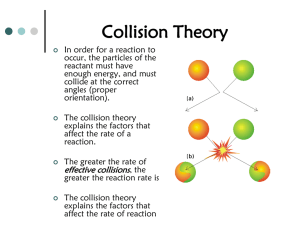
Unit 16 Test Review WS 1. 2. 3. Chemist:__Elham Ghiasi_____ The transfer of energy is called _heat_________________. The way we measure heat energy is __temperture____________. During an exothermic reaction, energy is ___released_______________. The enthalpy or ______ is negative. The reaction container will feel ___warmer________________. The enthalpy or energy of the product is ____lower____________ than the enthalpy or energy of the reactants. If energy is shown in the chemical equation, it will be a __products_. 4. Label each of the following as representing an endothermic or exothermic reaction: 5. D minus A represents the ___________ for the forward reaction in the diagram to the left 6. Using the reaction curve to the right, calculate the enthalpy for the reaction._______________ 7. If the enthalpy is negative, the reaction is __exothermic_____(endothermic/exothermic). 8. 9. N2 + 2O2 + energy 2NO2 Is this reaction endo- or exothermic? _endothermic________ In an endothermic reaction, heat is _absored______________. The enthalpy is __positive________________. The energy of the products is ____more_____________ than the energy of the reactants. 10. Label the following on the graph to the right: energy of reactants, energy of products, enthalpy of the reaction 11. The energy required to form the transition state (activated complex) from reactants is called the ___activation_________________ energy. 12. What does a catalyst do to a reaction? It speeds up the rate and lower the activation energy ______________________________________________________ 13. Which letter in the diagram represents the activation energy?__B___ 14. Using the reaction curve to the right, calculate the activation energy. __200 KJ___________________ 15. The addition of a catalyst to a reaction lowers the __activation _energy__ required for the reaction to occur. 16. Label the following on the graph below: energy of reactants, energy of products, transition state (activated complex), activation energy 17. For a reaction to be at equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction must ____equal__________ the rate of the reverse reaction. The forward and reverse reactions are continuous, meaning that they do not ____stop_________. Once equilibrium has been established the amount of reactants and products remains ___constant___________. 18. According to Le Chatelier, when a stress is made to a system at equilibrium, they system will change to _counteract_______________ the stress. If pressure is added to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift to toward the fewest _____number of gas particles __________________. 19. Use the equation below to answer the following: 2Mg(s) + O2(g) ↔ 2MgO(g) + 2500 kJ a. Which direction will the reaction shift if the pressure is increased? __________________ b. Which direction will the reaction shift if the [O2] is decreased? __________________ c. Which direction will the reaction shift if temperature is decreased? 20. __________________ Write the equilibrium expression for each of the following reactions. a. 2NO2(g) ↔ N2O4(g) b. C(s) + O2(g) ↔ CO2(g) c. H2SO4(aq) ↔ 2H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) 21. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) The following concentrations were found once equilibrium was reached: [N2] = 2.3 x 10-2 M [H2] = 1.5 x 10-1 M [NH3] = 4.5 x 10-2 a. Write the equilibrium constant expression for the reaction above. b. Calculate the value of K for the above reaction L.O. Extensions Test Review Section 1. Which of the following reactions has the largest positive value of S? a. 2 H2S(g) + SO2(g) 3 S(s) + 2 H2O(g) c. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) MgCl2(s) b. 2 SO3(g) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) d. H2(g) + ½O2(g) H2O(l) 2. The graphs above show concentration versus time data for three trials of a reaction using different initial concentrations of reactant and product. a. Is X1 a reactant or product? Justify your answer. Because the amount decreases over time b. Is X2 a reactant or product? Justify your answer. Because the amount increases over time c. How can you determine the rate of the reaction at any given time? The slope of the tangent to the curve. d. When is the rate of the reaction the fastest? When is it the slowest? Justify your answers. fastest at the beginning because of the slope. Slows down because cause of the slope . e. Draw a vertical line on the graph to indicate the time at which equilibrium is established. 3. As any reaction proceeds at constant temperature, the rate of the reaction a. b. c. d. remains the same as long as no catalyst is added remains the same because the temperature is constant decreases because the concentrations of the reactants decrease decreases because the effectiveness of collisions between molecules decreases 4. Consider the following equilibrium: 2H2(g) + X2(g) 2H2X(g) + energy Addition of X2 to a system described by the above equilibrium a. b. will cause [H2] to decrease will cause [X2] to decrease c. d. will cause [H2X] to decrease will have no effect 5. H2(g) + I2(g) 2 HI(g) 0 Which of the following changes to the equilibrium system represented above will increase the quantity of HI(g) in the equilibrium mixture? I. Adding H2(g) II. Increasing the temperature III. Decreasing the pressure a. b. c. d. I only III only I and II only I, II, and III 6. Suppose the following reaction has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 2.5 x 10-2 at 100 K and 1 atm. C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) (a) Write the equilibrium constant expression for the above reaction. (b) At 100 K and 1 atm, which are present at a higher concentration, the product or the reactants? Justify your answer. reactants because K<1 (c) If the reaction is endothermic, predict whether the value of Keq at 200 K would be greater than, less than, or equal to the value of Keq at 100 K. Justify your answer. K would have adding energy causes a shift towards the products.