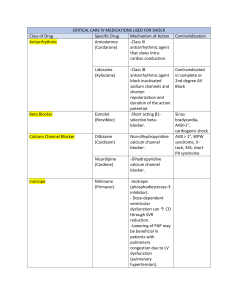
Quizzes (best 2/3) % 20% Mid-term 30% Final 50% • • • ! •$ %& " # ' Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 11th Edition (Bertram G. Katzung, Susan B. Masters, Anthony J. Trevor) Principles of Pharmacology: The pathophysiologic Basis of Drug Therapy (David E. Golan, Armen H. Tashjian. Ehrin J. Armstrong, April W. Armstrong). 3rd Edition I Rang & Dale's Pharmacology, 6th Edition (H. P. Rang , M.M Dale, J. M. Rod, R. J. Flower) •( 'Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, Eleventh Edition( Laurence Brunton, John Lazo, Keith Parker) )* + •, + • -( • • ' . & " - / 0 %, * 1 %$ 0& 4 5 23 67 • 0 " 2 • 6 • & • )* & 8 & 8 2 8 2 • 1 & % 8 1 % 8 & % • 0 8 1 89 . 9 9 : the study of substances (the effect and mechanism ) that interact with living systems altering body processes% 2& Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics /7;<< !!! " # % $ Activating/blocking % Activating/inhibiting ' Altering activity & Opening/Closing ()*+, " &( &( - ' & . ' & . & ' ! $ • • $= ' • > & . . #8 & 8 8 • 0 ' – & 8 #8 @A –0 • ) . –7 & ? & 1 ' 8 1 *% • ' 1 $@ ) 54 % & Affinity/Efficacy? 2 effect No ligand Full agonist Drug binds mainly to Ra Antagonist Partial agonist Drug binds Ra>Ri Inverse agonist?? Drug binds Ra=Ri 0 Maximum response to agonist will be depressed Partial agonist can act as an antagonist…how?? chemically reacts with the substance, usually used for neutralizing toxins opposes the effect of an agonist (mediated by different receptors) $ && & % # & / &0 / 1# & % 2 • B • 6 • • = . & B0 B 02& & 8 1 Ligands must be lipid soluble, eg corticosteroids, …..why? % 2 2 # &# & # 3 2 & # & 3 # # 3 4 %) # $ • )* 2 2 & C # 2 # &# & " % " & 5 & # ' 0 ' # && # 6 %) # $ 2 Intracellular protein D%6 • • )% 2 & 8 0>0 0 2 # &# & & # D%6 2 E% 2 • • 6 & 6 & 0 1 2 7 . )(() 1 . ) # & 1 . & % E% 2 E% 2 2 # &# & # # / /3" 7/ "5 / " 6 # 3 &4 / " 7/3" / " # # & E% 2 Gs/Gi Gq G0 E% 2 0 & Protein phosphorylation Effect E% 2 & Protein Phosphorylation Effect Effect