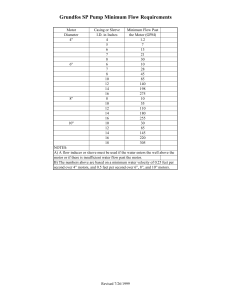
10 Science Quarter 2 – Module 6 of 6: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM (Operation of Simple Electric Motors and Generators) Science 10 Self-Learning Module (SLM) Quarter 2 – Module 6: Operation of Simple Electric Motors and Generators First Edition, 2020 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Development Team of the Module Writers: Kristine Joy D. Bunda Editors: Randy E. Porras Reviewers: Jennifer P. Cajandig Illustrator: Kristine Joy D. Bunda Layout Artist: Kristine Joy D. Bunda Cover Art Designer: Reggie D. Galindez Management Team: Allan G. Farnazo, CESO IV – Regional Director Fiel Y. Almendra, CESO V – Assistant Regional Director Miguel P. Fillalan Jr., CESO VI - Schools Division Superintendent Levi B. Butihen, - Assistant Schools Division Superintendent Gilbert B. Barrera – Chief, CLMD Arturo D. Tingson Jr. – REPS, LRMS Peter Van C. Ang-ug – REPS, ADM Arlene Rosa G. Arquiza, CID Chief Ma. Dianne Joy R. dela Fuente – OIC - LRMS Jesus V. De Gracia - Division ADM Coordinator Randy E. Porras, -EPS (Science) Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education – SOCCSKSARGEN Region Office Address: Telefax: E-mail Address: Regional Center, Brgy. Carpenter Hill, City of Koronadal (083) 2288825/ (083) 2281893 region12@deped.gov.ph Introductory Message This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners, can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions, exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson. Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you step-bystep as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you. Pre-test are provided to measure your prior knowledge on lessons in each SLM. This will tell you if you need to proceed on completing this module, or if you need to ask your facilitator or your teacher’s assistance for better understanding of the lesson. At the end of each module, you need to answer the post-test to self-check your learning. Answer keys are provided for each activity and test. We trust that you will be honest in using these. In addition to the material in the main text, Notes to the Teachers are also provided to the facilitators and parents for strategies and reminders on how they can best help you on your home-based learning. Please use this module with care. Do not put unnecessary marks on any part of this SLM. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises and tests. Read the instructions carefully before performing each task. If you have any questions in using this SLM or any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Thank you. What I Need to Know Hello! How was your day going? Hope you are excited to learn something today! This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you master the Force, Motion and Energy, specifically the Electricity and Magnetism. The lessons are arranged following the content standards of the Science 10 curriculum guide with their corresponding learning competencies. Most Essential Learning Competency Explain the operation of a simple electric motor and generator Lesson Objectives After going through this module, you are expected to: 1. Differentiate simple motor and generator 2. Explain the operation of a simple electric motor and generator. 3. Create a simple electric motor using household materials Before we start, kindly answer the 10-item test to check what you know about our lesson. 1 What I Know Direction: Read each question carefully. Encircle the letter of the best answer. 1. What basic principle enables ALL electric motors to operate? A. Iron is the only element that is magnetic. B. Opposite electric charges attract and like charges repel. C. A moving conductor within a magnetic field will experience an electromotive force. D. A current-carrying conductor placed within a magnetic field will experience a magnetic force. 2. What transformation will take place in an improvised generator? A. mechanical energy into electrical energy B. electrical energy into mechanical energy C. alternating current into direct current D. direct current into alternating current 3. Which of the following transfer of electricity will be observed in a motor? A. electrical to mechanical B. physical to potential C. mechanical to electrical D. chemical to mechanical 4. How is transfer of electricity in a generator characterized? A. Electrical to Mechanical B. Physical to Potential C. Chemical to Light D. Mechanical to Electrical 5. Which of the following materials will facilitate you making an electric motor? A. Battery, pencil and