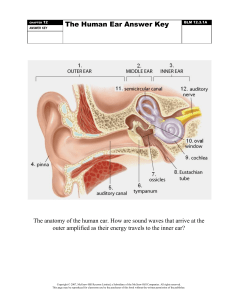
Shade eye from sunlight Eyebrows Keep debris out of eye Also called palpebrae; thin, skin-covered folds Eyelids that protect eye anteriorly Transparent mucous Accessory functions of membrane that the eye Conjunctiva produces a lubricating mucous secretion Consists of lacrimal gland and ducts that Lacrimal apparatus drain into nasal cavity Six straplike extrinsic Extrinsic eye muscles eye muscles Opaque posterior Vision Sclera region Outermost layer; dense avascular connective Fibrous layer Taste tissue Transparent anterior one-sixth of fibrous Cornea Special senses layer Supplies blood to all Hearing Choroid layers of eyeball Smell Equilibrium Consists of smooth muscle bundles, ciliary muscles, that control Ciliary body Middle pigmented layer Vascular layer of eye, also called uvea shape of lens Olfactory epithelium: Structure of eyeball organ of smell In order to smell Colored part of eye that lies between cornea and lens, continuous with Physiology of smell Iris volatile The eye and vision ciliary body Smell Absorbs light and Vision receptors for bright light Dim light, peripheral vision receptors Odorant binds to receptor, activating a G pigmented layer prevents its scattering protein Retina originates as an Inner layer outpocketing of brain Cones Photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells substance, it must be G protein activation causes cAMP (second neural layer Smell transduction Rods messenger) synthesis cAMP opens Na+ and Ca2+ channels Opsin and 11-cis retinal combine to form Pigment synthesis Na+ influx causes rhodopsin in dark depolarization and impulse transmission When rhodopsin surrounding ear canal pigment captures absorbs light, 11-cis isomer of retinal shell-shaped structure process by which Pigment bleaching changes to all-trans Capturing light photon of light energy, which is converted into Auricle Phototransduction sound waves into auditory canal A&P Ch. 15 a graded receptor isomer that functions to funnel potential Short, curved tube lined All-trans retinal converted back to 11-cis with skin bearing hairs, Pigment regeneration sebaceous glands, and isomer External ear Both rods and cones are strongly stimulated glands meatus Light Transmits sound waves to eardrum Pupils constrict Light and dark adaptation Cones stop functioning in low-intensity light External acoustic ceruminous (earwax) Tympanic membrane (eardrum) Boundary between external and middle ears Dark Pupils dilate Malleus Equilibrium is response Vestibular apparatus: to various movements equilibrium receptors in of head that rely on semicircular canals and input from inner ear, vestibule eyes, and stretch The ear and hearing Equilibrium the “hammer” is secured to eardrum Major areas of the ear Middle ear made up of auditory ossicles receptor Incus Stapes Vestible the “anvil” the “stirrup” base fits into oval window Central egg-shaped cavity of bony labyrinth Three canals oriented in Inner ear Also referred to as the labyrinth (maze) Semicircular canals three planes of space: anterior, lateral, and posterior A small spiral, conical, Cochlea bony chamber, size of a split pea