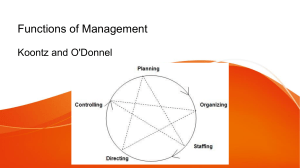
REVIEW QUESTION IN CHARATER FORMATION 2 By: DR. JOSEPH F. TAMACAY TEST I – MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read each of the following questions, then choose the letter of the correct answer. Shade the corresponding letter on your answer sheet. 1. It requires a formal structure of authority and direction through which work subdivisions are defined, arranged, and coordinated so that each part relates to the other part in a coherent manner so as to attain the prescribed organizational objectives. a. Budgeting b. Staffing c. Organizing d. Directing 2. This management function is concerned with leadership, communication, motivation, and supervision so that employees perform their activities in the most efficient manner possible, in order to achieve the desired goals. a. Organizing b. Directing c. Organizing d. Staffing 3. This tool can provide clarity when dealing with different choices and variables in order to make a final decision. a. Attitude matrix b. Decision matrix c. Formal matrix d. Action matrix 4. This technique helps identify changes that Will be the most effective actions for an organization. a. Matrix analysis b. SWOT analysis c. Marginal analysis d. Pareto analysis 5. It is a style of leadership when a leader leads from the front, constantly sets high standards for their team and expect them to exceed with minimal management. a. Pacesetting leadership style b. Autocratic leadership style c. Democratic leadership style d. affiliative leadership style 6. This is a type of group decision-making which can be effective when you need to raise potential ideas and solutions to address an organizational problem. a. groupthink session b. weighing session c. mapping session d. brainstorming session 7. He is a 20th-century American psychologist who suggested that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. a. Abraham Lincon b. Abraham Maslow c. Abraham Morn d. Abraham Marslo 8. What kind of Motivation is being practiced by the employee, when he/she is doing something because he/she enjoys it or finds it interesting and not just because someone told him/her to do i. a. Intrinsic b. Extrinsic c. Positive d. Negative 9. A theory of leadership which states that excellent leaders are born (not developed) and possess the natural attributes of intelligence, courage, confidence, intuition, and charm, among others. a. Implications of Trait Theory b. The great man theory c. behavioral theory d. Contingency theory 10. Which of the following is not included in the resources of an organization that are indispensable in the pursuit of its vision and mission. a. Time b. Logistics c. Financial d. Human 11. He is a psychologist from Australia, who has been regarded as a father of human resources management because of his experiment on human behavior which gave emphasis on the influence of human relations on the productivity of workers. a. Elton Mayo b. Peter Dracker c. Peter Koontz d. William O’Donnell 12. It is a power that derives from the organizational position or level, not from the actual person occupying the position. A. Coercive power B. Legitimate power C. Informational power D. Expert power 13. It is an authoritarian form of leadership where the leader exercises complete control over all key decisions, whether they are policy or procedural matters. A. Autocratic leadership style B. Democratic leadership style C. Pacesetting leadership style D. affiliative leadership style 14. It is a style of leadership in which leaders uses their communication skill, persuasiveness, and charm to connect with people on a deep level especially valuable within organizations that are facing a crisis or are struggling to move forward. A. Charismatic leadership style B. affiliative leadership style C. Laissez-faire leadership style D. Transactional leadership style 15. It is a style of leadership in which leaders interacts with others either in a management or fellow employee capacity to achieve authority rather than power. A. Collaborative leadership style B. Behavioral leadership style C. Task-Oriented Functions style D. Servant leadership style 16. Which of the following is not included in the three dimensions of Management? A. Management of work B. Management of people C. Management of operations D. Management of time 17. A famous thinker who proclaimed that, ‘effective management was becoming the main resource of developed nations and that it was the most needed resource for the development of any nation.’ A. Harold Koontz B. Peter F. Drucker C. Alan Price D. James Taylor 18. This leadership theory is based on the idea that managers give employees something they want in exchange for getting something they want. It posits that workers are not self-motivated and require structure, instruction and monitoring in order to complete tasks correctly and on time. A. Behavioral leadership theory B. The great man theory C. Transactional leadership theory D. Contingency theory 19. This style is a pure compromise in which leaders try to achieve adequate overall results by using limited authority and balancing the needs of production with the needs of the people. A. Middle of the Road Style B. Team Management Style C. Situational style D. Contingency theory 20. This technique is ideal to use in a situation where your team has many ideas for possible solutions but has not necessarily considered the implications of each decision thoroughly. A. Weighted scoring B. Scaled scoring C. Raw scoring D. Graphed scoring 21. Who gave this definition of ‘Management – “an art of getting things done through and with the people in a formally organized group.” A. Alan Price B. Harold Koontz C. Peter F. Drucker D. James Taylor 22. This theory of leadership puts forth the idea that the success of a leader hinges on the specific situation