wire B. Battery, nail and string C. Wire, battery and iron ore (nail) D. String, battery, rubber strip 6. In large generators in power plants, ___________ rotate inside a coil of wire to produce an electric current. A. Water B. Wind C. Magnets D. Circuits 7. Which device uses mechanical energy to produce electrical energy? A. Solar Cell B. Generator C. Magnet D. Electric Motor 8. Which of the terms below turns the magnet inside a generator when mechanical input is supplied? A. Electromagnet B. Solar panel C. Turbine D. Pinstock 2 9. What energy do you put IN to a generator? A. Mechanical B. Thermal C. Electrical D. Potential 10. What type of energy comes OUT of a generator? A. Mechanical B. Thermal C. Electrical D. Potential 11. In a simple generator with a rotating coil, the function of sliprings and brushes is to: A. ensure a constant torque on the coil. B. provide the external magnetic field. C. pass current from the external circuit into the coil. D. pass induced current from coil to the external circuit. 12. What do we call a device that converts electricity into mechanical movement? A. Electric Generator B. Electric Coil C. Electric Charge D. Electric Motor 13.Which of the following is an example of generator? A. Electric Fan B. Electric Car C. Hydro power Dam D. All of the above 14. What term is used to describe how a magnetic field is created by the flow of electric current? A. Magnetic Force B. Electrolysis C. Electromagnetism D. Hydro power Dam 15. You can find the direction of the magnetic field by using the ______ rule. A. High Five B. Right Hand C. Sleight of Hand D. Upper Hand 3 Lesson 9 Operation of Simple Electric Motors and Generators In this module you will be reacquainted with basic magnetism and its relationship with electricity by exploring the operations of Electric Motors and Generators. What’s In Great job! You have successfully answered the questions above. In this part, let us try to test what have you learned on the previous topic. Activity 1. Magnetic or Non-Magnetic Classify the given household objects whether or not they would be attracted to a magnet. Pencil Nail Broom Keys Screw Nail Hammer Paper Clips Toothbrush Wire Magnetic Scissors Non-magnetic 4 What’s New What is Magnetism? Magnets exert either a force of repulsion or attraction. If a force of attraction only is possible between an object and a magnet, then the object interacting with the magnet contains a ferromagnetic substance and is considered naturally magnetic. If a force of repulsion is also possible between an object and a magnet, then the object interacting with the magnet may also be a permanent magnet or a temporarily magnetized ferromagnetic material. Figure 1. Magnetism Lifted from: https://adflipped.weebly.com Let’s try this next activity. Activity 2 Make a list of all the devices and appliances in your home that use electricity. Device or Appliance that What the Electric Motor does? uses Electricity 1 Example: Electric Fan Spins propeller to circulate air 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 What do they have in common? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ A. Make a list of energy resources in the Philippines that an electric utility/company might use to produce electricity. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ What do they have in common? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 5 What is It GUIDE CONCEPTS A motor is generally defined as a device that converts other forms of energy into mechanical energy and may range from lawn mowers and automobile engines to rocket engines. Electric motors are a specific member of the motor family—they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, which usually appears as a spinning or rotating motion. Electric motors are made in a wide range of sizes and are used to run things ranging from toys to heavy industrial machinery and urban subway trains. The efficiency of electric motors is high; small motors convert electricity into motion with 60 to 75 percent efficiency, while large motors have efficiency as high as 90 to 97 percent. Motors can be made to use electricity produced by batteries and solar cells (photovoltaic cells) or the electricity produced by an electric utility’s power plants and distributed by its transmission lines. Like electric motors, generators come in many sizes, ranging from the generator of bicycles used to light a small headlamp to the large generator power plants use to produce electricity. Power plant generators are extremely efficient, converting up to 99 percent of mechanical energy into