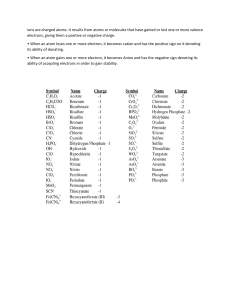
Chemical Naming (Nomenclature) NAME: PERIOD: S154 LEWIS Dot Diagrams for Atom, Ions, and Atoms & Ions Atoms Ionic Compounds same number of protons as they have electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost energy level. The number of valence electrons can be determined from an atoms position on the periodic table. Ions are charged particles or atoms that have lost (transferred away) or gained electrons in order to have a stable (full or empty) energy level like the noble gas closest to it on the periodic table, When an atom loses electron(s) it becomes positively charged because it has more protons than elecfrons. When an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged because it has more are neutral, that is they have the electrons than protons. Elements in group 1 (alkali metals) have one valence electrom In a dot diagram of the atom, the electron is shown by a single dot above the symbol. When an atom loses its electron the dot diagram is now just the symbol of the element, with no dot (because they were lost), brackets are drawn around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge of the atom is shown as a super script to the right of the brackets. Ion of Lithium Example: Lithium, Li Atom of lithium Neutral atom ----> Elements in group 2 (alkaline earth metals) have two valence electrons. In a dot diagram of the atom, the elecfrons are shown by two dots above the symbol. When an atom loses its electrons the dot diagram is now just the symbol of the element, with no dots (because they were lost), brackets are drawn around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge of the atom is shown as a super script to the right of the brackets. Example: Beryllium, Be Ion Be of Beryllium Atom of Beryllium Neutral atom ----> Be [Be]2+ Elements in group 13 have three valence electrons, In a dot diagram of the atom, the electrons by a two dots above the symbol alid one to the right of the symbol.. When an atom loses its electrons, the dot diagram is now just the symbol of the element, with no dot (because they were lost), brackets are drawn around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge of the atom is shown as a super script to the right of the three dots, brackets. Example: Boron, D Atom of Boron Ion of Boron, B3+ Neutral atom ----> Elements in group 14 have four valence electrons and tend not to form ions. In a dot diagram of the atom, the electrons are shown by a four dots, two dots above the symbol, one to the right of the symbol, and one below, Or one dot each above, below, and one each side. Exampl.e: Carbon, C Atom of Carbon or Neutral atom ----> Elements in group 15 have five valence electrons. In a dot diagram of the at0in, the electrons are shown by a five dots, two dots above the symbol, one to the right of the symbol, one below, and one to the left.. When an atom gains 3 electrons, the dot diagram is now the symbol of the element, with eight dots (showing a full valence energy level), brackets are drawh around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge oftbe atom is shown as a super script to the right of the brackets. Example: Nitrogen, N Atom of Nitrogen, N Ion of Nitrogen, Neutral atom ----> Page 1 Elements in group 16 have six valence electrons, In a dot diagram of the atom, the electrons are shown by six dots, two dots above the symbol, two to the right of the symbol, one below, and one to the left.. When an atom gains 2 electrons, the dot diagram is now the symbol of the element, with eight dots (showing a full valence energy level), brackets are drawn around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge of the atom is shown asa super script.to the right..of.the Example: Oxygen, O brackets. Atom of Oxygen; O Ion of Oxygen, 02- Neutral atom ----> Elements in group 17 ( the halogens) have seven valence electrons. In a dot diagram of the atom, the elecfrons are shown by a seven dots, two dots above the symbol, two to the right of the symbol; two below, and one to the left,. When an atom gains one electron, the dot diagram is now the symbol of the element, with eight dots (showing a full valence energy level), brackets are drawn around the symbol showing it is an ion, and the charge of the atom is shown as a super script to the right of the brackets, Atom of Fluorine, F Ion of Nitrogen, FExample: Fluorine, F Neutral atom ----> Elements in group 18 (noble gases) have full set of 8 valence electons (2 in the case helium). In a dot diagram of the atom, the electrons are shown by a eight dots, two dots above the symbol, two to the right of the symbol, two below, and two to the left. Because the are full (stable) they do not form ions. Examples: Helium, H (full with 2 electrons) Neon, Ne Page 2 Name Drawing Dot Diagrams of Ionic Compounds Draw the dot made from the iven cation and anion. Example: Cation Cation = Na = 02 Anion Anion 3. 