at hand. A. The path-goal theory B. Contingency theory C. Transactional leadership theory D. Behavioral leadership theory 23. It is a behavior of a leader that informs their followers on what is expected of them. Leaders tell the followers what to do, how to perform a task, and coordinate the work. A. Directive-oriented leader behavior B. Great-man leader behavior C. Servant leadership style D. Collaborative leadership style 24. It is an idea that for complex issues we cannot be completely rational because it cannot fully grasp all the possible alternatives, nor can it understand all the implications of every possible alternative. A. Bounded rationality B. Equal rationality C. Regular rationality D. Limited rationality 25. It is the tendency of decision-makers to remain committed to a poor decision, even when doing so leads to increasingly negative outcomes. A. Regular rationality B. Bounded rationality C. Escalation of commitment D. Equal rationality 26. Which among the choices is not included in the tree-factor theory of Motivation. A. Achievement B. Affiliation C. Power D. Knowledge 27. This theory suggests that when you want to get something done, motivation is generated by first building up your expectation of success. A. Theory of needs B. Theory of X and Y C. Theory certainty D. Theory of expectancy 28. It is a strategic planning and strategic management technique use to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning. A. SWOT Analysis B. WOST Analysis C. SOWT Analysis D. STOW Analysis 29. Which of the following choices is not included in the 3 basic personal skills of effective leadership or management According to Katz. A. technical B. Mechanical C. human D. conceptual 30. This defines the process of identifying problems, considering and evaluating the alternatives, arriving at a decision, taking action, and assessing the outcome. A. Problem solving B. decision making C. Plan making D. Research solving 31. What steps to effective decision making, if the leader collects some pertinent information before he makes a decision. A. Step 3: Identify the alternatives B. Step 1: Identify the decision. C. Step 2: Gather relevant information D. Step 4: Weigh the evidence 32. It is a condition under which the manager is well informed about possible alternatives and their outcomes. A. Risk B. Uncertainty C. Certainty D. Danger 33. This is a motivation model that focuses on extrinsic factors like rewards that motivate a person’s behavior toward desired goals and objectives. A. Process model B. Accomplishment model C. Output model D. Outcome model 34. It is the act of stimulating someone or oneself to get a desired course of action and to push the right button to get the desired results. A. Motivation B. Morale C. Reward D. Incentive 35. What kind of leadership skills are applied by a Leader when he inspires and builds employees’ self-esteem through recognition, rewards/incentives, promotion, or increased salary due to the employees’ outstanding accomplishment in the organization? A. Motivation B. Delegation C. Separation D. Designation 36. It is the measurement & correction of performance activities of subordinates in order to make sure that the enterprise objectives and plans desired to obtain them as being accomplished”. A. Staffing B. Controlling C. Directing D. Coordinating 37. Who developed the ten "Cs" (cost-effectiveness, competitive, coherence, credibility, communication, creativity, competitive advantage, competence, change, and commitment) of the human resources management framework. A. Elton Mayo B. Alan Price C. Peter Dracker D. Harold Koontz 38. This technique is best suited for multi-dimensional problems, with interconnected relationships throughout the business, and involves several steps to coming to a final decision. A. Consensus mapping B. Dimensional mapping C. Brain mapping D Geographical mapping 39. The word POSDCORB, which generally represents the initials of the seven functions of management stands for; P - Planning, O - Organizing, S - Staffing, D - Directing, Co - Coordinating, Rreporting & B stands for _____________. A. Buying B. Bulging C. Budgeting D. Bystanding 40. The word motivation derives from the latin word _____________. A. Movere B. Drive C. Move D. Act 41. Who are these famous thinkers who said that “Managerial function of staffing involves manning the organization structure through the proper and effective selection, appraisal & development of personnel to fill the roles designed in the structure”. A. Kootz & O’Donnell B. Katz & Kahn C. Murdick & Schuster D. Kllatt, Murdick 42. Which of the following choices is not included in the theory of Alderfer on human motivation? A. Existence B. Development C. Relatedness D. Growth 43. These needs are basic to human life which include food, clothing, shelter, air, water, and life requirements. A. Self-actualization needs B. Safety needs C. Social needs D. Esteem needs 44. Before an individual can achieve a higher level of motivation he/she must be successful in meeting first the lower level of needs, which is the _____________. A. Safety B. Physiological C. Esteem D. Love 45. What is the final step in the process of motivation? A. Report B. Reecho D. Response 46. Two-factor theory argues that achievement is based on both ability and _____________. A. B. Dissatisfaction C. Satisfaction D. Sadness 47. Who formulated the theory of Expectancy which states that a person will be motivated if he/she believes that his/her effort will result in success and if his/her work will be rewarded. A. Victor Vroom B. Victor Neri C. Victor Voom D. Victor Zoom 48. This person came up with two distinct theories of human behavior, negatively named as X and Positively named as Y theory. A. Douglas Mc Gregor B. Douglas Mc Arthur C Douglas Murphy D. Douglas Quiano 49. This theory explains the