November 13th and 14th, 2013 AP Human Geography Agenda
advertisement
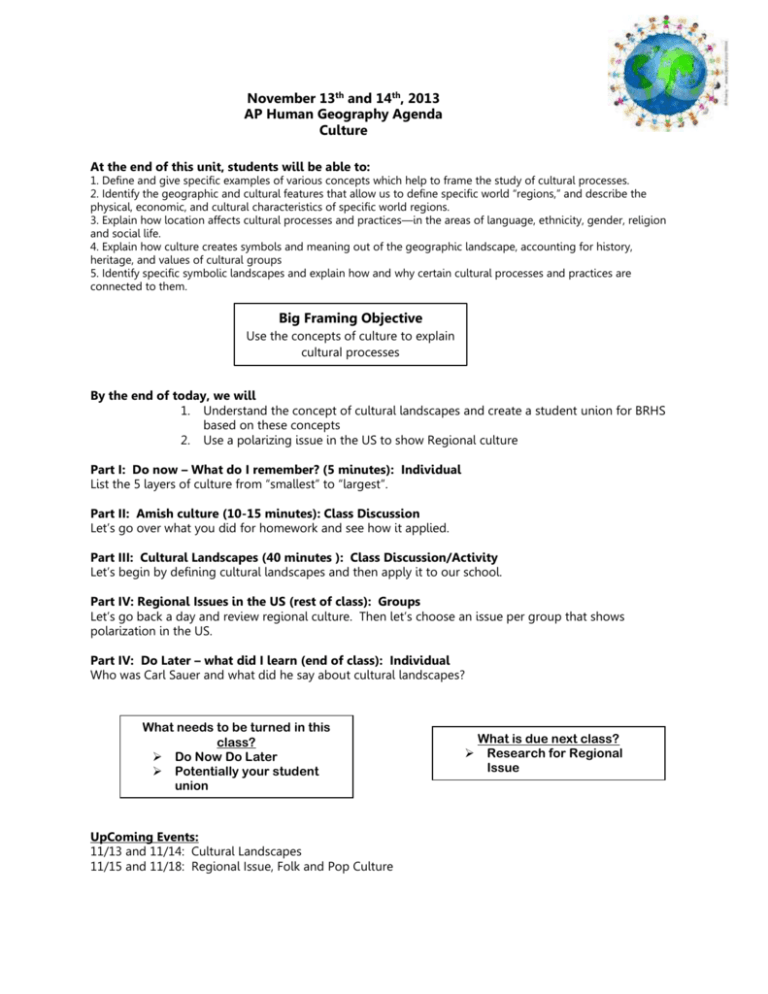
November 13th and 14th, 2013 AP Human Geography Agenda Culture At the end of this unit, students will be able to: 1. Define and give specific examples of various concepts which help to frame the study of cultural processes. 2. Identify the geographic and cultural features that allow us to define specific world “regions,” and describe the physical, economic, and cultural characteristics of specific world regions. 3. Explain how location affects cultural processes and practices—in the areas of language, ethnicity, gender, religion and social life. 4. Explain how culture creates symbols and meaning out of the geographic landscape, accounting for history, heritage, and values of cultural groups 5. Identify specific symbolic landscapes and explain how and why certain cultural processes and practices are connected to them. Big Framing Objective Use the concepts of culture to explain cultural processes By the end of today, we will 1. Understand the concept of cultural landscapes and create a student union for BRHS based on these concepts 2. Use a polarizing issue in the US to show Regional culture Part I: Do now – What do I remember? (5 minutes): Individual List the 5 layers of culture from “smallest” to “largest”. Part II: Amish culture (10-15 minutes): Class Discussion Let’s go over what you did for homework and see how it applied. Part III: Cultural Landscapes (40 minutes ): Class Discussion/Activity Let’s begin by defining cultural landscapes and then apply it to our school. Part IV: Regional Issues in the US (rest of class): Groups Let’s go back a day and review regional culture. Then let’s choose an issue per group that shows polarization in the US. Part IV: Do Later – what did I learn (end of class): Individual Who was Carl Sauer and what did he say about cultural landscapes? What needs to be turned in this class? Do Now Do Later Potentially your student union UpComing Events: 11/13 and 11/14: Cultural Landscapes 11/15 and 11/18: Regional Issue, Folk and Pop Culture What is due next class? Research for Regional Issue IF YOU LEARN ONLY 4 THINGS IN THIS UNIT . . . 1. 2. 3. 4. Folk Culture is practices by a relatively small number of people in a particular area. Popular Culture is diffused rapidly around the world through mass communication. Cultural Landscapes are the imprints humans leave on the earth. Culture has many layers: traits, complexes, regions, systems and realms. Culture is spread through diffusion Geography Facts Alabama George Washington Carver, who discovered more than 300 uses for peanuts Alaska The longest coastline in the U.S., 6,640 miles, greater than that of all other states combined Arizona The most telescopes in the world, in Tucson Arkansas The only active diamond mine in the U.S. California “General Sherman,” a 3,500-yearold tree, and a stand of bristlecone pines 4,000 years old are the world's oldest living things Colorado The world's largest silver nugget (1,840 pounds) found in 1894 near Aspen Connecticut The first American cookbook, published in Hartford in 1796: American Cookery by Amelia Simmons Delaware The first log cabins in North America, built in 1683 by Swedish immigrants This Day in History 1927 The world's first long, mechanically ventilated underwater tunnel, the Holland Tunnel, opened between New York and New Jersey. 1940 Walt Disney's Fantasia debuted. 1942 The minimum draft age was lowered from 21 to 18. 1946 Vincent Schaefer produced artificial snow from a natural cloud for the first time at Mount Greylock in Massachusetts. 1956 The Supreme Court struck down laws calling for racial segregation on buses. 1982 The Vietnam War Memorial, designed by Maya Lin, was dedicated in Washington, DC.