2. Cation = Cal+ Anion Anion 4. 5. Cation. A1 Cation Cation — Mg2+ =K Anion Anion 6. 7. Cation = Ga3+ Cation= Rb Anion Anion -02 = N3v 9. 8, Cation Cation B Anion = p3 Anion AS3 101 11. Cation = sr2+ Cation = Cs Anion = 02 Anion 13. Cation= Anion MO 2+ Ca Cation Anion 14. Cation Anion = Cation = An.ioti K — 82 Page 3 tonic (Metal Naming binary ionic compounds: Rules + Nonmetal) to follow: write iän with positive charge 2. the second word is first. formed by changing the ending to "ide'. examples: NaaO Sodium Oxido : MgCh: Magnesium Chloride Practice Problems: Use the rules above te complete the fol}owing: 1. Circle Magnesium Oxide Myo which of the following below are cations (positively charged) Barium Sulfide 2. c 3. K3P 3. Se Mn 4. N03N 4. H o S. BaF2 5. Write the chemical formulas for the following compounds: I. Calcium Bromide 2. Lithium 3. 1. Oxide Aluminum 5. Water More : 2. Potassium Fluoride 4. example Sulfide Sr As Ca symbol of positive and negative ions 1. write 2. criss No N — cross charges, if charge isn'f Calcium Oxide Ca -2 0b Cao Sodium Nitride Na p NO'P 3. ZERO 3. 4. 5. Practice (You can do it, yes you can!) l. NaH 1. 2. calcium*nitride 2. 7. Beryllium Fluoride 3. AIN 3. 8. K20 4. Strontium oxide 4. 9. HCI 5. Rb3P 5. 10. 6. 8. 9. Sodium chloride 10. Questions 1. What 2. What are a 3. What is is the difference between a binary and tertiary cation compound? and an anion? the difference between a superscript and a subscripl? Page 1: Naming Compounds Soldan revised 02/03 Page 4 Transitional Metals (groups 3 is used Roman Numerals: 12 on your Periodical Table) more than one, positive Transitional Metals have Roman Numeral — ionic charit. In order to determine the charge, o to indicate the charge. 3 1 8 VI" VII Ill 9 IX lox To determine the charge, look at the periodical table for the choices. If the chemical formula is written, un criss Remember *toss to figure the charge and indicate by a Roman Num. change the second ion's ending to "ide' to Examples: Iron (Ill) iodide Fe 13 SnC14 Tin (IV) chloride Practice Problems: copper (II) 2. Tin (IV) 3. Gold oxide bromide (Ill) fluoride Manganese 5. Nickel 6. TiN 7. CoF3 8. W20s 9. OsBr6 10. PbCi4 (II) (VI!) nitride chloride Questions 1. Where are 2. How do you transitional metals located on your periodical table? figure out the eharge once the transitional element is in a compound? Page 4 Transitional Metal Compounds Soldon revised 02/03 Page 5 Writinq Formulas for Binary Ionic Compounds Lithium suifiae 2. Aluminum 3. Magnesium oxide 4. Zinc phosphide 5. Rubidium chloride 6. Calcium telfunide 7. Strontium nitride 8. Barium fluoride 9. Silver chloride 10. Cadmium bromide iodide 11. Lithium chloride 12. Cesium hydride 13. Radium arsenide 14. Aluminum oxide 15. Potassium bromide Make 5 of your own! And. iustup for a review: 16. Sulfur dichloride 17. Tetraiodine nonoxide 18. Sulfur hexafluoride 19. Carbon disulfide 20. Phosphorous pentafluoride Page 6 Formulas Writinq 1. Copper 2. Iron 3. Copper 4. Tin 5. Nickel 6. Manganese 7. Titanium (IV) nitride 8. Cobalt 9. Lead 10. Chromium Iron (II) Binarv Ionic Compounds (with transition metals) sulfide oxide (II) oxide (l) bromide (II) phosphide (Ill) (Ill) (II) 12. Titanium iodide bromide (Ill) hydride (Ill) 13. Antimony (II) 15. Polonium (IV) fluoride selenide (Ill) 14. Cobalt for (Ill) iodide sulfide hydride (II) selenide Make upfor 5 ofa your own! just review: And. 16. carbon rmnoxide 17. calcium chloride 18. potassium oxide 19. water 20. strontium bromide Page 7 Naming Ionic (metal + nonmetal) Compounds Naming Chemical Compounds Worksheet Name the following 1) NaBr 2) Cao 3) Li2S 4) MgBr2 ionic compounds: 5) Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds: 6) potassium iodide 7) magnesium oxide 8) aluminum 9) sodium 10) calcium carbonate 11) lithium sulfate 12) beryllium phosphide 13) magnesium hydroxide 14) sodium phosphate 15) aluminum carbonate 16) calcium chloride 17) sodium cyanide 18) aluminum oxide 19) magnesium acetate 20) ammonium chloride nitrate chloride Page 8 Name. Naminq 1. Csi 2. CaBr2 3. Mgs 4. Bao 5. NaH 6. K20 Binary Ionic Compounds: 7. 