electrical energy. (However, the high efficiency of electric power plant generators should not be confused with the overall power plant efficiency, which is about 33 percent. Nearly all power plants produce electricity using generators. In turn, much of the electricity produced by generators is used by electric motors. In effect, what the two lists describe are major parts of today’s electrical system. Electric generators and motors—two simple, versatile devices that are actually the mirror images of one another—make this system possible. Let us see if you have understood what you’ve read above. Try doing the next activity (Activity 3). What’s More Great work! You can still recall your previous lessons. This time, you will be exploring different activities for you to discover the operations of electric motor and generator. Start working with Activity 3. Activity 3. Making Your Own Electric Motor Objectives: • Build a simple electric motor. • Explain the operation of a simple electric motor. 6 Materials: • 1 AA battery • 3 Neodymium magnets or any magnets that can be found at home • pliers or long nose • AWG #14 – 18 solid and bare copper wire (~30 cm) • science notebook and pen SAFETY PRECAUTIONS: WIRES CAN GET HOT WHEN CONNECTED TO THE BATTERY FOR A LONG TIME. OPEN THE CIRCUIT ONCE YOU ARE DONE WITH YOUR OBSERVATIONS. Procedure: 1. Assembly of the Electric Motor Model – Cut the length of copper wire into three pieces. With the use of the pliers, shape the three wires into a spiral, square, heart or any figure to your liking similar to what is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. A sample electric motor model using magnets http://ideas-inspire.com/simple-electric-motor/ 2. Make a sample pile of the three neodymium magnets, the battery and the shaped copper wire. Make adjustments to the length and width of the shaped wire. See to it that there is a bare connection between the wire ends and the neodymium magnet and also between the pivot part (balancing point) of the wire and the positive terminal of the battery. Scrape or sand off the material insulating the wire at these indicated points. Disassemble the set up when making the needed shape adjustments and sanding of the copper wire. 3. Testing of Model – Carefully pile with the three magnets and the battery on a level surface. Mount the shaped wire, with its pivot part as a rotating point, over the positive terminal of the battery. Check that the bottom ends of the wire curl loosely around the magnets forming a closed circuit. You now have a simple DC electric motor model that we will simply call a DC motor model. Give the current-carrying shaped wire a gentle spin. 4. Observe and record what happens to the shaped wire. Warning! Disconnect the DC motor model immediately after making observations. 5. If your DC motor does not work, stretch your tolerance, abilities, and knowledge. Have fun making your motor model. Guide Questions: Q1. What happens to the shaped wire once positioned over the battery’s positive terminal and with both wire ends curled loosely touching the magnets? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 7 Q2. What other observations have you made regarding your electric motor model? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q3. What will happen if the number of magnets used in the model is reduced? Increased? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q4. Based on the activity, how will you explain the operation of a simple electric motor? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Let’s have another Activity! Activity 4 Objectives: Students will be able to compare and contrast Electric Motor and Generator Students will be able to explain the operations of Electric Motor and Generator Materials: Pen Paper Procedure: Analyze the given picture of an electric motor A B F C D E Figure 3. Electric Motor Lifted from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_motor electromagnet? Q1. What is an ___________________________________________________________________________________ _________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 8 Q2. What is the relationship between electromagnet and electric motor? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________ Q3. Label the parts of the electric motor A- ________________________________________________________________________________ B- ________________________________________________________________________________ C- ________________________________________________________________________________ D- ________________________________________________________________________________ E- ________________________________________________________________________________ F- ________________________________________________________________________________ Q4. How do electric motor works? