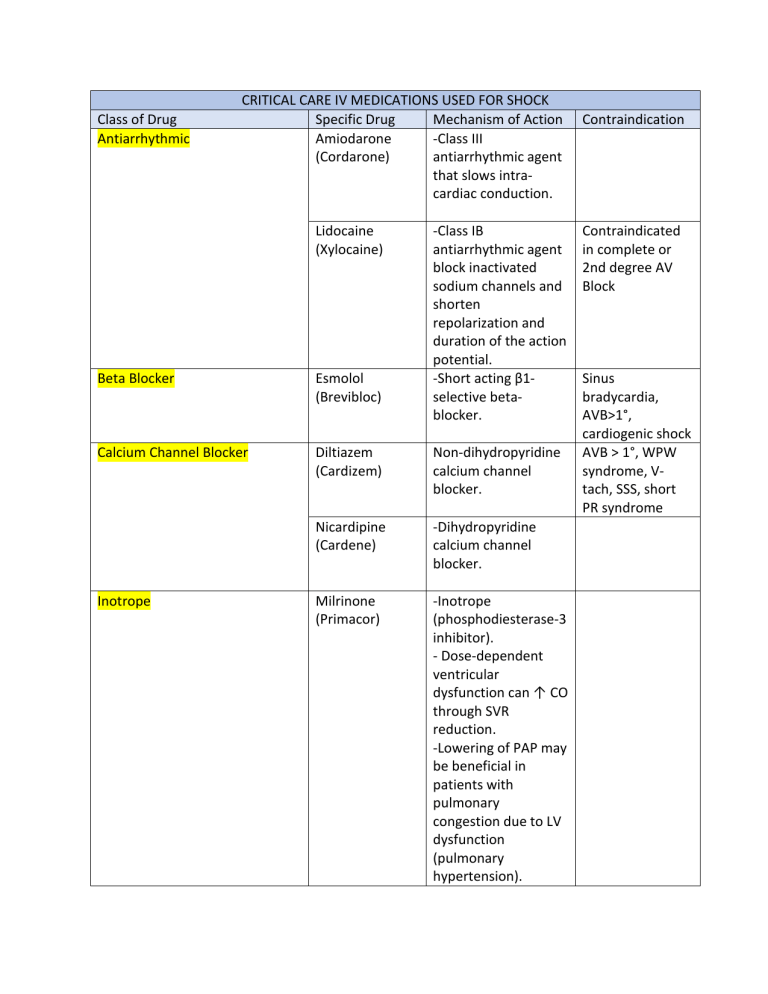
Class of Drug Antiarrhythmic CRITICAL CARE IV MEDICATIONS USED FOR SHOCK Specific Drug Mechanism of Action Amiodarone -Class III (Cordarone) antiarrhythmic agent that slows intracardiac conduction. Lidocaine (Xylocaine) -Class IB antiarrhythmic agent block inactivated sodium channels and shorten repolarization and duration of the action potential. -Short acting β1selective betablocker. Beta Blocker Esmolol (Brevibloc) Calcium Channel Blocker Diltiazem (Cardizem) Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Nicardipine (Cardene) -Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. Milrinone (Primacor) -Inotrope (phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor). - Dose-dependent ventricular dysfunction can ↑ CO through SVR reduction. -Lowering of PAP may be beneficial in patients with pulmonary congestion due to LV dysfunction (pulmonary hypertension). Inotrope Contraindication Contraindicated in complete or 2nd degree AV Block Sinus bradycardia, AVB>1°, cardiogenic shock AVB > 1°, WPW syndrome, Vtach, SSS, short PR syndrome CRITICAL CARE IV MEDICATIONS USED FOR SHOCK Class of Drug Specific Drug Mechanism of Action Dobutamine -Potent beta-1 (Dobutrex) agonist: strong positive ionotropic activity -Some beta-2 and alpha agonist activity. Because of beta-2 activity, does not cause vasoconstriction may ↓ BP. Sympathomimetics Dopamine -Dopamine receptor (Intropin) agonist, at higher doses activates alphaand beta-adrenergic receptors. Sympathomimetics/Vasopressors Norepinephrine -Potent alpha-1 (Levophed) agonist activity, weak beta-1 activity (may see ↑ HR). Phenylephrine -Acts as a pure alpha(Neo1 agonist ONLY. Synephrine) Vasopressin -Stimulates (Pitressin) vasopressin receptor resulting in vasoconstriction and free water retention (no inotropic or chronotropic effects). Vasodilators Sodium -Direct vasodilator nitroprusside potent arterial (Nipride) vasodilator. Nitroglycerine (Tridil) -Coronary vasodilator and peripheral vasodilator (reduces preload). Contraindication Uncorrected tachyarrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, septic shock