inherent behavior of a worker being always motivated and accepting responsibilities. A. Theory X B. Theory Y C. Theory A D. Theory B 50. This theory proposes that employees analyze their contributions (job inputs) and their rewards (job outcomes). A. Balance theory B. Equal theory C. Single theory D. Equity theory 51. This is a model of Motivation which focuses on intrinsic factors that stimulate a person’s ability to achieve things in a particular situation. A. Process model B. Outcome model C. Accomplish model D. Moral Model 52. Who developed the other situational theory of leadership that incorporates the concept of emotional intelligence. A. Daniel Goleman B. Daniel Riggs C. Daniel Gore D. Daniel Riles 53. Which of the following resources of an organization that is considered the most difficult to manage and indispensable in attaining the organizational objectives. A. Time B. Logistics C. Financial D. Human 54. It is the process of influencing the activities of an individual or a group in efforts toward goal achievement in a given situation.” A. Leadership B. Directorship C. Supervisorship D. Commandership 55. A theory of leadership which states that excellent leaders are born (not developed) which possesses the natural attributes of intelligence, courage, confidence, intuition and charm, among others. A. Transactional leadership theory B. The great man theory C. Behavioral theory D. Contingency theory 56. It is a power that derives from the organizational position or level, not from the actual person occupying the position. A. Expert power B. Coercive power C. Legitimate power D. Referent power 57. It is the ability to control access to important information about organizational operations and plans, organization members and the external environment. A. Expert power B. Coercive power C. Legitimate power D. Informational power 58. It is a leadership skill that a leader can clearly and succinctly explain to the employees everything from organizational goals to specific tasks. A. Communication B. Conveyance C. Report D. Transmission 59. It is a style of leadership in which leaders promote compliance by followers through both rewards and punishments to keep followers motivated for the short-term. A. Laissez-faire leadership style B. Collaborative leadership style C. Team management style D. Transactional leadership style 60. These functions relate to providing solution to the problems faced by the groups, in performing job and activities. A. Service-Oriented Functions B. Task-Oriented Functions C. Mission-Oriented Functions D. Output-Oriented Functions 61. This type of leader often possesses the natural attributes of intelligence, courage, confidence, intuition and charm, among others. A. Tall-man leader B. Great-man leader C. Prominent-man leader D. Middle-man leader 62. This is a leadership skill where a leader empowers an individual by assigning some of his duties/tasks to each employee based on their skill. A. Supervising B. Assigning C. Tasking D. Delegating 63. This pertains to the proper utilization of available skilled workforce and also to make efficient use of existing personnel in the organization. A. human resource management B. Financial resource management C. Logistical resource management D. Time resource management 64. It is the process of analyzing an organization’s needs for various employees in accord with its goals and devising activities to meet those needs. A. Organizing B. Planning C. Staffing D. Directing 65. It is an array of tasks and responsibilities given to an employee in order to meet organizational goal. A.Assignment B. Job C. Work D. Tasks 66. It is the process of attracting and selecting employees for positions in accordance with organizational goals. A. Staffing B. Directing C. Budgeting D. Planning 67. It is a systematic approach to providing monetary value to employees in exchange for work performed. A. Salary B. Allowance C. Benefits D. Compensation 68. It is the process of achieving organizational goals through planning, organizing, leading and controlling the human, physical, financial, and information resources of the organization. A. Organization B. Management C. Administration D. Staffing 69. It is a course of action purposely chosen from a set of alternatives to achieve organizational or managerial objectives or goals. A. Decision B. Discretion C. Judgement D. Action 70. This is a technique or tool use by the leader to help the organization allocate resources to increase profitability and benefits and reduce costs. A. Weighted analysis B. Groupthink analysis C. Marginal analysis D. SWOT Analysis 71. It is a type of participatory process in which multiple individuals acting collectively, analyze problems or situations, consider and evaluate alternative courses of action, and select from among the alternatives a solution or solutions. A. Group decision making B. Individual decision making C. Departmental decision making D. Organizational decision making 72. This occurs when a members want to minimize conflict and reach a comfortable decision at the expense of a critical evaluation of other ideas and viewpoints. A. Group think B. Personal think C. Individual think D. Organizational think 73. It is a broad term indicating any type of activity that attempts to imitate an existing system or situation in a simplified manner A. Consensus model B. Simulation model C. Escalation model D. Group decision Model 74. This technique is a structured decision- making process in which group members are required to compose a comprehensive list of their ideas or proposed alternatives in writing. A. Consensus group technique B. Simulation group Technique C. nominal group technique D. rational group technique 75. Which of the following is not included in the important terms under the definition of management. A. Assembly B. process