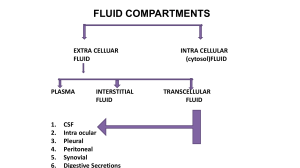
Lifespan Consideration Racial/Ethnic Groups Greater genetic predisposition to insulin resistance. Older adults Reduced insulin production Increased visceral fat and less lean muscle mass. Infants Increased energy needs and insufficient glycogen stores Hypoglycemia in reference to neonatal hyperinsulinemia At risk if mother had gestational diabetes Pregnant Women Associated risk for hyperglycemia, higher postprandial. Produce a state of insulin resistance Assessment Data History - Social history Family history: diabetes and obesity. Personal medical history. Polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria, retinopathy, poor wound healing, sleep apnea, depression, chronic fatigue, and peripheral neuropathy. Diagnostic Tests - Blood glucose testing, antibody testing, lipid analysis, renal function tests, creactive protein Examination Findings - Vital signs - Skin tags - Foot exam - Visual acuity - Concept Fluid and Electrolytes The process of regulating the extracellular fluid volume, body fluid osmolality and plasma concentration of electrolytes. Risk Factors Scope There is either an optimal balance or an imbalance. Two aspects: extracellular volume and osmolarity. Age - The very young and the very old. - Preterm infants are at risk because of their immature kidneys and large surface area of skin and lungs. - Adults have a blunted thirst sensation and decrease renal reserve due to a loss of nephrons. Conditions - Vomiting, diarrhea, fever, inadequate or excessive fluid and water intake. Health Promotion Primary Prevention (Education) - Exercise Diet Maintaining a safe-healthy body weight. Physiological Process Intake and absorption – oral are the most common route. Fluids must be absorbed by the blood stream. Distribution – necessary for optimal function. Filtration distributes the ECF between the vascular and interstitial extracellular compartments. Osmosis distributes water between ECF and cells. Output – urine, feces, sweat, and lungs. Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances. - Output is greater than intake and absorption. - Output is less that intake absorption. - Distribution is altered. Secondary Prevention (Screening) - A1C measurements at least twice a year Monitor thyroid function Lipid and renal tests Screening for hypoglycemia 1 of 2