked with the help of CAD programs, called as *logic simulation'. The subject of the logic design is to decade their interconnection pattern. the overall structure of blocks, to specify the structure of data path in addition to control sequences ofdata path. Simulator analyses whether the network consists of hazard analysis. Logic design as well as simulation is a principal issue ofVLSI CAD. LEVELS OF REPRESENTATION DESIGN: There are four types of logic simulators according to the levels of abstraction of simulated l. Switch 2. Gate 3. Function VISI chips arc classified by thc approach used to impletncnt and build the circuit. A till' custom design is onc where every circuit is custom dcsigncd for the projcctw This is an extrcmcly tedious makes designing an System, ication-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) allow digital designers to create ICs. For particular applications. ASICs •ire Very popular for prototyping or low-volume production runs, They are designed using an extensive suite ofCAI) tools that portray the system design terms of standard digital logic constructs: state diagrams function tables. and logic diagrams. Usually, an ASIC designer does not need any knowledge Of the underlying electronics or the actual structure of silicon chip. Design automation CAD tools arc responsiblc for taking the logic design and building "lost of the chips, One drawback of ASIC design is that all the charactenstics such speed are sel by t11C architectural design: the designer does nol have access to the electronics, so delay times cannot be changed. Modern ASICs have evolved a high level of sophistication, and are generally capable of providing solution to a large class of problems. BASICCONCEPTS: VLSI design is a systetll design discipline. Many aspects can be taught without any reference to silicon System solutions can be generated using the CAD and the necessary data turned over to the manufacturing group for production, Simplifying t11C design processes is important. However, many of the most powerful techniques and ideas of VLSI reside at lower levels and are therefore lost. Circuits work, but they are not as fast or small CIS they could have SCHEMATIC SIMULATION MOSFET is the common term for the Insulated Gate Field Transistor (IGFET). There arc two basic forms or MOSFETŽ I. Enhancement MOS FET 2. Depiction MOSFET. electric field semiconductor material can be managed. is deposited the lil depletion MOSFET. the constraining electric field decreases the number of majority carriers that are available for conduction when in fact in the enhancement MOSFET, application of produces an increment in majority carrier density in conducting Of the transistor. The MOS circuits composed Of bidirectional switching elements which are connected by bidirectional wires with memory because or the interconnected devices and also device capacitances, GATE LEVEL SIMULATION: The Boolean logie gate model has performed the theoretical basis for logic design ever sinee the advent Of electronic logic. In this model a circuit is composed or seven' logic gates connected by unidirectional memory less uires. A logic gate may be a simple inverteri gate. NOR gate. or -a more complex tinctional unit such as a flip-flop or a register. The logic gates compute Boolean functions of their input signals and transmit these values along wires to the inputs of Other gates to which it might be Each gate has Signal Information is stored only in feedback paths ofsequential circuits. swrrcH LEVEL SINICLATION: A set Of digital simulators known as switch level simulators has emerged recently as an alternative to conventional gate-level sintulators. especially for the MOS circuit simulations. One 5. Solving the tilll original matrix. FAST Some of the techniques used by the digital simulators are: - They do not maintain DC operating points. 2. Makes use ofsimpl ified device models, 3. Divide up into sub-circuiis and solve ihe matrix independently. 4. Use simulations that are event driven. 5_ They use block level simulator tuning, 6_ Make use of hierarchy to represent the redundant circuits. ANALOG FAST SPICE: It uses all the techniques of traditional SPICE to deliver true accuracy. These devices often provide a better accuracy when compared to the other types. SPICE simulators are those which maintain true SPICE accuracy but the performance and capacity are limited. Digital fast SPICE simulators have increased performance as well as capacity but they have to compromise with accuracy, Analog tast SPICE simulator on other hand gives accurate waveforms to the spice noise floor 5x-10x Faster, with Sx-10x higher capacity. IC LAYOUT INTRODUCTION: Intcgratcd circuit is an arrangement of small circuits on a single chip, Silicon chip is usually preferred as it is a semiconductor. Today the integrated circuits have become an important part of most of the electronic equipments. ICs are also preferred rot thetr low cost. ICs be made very compact, producing up to several billion transistors and other electronic components in an area us small as the size of a fingernail. TO IC g.AVOUT: IC layout is the placement of the circuits and electronic components on a chip. It is the to the oxide or semiconductor layers that make up the components or the integrated circuit. The performance or an integrated circuit depends on the IC layout and hence one has to be caretill with the inter-connections and the geonuetric shapes and their placements. A layout engineer must keep in mind the criteria like performance, size, density, and manufacturability during the process of layout At' the chip, LAYOUT RULES: Design rules are essentially required to know the physical limitations of a particular manufacturing process The design rules specify the geometric and connectivity restrictions in a semiconductor process_ These rules are necessary ensure whether or not of the chips are working after the it'bric.ation_ first and bxsic rules arc the single layer rules, The width rule specifies the width of any CONCLUSION the terms AND PCB DESIGN can be better related to the process now involved in deploying an IC(lntegrated Circuit) into production environment. VISI or very large scale integration is a technology that helps us integrate millions of transistors in one small chip. It is structured design flow that enables millions Of transistors to sit together and work on a single microchip by saving microchip area. This comes under the circuit design process flow VI-IDL or VI-IStC HDL Or Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Hardware Description Language is a programming language that help us automate the design of ICs. It enables us to simulate our designs before actually sending it out to fabrication. REFRENCES Student Reference Guide on AND DESIGN' by education academia program 2. Search Engines such as Google Chrome