C. effectively D. efficiently 76. A person who takes the role in influencing the behavior of other members of the group to accomplish a certain task or activity of the organization. A. Supervisor B. Leader C. Manager D. Boss 77. Who developed the most widely accepted classification of power? A. Alan Price and Peter Dracker B. Elton Mayo and Harold Koontz C. James Taylor and Abraham Maslow D. John R.P. French Jr and Bertram H. Raven 78. The ability to reprimand, demote, withhold salary, dismiss or to use other means of penalizing employees due to the inability to perform the tasks or has violated any policies of the organization. A. Coercive power B. Expert power C. Referent power D. Legitimate power 79. A type of leadership style in which the leaders are hands-off and allow the employees to make the decisions on their assigned tasks. A. Laissez-faire leadership style B. Charismatic leadership style C. Servant leadership style D. Behavioral leadership style 80. It is the process of determining the appropriate responses or actions necessary to alleviate or solve the problem encountered by the organization. A. Mathematical solving B. Problem solving C. Trouble solving D. Dispute solving 81. This power is from the manager’s personal skills, technical knowledge and experience. A. Coercive power B. Referent power C. Expert power D. Informational power 82. It is a leadership style which requires empathy and the ability to build relationship through a range of communication. A. Charismatic leadership style B. affiliative leadership style C. Laissez-faire leadership style D. leadership style 83. This power stems directly from the individual’s personal qualities which evoke a response in others. A. Expert power B. Referent power C. Coercive power D. Legitimate power 84. This theory states that a leaders’ behavior is contingent on the satisfaction, motivation and performance of their employees. A. The Contingency theory B. The Path-goal theory C. The Implication of Trait theory D. The Great-man theory 85. Maslow theorized that humans are born with a series of needs that must be fulfilled for survival, growth and ____________________. A. Self esteem B. Self actualization C. Self fulfillment D. Self analysis 86. There are studies showing that certain mental states lead directly or indirectly to increased levels of activation within certain parts of our brain called “Prefrontal cortexes”, which control things like; moods, actions, and _____________________. A. Self image B. Self fulfillment C. Self analysis D. Self esteem 87. This occurs when a person improves in at least one of these five areas of growth, knowledge, skill, ability, attitude and self-concept. A. Individual growth B. Organizational growth C. Group growth D. Personal growth 88. He is a British theoretical physicist and Cambridge professor who expressed about destruction of Middle class jobs due to raise of artificial intelligence maintained by the business firm or office to increase their production and improve their services. A. Stephen Hawking B. Stephen Shawn C. Joseph Hawking D. Stephen Owen 89. This planning consists of forecasting an organization’s needs for employees in accordance with organizational goals and determining both the components of each jobs necessary to meet those goals and the characteristics of the people needed to fill each jobs. A. Human resource management B. Strategic planning C. Human resource planning D. Strategic decision 90. Which of the following choices is not included in the 3 basic motivational techniques. A. Social network B. Super ego network C. Achievement network D. Ego network 91. It is one of the core principles of human resource management that supports an organization’s growth and development. A. Competence B. Ability C. Talent D. Skill 92. It is the process of choosing the most qualified applicants who best suit the vacant position and organizational needs. A. Promotion B. Selection C. Designation D. Qualification 93. It is a system used by an organization to improve the skills and performance of an employee. A. Disciplining B. Retiring C. Dismissing D. Training 94. It is a systematic approach undertaken by the organization of providing monetary value to employees in exchange for work performed. A. Human management B. Personnel management C. Office Management D. Compensation management 95. This theory has the key concept of conditioning which states that a person will be more likely to act or lead in a certain style as a result of environmental responses to behavior. A. Behavioral theory B. Transactional leadership theory C. The great man theory D. Contingency theory 96. It is a strategic action of the organization to keep employees motivated and focused so they opt to decide to remain employed and fully productive for the benefit of the organization. A. Employee benefits B. Employee welfare C. Employee retention D. Employee promotion 97. This systematic approach to decision making helps managers avoid making quick decisions without adequately considering the consequences to the organization. A. Decision making pitfalls B. Problem solving pitfalls C. Decision oriented pitfalls D. Decision pitfalls 98. This technique help a manager improve the over-all quality of decision making. A. Consensus group technique B. Simulation group Technique C. nominal group technique D. Quantitative technique 99. This tool shows a complete picture of a potential decision and allows a Manager to graph alternative decision paths. A. Decision tree B. Problem tree C. Solution tree D. Alternative tree 100. It is a management practice in which members of a leadership team work together across sectors to make decisions and keep their organization thriving. A. Laissez-faire leadership style B. Charismatic leadership style C. Collaborative leadership style D. Servant leadership style