Electrical Engineering Exam Problems: Transformers & Generators
advertisement

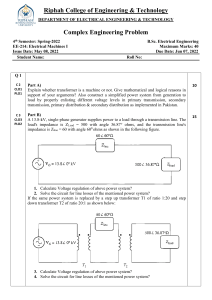
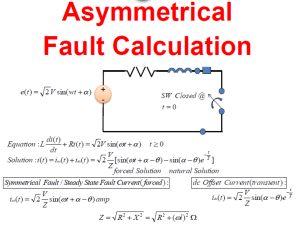
Prob. 1 A three-phase step-up transformer is rated 26/345 kV, 850 MVA and has a series impedance of 0.0035 + j 0.087 per unit on this base. It is connected to a 26 kV, 800 MVA generator, which can be represented as a voltage source in series with a reactance of j1.57 per unit on the generator base. (a) Convert the per unit generator reactance to the step-up transformer base. (b) The unit is supplying 700MW at 345 kV and 0.95 power factor lagging to the system at transformer high voltage terminals. 1. Calculate the transformer low-side voltage and the generator internal voltage behind its reactance in kV. 2. Find the generator output power in MW and the power factor. Prob. 2 A 15 KVA, 8000/230 V distribution transformer has an impedance referred to primary of 80 +j300 . The components of the excitation referred to the primary side are Rc= 350 k, and XM= 70 k. (a) If the primary voltage is 7967 V and the load impedance is Zl= 3.2+j1.5 . What is the secondary voltage of the transformer? what is the voltage regulation of the transformer? (b) If the load is disconnected and a capacitor of -j3.5 is connected in its place, what is the secondary voltage? What is its voltage regulation under these conditions? Prob.3 A 3-phase, wye-connected, round rotor synchronous generator rated at 10 KVA, 230 V has a synchronous reactance of 1.2 per phase and an armature resistance of 0.5 per phase. (a) Calculate the percentage voltage regulation at full load with 0.8 lagging power factor. (b) Repeat the previous problem for the case of 0.8 leading power factor, other data remaining unchanged. (c) Determine the excitation voltage when the generator is delivering full load at power factor of 0.7 lagging. (d) Determine the maximum power that can be converted from mechanical to electrical form without loss of synchronism if the field current is unchanged. (e) The value of Current Ia for this condition