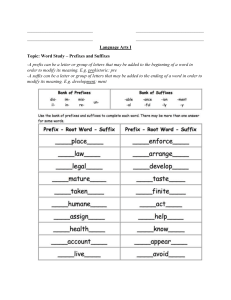
WEEK 1 DEMONYMS A Demonym is a proper noun used to identify the natives or residents of a particular place. It is usually derived from the name of a country or the name of a state or city or neighbourhood within a country. Some examples of demonyms include the following. 1. Nigeria - Nigerians 2. Ghana - Ghanaians 3. Republic of Niger - Nigeriens 4. Republic of Benin - Beninese 5. Philippines –Filipinos 6. Cameroon – Cameroonians 7. Congo - Congolese 8. Hungary - Hungarians 9. Gambia - Gambians 10.Kenya – Kenyans WEEK 2 WALT: spell silent letter words, learn and explain the rules. Silent letters have their origin from different languages. A silent letter is a letter that, in a particular word, does not correspond to any sound in the word’s pronunciation. It can be found at the beginning of words e.g. ‘write, knife’; at the middle, e.g. ‘whisper, rhubarb’ and at the end of words e.g. ‘autumn, hymn.’ Striking Words Silent u 1. Guard 2. Guess Silent h 3. Exhibition 4. Rhombus 5. Rhyme 6. Rhythm Silent t 7. Castle 8. Listening Silent n 9. Autumn 10.Column 11.Environment 12.Hymn WEEK3 WORDS RELATING TO ENVIRONMENT 1. Tropical 2. Latitude 3. Hemisphere 4. Flora 5. Equator 6. Erosion 7. Moor 8. Soil 9. Humid 10.Seashore 11.Covenant 12.Abstract 13.Democracy 14.Neighbour 15.Evacuated WEEK4 Prefixes A prefix is a letter or group of letters added to the beginning of a root word to give that word a new meaning. For example, mis + fortune = misfortune. A root word stands on its own as a word but you can make new words from it by adding a prefix. Every prefix has a meaning. For example: Prefix Meaning Examples uni One, single unilateral, unicellular a, an without, lack of, not acellular , anhydrous micro very small microcosm, microbe macro large, prominent macrocosm, macroeconomics anti against, opposite of antiseptic, antibody Note: Sometimes, adding a prefix creates a double letter. Example: un + necessary = unnecessary Some words contain the same string of letters as a prefix, but upon closer examination you’ll find that they are not prefixes. The re in real is not a prefix. Other examples include uncle, pretty and interest. A hyphen is sometimes used after the prefix re to prevent confusion with another word. For example: re-cover vs re-cover OR ‘Please relay the message that they will re-lay the tiles’. SPELLING LIST 1. Headquarters 2. Incredible 3. Landmark 4. Donate 5. Conscience 6. Guilty 7. Chore 8. Devalue 9. Illegal 10.Upbeat 11.Upgrade 12.Hyperactive 13.Circumnavigate 14.Disagreeable Dissect WEEK 5 Suffixes A suffix is a group of letters that can be added on to the end of a root word to change its meaning. Like prefixes, there are many suffixes used in the English language. These include • Noun Suffixes • Adjective Suffixes • Verb Suffixes • Adverb Suffixes Some of the most common suffixes are listed below with examples of words they form. Suffixes that make Nouns Suffix Meaning Example –age A result Wreckage –ance An action or state Importance -ant A person Assistant –ee A person Referee -ence An action or state Difference -er/or A person Teacher –ery A type or place of work Bakery –ess Makes a feminine form Waitress -ful As much as will fill Spoonful –ing An action or result Painting -ion A process, state or result Decoration –ism A belief or condition Judaism -ist A person Florist –ment An action or state Measurement Suffixes that make Adjectives Suffix Meaning Example -able Able to be Inflatable -en Made of Woolen -ful Full of Beautiful -ible Ability Flexible -ish A little Greenish -less Without Careless -like Similar to, like Lifelike -ous Full of Joyous -some A tendency to Quarrelsome Suffix Meaning Example -ly In a manner Quickly -ward Shows direction forward -ways Shows direction Sideways Suffixes that make ADVERBS Suffixes that make Verb Suffix Meaning Examples -ate To bring about a state communicate -en To become shorten -ify To make something, to become clarify -ise To do something, to become realise SPELLING LIST Find the meaning of these words using a dictionary and write out them out in your Spelling notebook. 15.Navigation 16.Expedition 17.Rapids 18.Crew 19.Astronomy 20.Observatory 21.Admiral 22.Nobleman 23.Mutiny 24.Cartographer 25.Wreckage 26.Demonstrate 27.Measurement 28.Simplify 29.Strengthen 30.Inflatable 31.Perseverance 32.Conscience 33.Descriptive 34.narration WEEK6-7 Mnemonics WALT: Explain mnemonic devices and list and use the different types of mnemonic devices. A mnemonic device is a tool that helps you remember large amounts of information. It is a learning technique that you can use to retain information or remember certain facts or numbers. People tend to remember the unusual, the funny and/or the personal ones the best. There are different types of mnemonic devices. 1. Acronyms – The most common everyday use of mnemonics. The first letter from each word is taken to spell out a simple word or phrase. Example ROY G BIV Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet Colours of the rainbow 2. Acrostic – An invented sentence where the first letter of each word is a cue to an idea you need to remember. Example Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally Math: Order of Operations (Parentheses, Exponent, Multiply, Divide, Add, Subtract.) 3. Rhymes – Placing the facts to be memorized into a rhyme or poetry form. Example – The Alphabet Song 4. Visual Association – Involves linking a picture with the item you need to remember. 5. Chunking – Involves reducing items that you need to memorize into organized groupings. Example Phone number – 0833 -645-6789 SPELLING LIST 1. Wellbeing 2. Queue 3. Discipline 4. Criminal 5. Profession 6. Considerate 7. Citizenship 8. Authority 9. Lightning 10.Signify 11.Commandment 12.Covet 13.Witness 14.Stern 15.Smugly 16.Stuffy 17.Benefit 18.Slung 19.Jolt 20.conscience