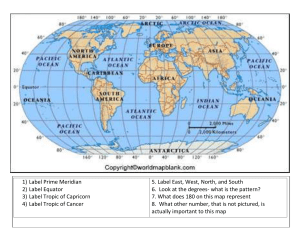
Multiple Choice – Circle the correct answer below. 1. What is used on a map to show direction? a. compass b. scale c. legend d. border 2. If a map’s scale is 1cm = 10km, 20cm is equal to… a. 500km b. 100km c. 20km d. 200km 3. Scale can also be written as a ratio. Which of the following means the same as 1:100 as a scale for a map? a. 1cm = 10km b. 10cm = 10km c. 1cm = 1m d. 1cm = 100km 4. The ___________ is a circle of latitude, about 40,075 km in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. a. Equator b. Greenwich Meridian c. Tropic of Capricorn d. Pacific Ocean 5. The ____________ is an imaginary line that is used to indicate a longitude of 0 degrees. a. Greenwich Meridian b. Tropic of Cancer c. Equator d. Antarctica 6. What are the two things required for a bushfire to occur? a. Grass & Lightning b. Fuel & Ignition Label the BOLTSS on the map below: c. Rainfall & Winds d. Drought & Fire Short Answer Questions – Remember to use full sentences in an exam. 1. Write your own definition for the term ‘Geography’ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. Discuss the difference between a natural hazard and a natural disaster. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3. What are the four ways that humans value landscapes? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 4. Describe one economic impact of natural hazards. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 5. Explain ONE natural and ONE human induced cause of bushfires. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 6. Choose one example of a natural disaster and discuss what causes it to occur. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 7. Choose one example of a landform and discuss the processes behind its formation. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Label the diagram below with the lines of latitude and longitude Tropic of Capricorn Arctic Circle Antarctic Circle Equator Tropic of Cancer North Pole South Pole Prime Meridian Using the map, answer the following questions: 1. Which three continents does the Prime Meridian run through? _________________________________________________________ 2. Name three countries east of the Prime Meridian _________________________________________________________ 3. Name three countries west of the Prime Meridian _________________________________________________________ 4. Name the continents that the Tropic of Cancer runs through _________________________________________________________ 5. Name the continents that the Tropic of Capricorn runs through _________________________________________________________ 6. Which of the lines of latitude divides the globe into the Northern and Southern hemispheres? _____________________________________________ Match the following terms to their definition The measurement of distance north or south of the Equator All the visible features of an area of land A natural phenomenon that might have a negative effect on humans and other animals, or the environment The process of wearing or being worn by long exposure to the atmosphere. The action of making use of and benefiting from resources They run north to south from pole to pole, and they measure the distance east or west The envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet A natural feature of the earth's surface. The rigid, rocky outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and the solid outermost layer of the upper mantle. A natural event such as a flood, earthquake, or hurricane that causes great damage or loss of life. All the waters on the earth's surface, such as lakes and seas, and sometimes including water over the earth's surface, such as clouds. The process of eroding or being eroded by wind, water, or other natural agents The action of depositing something The regions of the surface and atmosphere of the earth or another planet occupied by living organisms. Reading Comprehension – read through the following passage and answer the short answer questions. Changing Landscapes All life on Earth depends on landscapes. Soils produce food, plants provide oxygen, and minerals and timber contribute to the production of goods. All landscapes contain the imprint of human use and hold aesthetic, cultural, emotional, and spiritual values for different people. Over time, humans have changed the land. In some locations they have caused a decline in output that has affected the land’s ability to provide resources, such as food. This is called land degradation, which affects 1.5 billion people globally. Human activities have resulted in landscape degradation – tourism and mountain biking has caused soil erosion. Air pollution from industry has contributed to acid rain. Mining has caused pollution of water sources and permanently changed the shape of hills and mountain landscapes from digging mines. Many human activities also increase the rate at which natural processes shape landscapes, for example: • Erosion – from overcropping, overgrazing animals, logging forests for settlements, bush walking, mountain biking and driving off-road vehicles. • Air pollution – from acid rain speeding up the weathering of Earth’s surface. Changing Waterways We have also seen the vast impact of humans on our waterways and aquatic environments. Humans have changed aquatic landscapes by constructing features to reduce the impact of sea level rises like seawalls and to improve transport like the canals in Venice. Of the world’s 228 largest rivers, approximately 60% have been changed by the construction of dams, weirs, and canals. The construction of 48 000 dams around the world has displaced natural landscapes, such as forests, as well as agricultural lands and settlements. Dams have caused the degradation of wetland and riverine ecosystems, and their reservoirs have changed biodiversity, because water temperature is colder behind the dam wall where the water is deeper. Fish such as salmon are unable to migrate upstream to breed, although in many cases fish ladders have been built to assist their migration. A dam collapse from an earthquake or faulty construction increases the change of floods downstream. Traditional Land Management Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples have managed their landscapes for over 60 000 years. Their knowledge has contributed to the sustainable management of landscapes and their distinctive landform features. Traditional methods of backburning were used to control the severity of bushfires through the removal of forest materials. The patterns of burning used by Aboriginal communities were quite sophisticated. They were very careful to avoid plant communities that are fire-sensitive to ensure greater biodiversity across the entire landscape. Comprehension Questions 1. Explain the importance of landscapes ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. What is meant by the term land degradation? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3. List 3 causes of land degradation ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 4. How are human activities changing the rate of natural processes? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 5. Explain how dams can cause land degradation ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 6. How have Indigenous people traditionally managed the landscape? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Describe the human activities and how they are impacting the landscapes ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ _________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Bushfires in Australia There are two main factors responsible for bush fires: _______ and ignition. Bush fire fuel is any materials which can feed a fire such as dry plant materials like grass and trees. Ignition is an event which ignites the fire such as a ___________ strike, out of control back burning or a lit cigarette. The Bush Fire _________ Ratings give you an indication of the possible ___________ of a fire if one was to start. Bush Fire Danger Ratings are based on conditions such as temperature, ___________, wind and the dryness of the landscape. Bush fires are more likely to __________ and cause damage on days when the weather is very hot, dry, and windy. These are usually on very high to ___________ fire days. In a ________ ______ _____ no fire may be lit in the open and all fire permits are suspended. Hazard _____________ is just one way of preparing for bush fires. There are different methods of reduction including controlled burning, land clearing with machinery and reducing ground ________ by hand. ______ __________ was originally used by Indigenous people as a form of fire and land management more than 50 000 years ago. Every year, Australian _______________ face devastating losses caused by disasters. Bushfires and their associated consequences have significant _____________ on communities, the economy, infrastructure and the environment. Word Bank: communities humidity litter extreme Danger total fire ban reduction impacts Back burning spread fuel severity lightning State the directions of the symbols on the compasses below: Brainstorm Challenge – Write down as many examples of landforms as you can.