8. NaCi 9. Ag2S 10. RaSe 11. AlBr3 12. RbF 13. Cd3P2 14. znC12 15. BeO And. just for a review: Ca 3 P 2 16. BC13 BaCl2 17. so-3 18. Cs N 3 NH3 19. Potassium Bromide HO 22 20. Strontium Selenide Page 9 Naming & Writing Formulas Name (There are no roman numerals or polyatomic ions on this page) Fill in the table with the missin Cation Anion ions, formula or Formula names from the given ions, formula, or name. Name Be 5. 6. Cao Ga2S3 sr3P2 Mg12 10. ZnO 11. Aluminum Nitride 12. Calcium Chloride Magnesium Sulfide 14 Gallium Chloride 15 Cadmium Bromide Page 10 Naming & Writing Formulas for Elements With more than one Oxidation Numbers Fill in the table Cation 1. with the missing Anion ions, Name fonnula or names from the •ven ions, formul or name. Name Formula cu 2. 3. 6. Cuo 7. 8. Ni3P2 9. Pb12 10. ZnO Nickel 12. 13. 14 15. Tin (111) (II) Cobalt Chloride (11) Chromium Nitride Sulfide (Ill) Chloride Cadmium Bromide Page 11 Naming & Writing Formulas for Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic ions #3 Fill in the table Cation Name with the missing ions, formula or names from the Anion iv.en• ions, formula, or name. Name Formula cu Oil 2. C03 Cr 6. cuS03 8, 10. 11, 12. 13. 14 15 NiS04 Tin (11) Copper Phosphate (II) Chromium Manganese Chlorate (Ill) (II) Sulfate hydroxide Lead (I V) Nitrate Page 12 Covalent naming rule reminders: 1) Change the ending of the second element to -ide. 3.) Never use 'mono' on the first element. 2) Add a prefix to each element to indicate how many of it there is. Name Naming Covalent Compounds Naming Covalent (nonmetal+nonmetal) Compounds mono Prefixes: penta 1-10. one = 5 hexa octa = 8 hepta = 7 tetra = 4 nona = 9 deca = 10 Write the correct formula from the even name. Name Formula 1. Chorine monoxide 2. Oxygen difluoride Dinitrogen monoxide Nitrogen trichloride Sulfur tetrabromide 6. Carbon dioxide Diphosphorous pentoxide Bromine pentafluoride Disulfur dichloride 10, Tetraarsenic decoxide 11-20. Write the correct name from the Name 11. Dinitrogen Pentasulfide "ven formula. Formula N2S5 12. co 13. S03 N203 N20 16. xeF6 PC15 18. SiC14 19. C102 20. ICl Page 13 Dot Diagrams of some Covalent Compounds Name Draw dot diagrams for the following covalent compounds. 02 (Oxygen gas) 2. HI 3, H2Se (Hydrogen selenide) 4. NH3 5. CF4 (Carbon tegafluoride) 6. C2H6 1. iodide) (ammonia) 4. (ethane) .9 7. HFO 9. Nz (hypoffiorous acid) (nitrogen gas) 8. 10. OBr2 (oxygen dibromide) CHC13 (friChlor.omethane) Page 14 nonmetal + nonmetal Covalent Compound Naming Practice Name the following covalent compounds: 1) seF6 2) Te03 3) H20 4) scu 5) PC12 6) NC13 7) Bra 9) S04 10) IF7 Write the formulas of the following covalent compounds: monoxide 11) sulfur 12) tellurium tetrachloride 13) dinitrogen trioxide 14) tetrasulfur dinitride 15) carbon tetraiodide 16) dicarbon tetrabromide 17) hydrogen chloride 18) carbon diselenide 19) triboron silicide 20) tellurium dichloride mono mono Page 15 This wotk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution - NonCommercial 4.0 International License and is copyrighted (c) 2015 by Ian Guch. For more practice sheets and tutorials, visit www.chemfiestacom Naming Chemical Compounds This a mixture of naming and formula writing. is ionic or covalent. Make sure you determine Covalent compounds have 2 non-metals. LOOK at the if this is periodic table. Ionic salts are metals + non-metals. Ionic or Covalent 1. Name this a ro riatel NaBr 2. 4. 5. FeP04 7. so 8. CuOH For each of the following questions, determine whether the compound covalent and write the appropriate formula for Ionic or Covalent is ionic or it. Write thea ro riate formula 10. Silicon dioxide 11. Nickel (111) sulfide 12. Nickel sulfate 13. Silver acetate 14. biboron tetrabromide 15. Carbon tetrachloride 16. Potassium carbonate 17. Iron (II) carbonate 18. Tin (IV) selenide 19. Chlorine as Page 16 Naming Chemical Compounds 2 This a mixture of naming and formula writing. is ionic or covalent. Make sure you determine Covalent compounds have 2 non-metals. if this is LOOK at the periodic table. Ionic salts are metals + non-metals. Ionic or Covalent 1. NazC03 3. NH 5. FeS04 Si02 6. Gact3 7. coBrz 9. co 4. Name this a ro riatel For each of the following questions, determine whether the compound covalent and write the appropriate formula for Ionic or Covalent 10. Dinitro 11. is ionic or it. Write thea ro riate formula en trioxide Diatomic nitro en 12. Lithium acetate 13. Phos horous trifluoride 14. Vanadium(V) oxide 15. Phos horus trifluoride 16. Aluminum h droxide 17. Zinc Sulfide 18. Silicon tetrafluoride 19. Silver hos hate Page 17