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q5. How do you make an electric motor more powerful? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Figure 4. Electric Motor Lifted from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_motor Q6. Identify and describe the basic parts of the generator model shown in figure 5 below. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 9 Figure 5. Generator Model Q7. What type of energy is inputted to a generator? What type of energy is the Output from an electric generator? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Q8. In what ways (if any) is an electric motor different from an electric generator? Consider their basic design and key components. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Q9. Explain what generators do play in producing electricity? Figure 6. Wind Turbine Lifted from: https://thumbs.dreamstime.com ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Q10. Site at least one example of Electric Power Station in Mindanao. Explain how they produce electricity. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 10 What I Have Learned Direction: Using a Venn diagram compare and contrast the operations of electric motor and generator. Electric Motor Generator What I Can Do Create a version of “Electricity Serves Our Community” for your own home or school. The diagram should include an energy source, a power plant, and a diagram of your home or school containing selected items that use electric motors. Figure 7. Electric Serves Community Poster Lifted from: https://lh3.googleusercontent.com 11 Assessment Alright! You are a step closer on finishing this module. Answer the following questions. Write the letter of the correct answer in the answer sheet. 1. What is the transfer of electricity in a generator? A. Mechanical to Electrical B. Physical to Potential C. Electrical to Mechanical D. Potential to Physical 2. Surrounding every magnet is a _________________. A. Magnetic Field B. Electrical Current C. Another Magnet D. None of the Above 3. In large generators in power plants, ________ rotates inside a coil of wire to produce an electric current. A. Wind B. Magnet C. Water D. Circuit 4. What force does a magnetic field apply without actually touching the object? How can a magnet move another object without touching it? A. A Push or Pull B. Friction C. Gravity D. Pressure 5. What energy do you put IN to a generator? A. Mechanical B. Thermal C. Electrical D. Potential 6. What type of energy comes OUT of a generator? A. Mechanical B. Thermal C. Electrical D. Potential 7. Electricity is the flow of __________ A. Protons B. Electron C. Neutrons D. Protons and Neutrons 8. What is the transfer of electricity in a motor? A. Chemical to Mechanical B. Mechanical to Electrical 12 C. Electrical to Mechanical D. Physical to Potential 9. Generators are devices that convert _______ energy into _____ energy. A. Chemical; Mechanical B. Electrical; Mechanical C. Mechanical; Electrical D. Potential; Kinetic 10. What basic principle enables ALL electric generators to operate? A. Iron is the only element that is magnetic. B. Opposite electric charges attract and like charges repel. C. A closed-loop conductor within a changing magnetic field will have an induced electromotive force. D. A current-carrying conductor placed within a magnetic field will experience a magnetic force. 11. A generator converts A. electrical energy into mechanical energy. B. mechanical energy into electrical energy. C.mechanical energy into steam. D.steam into mechanical energy. 12. Which of the following statements best describes how a generator induces a current? A.The magnetic field strength is varied. B.A wire loop is moved in and out of the magnetic field. C.The orientation of the loop is changed with respect to the magnetic field. D.The rotation of the loop is reversed periodically. 13. What is the name of the device that changes a small ac applied emf to a larger one or a large applied emf to a smaller one? A.converter B.transformer C.inverter D.Exchanger 14. The current that flows in an electric circuit carries ____. A. Chemical Energy B. Mechanical Energy C. Thermal Energy D. Electrical Energy 15.There is a repulsive force between two charged objects when __________ A. charges are of unlike sign. B. they have the same number of protons. C. charges are of like sign. D. they have the same number of electrons. 13 Additional Activities Directions: Using Across and Down Clues. Write the correct words in the number grid below. 14 Answer Key 15 References: Printed Material: Acosta, H., Alvarez, L., Angeles, D., Arne, R., Carmona, M., Garcia, A., Gatpo, A., Macaida, J., Olarte, M., Rosales, M., Salazar, N. (2015). First Edition. Science 10 Learner’s Material. Department of Education. Republic of the Philippines Acosta, H., Alvarez, L., Angeles, D., Arne, R., Carmona, M., Garcia, A., Gatpo, A., Macaida, J., Olarte, M., Rosales, M., Salazar, N. (2015). First Edition. Science 10 Teachers Guide (Unit1). Department of Education. Republic of the Philippines Electronic Sources: ENERGY, GENERATORS, AND MOTORS. Retrieved from: https://www.ww2classroom.org/system/files/WWII1802_REAL_WORLD_SCIENCE_32_Energy-Generators-and-Motors.pdf Motors and Generators. Retrieved from: http://www.meprogram.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/KISS-NotesMOTORS-NA.pdf Electromagnets and Electric Motors Intro Power point. Retrieved from: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Electromagnets-and-ElectricMotors-Intro-PowerPoint-NGSS-MS-PS2-3-1761996 Electric Motors and Generators. (www.uwsp.edu) Retrieved from: https://www.uwsp.edu/cnrap/KEEP/Documents/Activities/Electric_Motors_Gene rators.pdf Science 10 Learner’s Material pp.3, 6-13 Hobart M. King, Ph.D., RPG. Map of Plate Boundaries. Retrieved May 8, 2020 from: https://geology.com/plate-tectonics.shtml Poulsen, T., Yastrebov, Y. (2019). Ural Mountain. Retrieved May 2020 from: https://www.britannica.com/place/Ural-Mountains Barrow, M.(2013).The Mountain environment .Retrieved May 26, 2020 from: http://www.primaryhomeworkhelp.co.uk/mountains.htm Marston, R., Eardley, A. (2020). Rocky Mountains. Retrieved May 2020 from: https://www.britannica.com/place/Rocky-Mountains Zimmerman, K.A. (2013). Andes: World’s Longest Mountain Range. Retrieved May 2020 from: https://www.livescience.com/27897-andes-mountains.html Aubrey Diem, Thomas M. Poulsen (2019).Alps. Retrieved May 2020 from: https://www.britannica.com/place/Alps 16 Figure 1. Earth’s Crust Retrieved May 25, 2020 from: https://www.slideserve.com/havyn/tectonic-plates Figure 3 : Map of the Philippines Retrieved May 13,2020 from: https://www.drivingdirectionsandmaps.com/wpcontent/uploads/country-maps/rp-country-map.gif Figure 5. Map of Mindanao Retrieved May 1, 2020 from PHILVOLC Figure 6. Map of Earthquake Distribution Retrieved May 15, 2020 from: http //marc.fournier.free.free.fr Figure 7. Map of Active Volcanoes Retrieved May 15, 2020 from: https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/volc/fig34.html Figure 8. Map of Major Mountain Belts Retrieved May 15, 2020 from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earthand-planetary-sciences/mountain-building Figure 9. Mountain Ranges of the World Retrieved May 15, 2020 from: http://www.clipart.dk.co.uk/1068/az/earth/mountain_ranges “Earthquakes and Volcanoes”: Retrieved May 12, 2020 from: https://www.clarkshawnee.k12.oh.us/userfiles/36/Classes/1702/chap08.pdf?id=2780&fbclid=IwAR 2XIC4hPxff9qwG2Xhe3puhlnCwwIbvM89xCvXNF3yeA1ZRpyo40DDxfno “Mountain Ranges”. Retrieved May 18,2020 from: http://www.clipart.dk.co.uk/1068/az/Earth/Mountain_ranges “Mountain Ranges” Retrieved May 25,2020 from: www.worldlandforms.com “Mountain range facts for kids”. Retrieved May 26,2020 from: https://kids.kiddle.co/Mountain_range#Major_ranges “Himalayas Facts” Retrieved May 2020 from: https://www.softschools.com/facts/geography/himalayas_facts/1707/ “Earthquakes, tsunamis, epicenter, magnitude and faults”. Retrieved May 2020 from: http://earthquake.usgs.gov//epicenter http://oceanservice.noaa.gov>facts http://www.livescience.com http://www.sciencelearn.org.nz 17 EDITOR’S NOTE This Self-Learning Module (SLM) was developed by DepEd SOCCSKSARGEN with the primary objective of preparing for and addressing the new normal. Contents of this module were based on DepEd’s Most Essential Competencies (MELC). This is a supplementary material to be used by all learners of SOCCSKSARGEN Region in all public schools beginning SY 20202021. The process of LR development was observed in the production of this module. This is Version 1.0. We highly encourage feedback, comments, and recommendations. For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – SOCCSKSARGEN Learning Resource Management System (LRMS) Regional Center, Brgy. Carpenter Hill, City of Koronadal Telefax No.: (083) 228 8825 / (083) 228 1893 Email Address: region12@deped.gov.ph